Human Genome Project
... (polygenic), and gene-environment interaction – Multifactorial • refers to a trait that is affected by many factors, both genetic and environmental – The Human Genome Project is an international effort to map the entire human genome • researchers have found that humans have only about 25,000 genes, ...
... (polygenic), and gene-environment interaction – Multifactorial • refers to a trait that is affected by many factors, both genetic and environmental – The Human Genome Project is an international effort to map the entire human genome • researchers have found that humans have only about 25,000 genes, ...
LINK project: Genetic control of meat quality (LK0626)
... were sampled and stored. Proteins and RNA (the messenger molecule that act as an intermediate between genes and proteins) were isolated. From comparisons of the proteins present in Duroc and Large White embryos of equivalent ages and from ...
... were sampled and stored. Proteins and RNA (the messenger molecule that act as an intermediate between genes and proteins) were isolated. From comparisons of the proteins present in Duroc and Large White embryos of equivalent ages and from ...
No, Humans Have Not Stopped Evolving
... people in the world today have sticky earwax. In contrast, many East Asians have dry, flaky earwax that does not stick together. Anthropologists have known about this variation for more than 100 years, but geneticists did not uncover the cause until recently. Dry earwax results from a relatively new ...
... people in the world today have sticky earwax. In contrast, many East Asians have dry, flaky earwax that does not stick together. Anthropologists have known about this variation for more than 100 years, but geneticists did not uncover the cause until recently. Dry earwax results from a relatively new ...
7th Grade Life Science: Genetics Unit Essential Question: How does
... DNA determines traits and traits are inherited. Unit Essential Question: How does DNA determine traits and how are traits inherited? ...
... DNA determines traits and traits are inherited. Unit Essential Question: How does DNA determine traits and how are traits inherited? ...
Mammals follow Mendel’s laws - University of California
... painful vasoocclusive crises and multiple organ damage in adults, to being relatively well even until old age. Increasing numbers of genetic loci have now been identified that can modulate sickle cell disease phenotype, from nucleotide motifs within the beta-globin gene cluster, to genes located on ...
... painful vasoocclusive crises and multiple organ damage in adults, to being relatively well even until old age. Increasing numbers of genetic loci have now been identified that can modulate sickle cell disease phenotype, from nucleotide motifs within the beta-globin gene cluster, to genes located on ...
Lecture Six: Causes of Evolution
... 1. Members of one sex compete against each other for mates. The ones that have traits that make them better able to compete will leave more genes. Example: Larger size of males in many mammal species. Thick manes in male lions. Antlers in male deer. 2. Members of one sex prefer a particular trait in ...
... 1. Members of one sex compete against each other for mates. The ones that have traits that make them better able to compete will leave more genes. Example: Larger size of males in many mammal species. Thick manes in male lions. Antlers in male deer. 2. Members of one sex prefer a particular trait in ...
Genetics
... – cross the organism with dominant character to an organism with homozygous recessive character – to test whether the organism with the dominant character is homozygous or heterozygous • Back cross – cross an organism with one of its parent ...
... – cross the organism with dominant character to an organism with homozygous recessive character – to test whether the organism with the dominant character is homozygous or heterozygous • Back cross – cross an organism with one of its parent ...
DNA & RNA
... to genetic drift after a small population inhabits a new region • Bottleneck effect: a small surviving group (near extinction) gives rise to a new population with a dramatically different gene pool ...
... to genetic drift after a small population inhabits a new region • Bottleneck effect: a small surviving group (near extinction) gives rise to a new population with a dramatically different gene pool ...
File
... • Gene – a unit of heredity; a section of DNA sequence encoding a single protein • Genome – the entire set of genes in an organism • Alleles – two genes that occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes and that cover the same trait (like ‘flavors’ of a trait). • Locus – a fixed location on a ...
... • Gene – a unit of heredity; a section of DNA sequence encoding a single protein • Genome – the entire set of genes in an organism • Alleles – two genes that occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes and that cover the same trait (like ‘flavors’ of a trait). • Locus – a fixed location on a ...
Definitions and explanations of terms
... The total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. Supplement A large gene pool indicates high genetic diversity, increased chances of biological fitness, and survival. A small gene pool indicates low genetic diversity, reduced chances of acquiring biological fitness, and ...
... The total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. Supplement A large gene pool indicates high genetic diversity, increased chances of biological fitness, and survival. A small gene pool indicates low genetic diversity, reduced chances of acquiring biological fitness, and ...
human-genome-project
... • Humans share most of the same protein families with worms, flies, and plants; but the number of gene family members has expanded in humans, especially in proteins involved in development and immunity. Scientists have identified about 3 million locations where single-base DNA differences (SNPs) occ ...
... • Humans share most of the same protein families with worms, flies, and plants; but the number of gene family members has expanded in humans, especially in proteins involved in development and immunity. Scientists have identified about 3 million locations where single-base DNA differences (SNPs) occ ...
Facing up to Complex Inheritance Patterns
... Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene In a prospective-longitudinal study of a representative birth cohort, we tested why stressful experiences lead to depression in some people but not in others. A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of the serotonin transporter (5-HT T) gene was found to moder ...
... Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene In a prospective-longitudinal study of a representative birth cohort, we tested why stressful experiences lead to depression in some people but not in others. A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of the serotonin transporter (5-HT T) gene was found to moder ...
Simple tandem repeats in mammalian genomes
... repeats of the sequence CTC - are called microsatellites. For some microsatellites, therefore called "polymorphic", the number of repeats varies in different individuals "Genes" are defined as those parts of DNA-molecules that specify (encode) RNA or proteins. Only around 3% of the human genome enco ...
... repeats of the sequence CTC - are called microsatellites. For some microsatellites, therefore called "polymorphic", the number of repeats varies in different individuals "Genes" are defined as those parts of DNA-molecules that specify (encode) RNA or proteins. Only around 3% of the human genome enco ...
Plant Ecology 03-55-468
... Gene flow brings alleles from other populations. Since this is a small, isolated population of compass plant, before gene flow its genetic diversity probably incorporates only a fraction of the total genetic diversity of compass plants in other remnants and larger prairie areas. Gene flow will carry ...
... Gene flow brings alleles from other populations. Since this is a small, isolated population of compass plant, before gene flow its genetic diversity probably incorporates only a fraction of the total genetic diversity of compass plants in other remnants and larger prairie areas. Gene flow will carry ...
Human Ancestors May Have Interbred With Chimpanzees
... If this theory proves correct, it will mean modern people are descended from something akin to chimphuman hybrids. That is a new idea, and it challenges the prevailing view that hybrids tend to die out. It also strongly suggests that some of the oldest bones of "proto-humans" -- including the 7 mill ...
... If this theory proves correct, it will mean modern people are descended from something akin to chimphuman hybrids. That is a new idea, and it challenges the prevailing view that hybrids tend to die out. It also strongly suggests that some of the oldest bones of "proto-humans" -- including the 7 mill ...
Document
... over several generations • Scientist or genetic counselor finds information and makes the chart to analyze it ...
... over several generations • Scientist or genetic counselor finds information and makes the chart to analyze it ...
Complementation
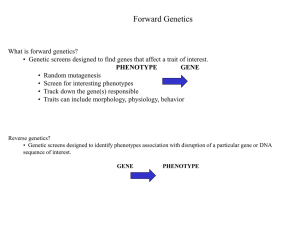
... • Track down the gene(s) responsible • Traits can include morphology, physiology, behavior ...
... • Track down the gene(s) responsible • Traits can include morphology, physiology, behavior ...
What is a gene? - World of Teaching
... • But when lzs/lzg females are crossed to lzs or lzg males, about 0.2% of the progeny are wild-type! • These must result from recombination between lzs and lzg , because the wild-type progeny always had recombinant flanking markers. Also, the frequency of 0.2% is much higher than the reversion rate ...
... • But when lzs/lzg females are crossed to lzs or lzg males, about 0.2% of the progeny are wild-type! • These must result from recombination between lzs and lzg , because the wild-type progeny always had recombinant flanking markers. Also, the frequency of 0.2% is much higher than the reversion rate ...
NATURAL SELECTION
... In every generation, individuals may survive out of sheer luck. The random survival of individuals will change the makeup of the next generation in random ways. Random survival does not lead to ...
... In every generation, individuals may survive out of sheer luck. The random survival of individuals will change the makeup of the next generation in random ways. Random survival does not lead to ...
Bioinformatics and Computational Bology notes
... officials (could be used for prosecuting poachers) – Detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air, water, soil, and food – Match organ donors with recipients in transplant programs – Determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds – Authenticate consumables such as caviar and wine ...
... officials (could be used for prosecuting poachers) – Detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air, water, soil, and food – Match organ donors with recipients in transplant programs – Determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds – Authenticate consumables such as caviar and wine ...
Questions to Ask Your Doctor: Genes and Inherited Breast Cancer
... Every cell in your body contains genes. Sometimes, people are born with an error in one of these genes called a mutation. Some gene mutations are linked to breast cancer (i.e., BRCA1 and BRCA2). A mutated gene can be inherited from either the mother or father. This inherited mutation may increase a ...
... Every cell in your body contains genes. Sometimes, people are born with an error in one of these genes called a mutation. Some gene mutations are linked to breast cancer (i.e., BRCA1 and BRCA2). A mutated gene can be inherited from either the mother or father. This inherited mutation may increase a ...
chapter 3: biological beginnings
... and its effect on some genetic diseases. Polygenic inheritance – The interaction of genes, forming the organism’s genotype and phenotype. Reaction range – Demonstrates the importance of an environment’s positive and negative effects. Canalization – Nature’s pathway to development thought to be a pro ...
... and its effect on some genetic diseases. Polygenic inheritance – The interaction of genes, forming the organism’s genotype and phenotype. Reaction range – Demonstrates the importance of an environment’s positive and negative effects. Canalization – Nature’s pathway to development thought to be a pro ...
Biology 4974/5974 Evolution
... • Loss of alleles causes loss of heterozygosity. In small populations, this process is inevitable. • The “rate of fixation” or probability of fixation is considered 1/2N, which gives the proportion of populations that eventually attain fixation. • For the first example: 1/10,000 is very small; but f ...
... • Loss of alleles causes loss of heterozygosity. In small populations, this process is inevitable. • The “rate of fixation” or probability of fixation is considered 1/2N, which gives the proportion of populations that eventually attain fixation. • For the first example: 1/10,000 is very small; but f ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.