document
... contain much to determinepeoples with some with the present living descendents. information about man'ssuch adaptive mechanisms to his environment. The degree of confidence study of evolution essentially would be impossible if bones were They bear witness toof burial and thus give evidence At birth, ...
... contain much to determinepeoples with some with the present living descendents. information about man'ssuch adaptive mechanisms to his environment. The degree of confidence study of evolution essentially would be impossible if bones were They bear witness toof burial and thus give evidence At birth, ...
Aim #74 - Manhasset Schools
... Summary Questions: 1) The driving force behind evolution is the interaction between the individual organisms and the __________. 2) In your own words, define what an adaptive variation is? 3) Explain what the following statement means, “Individual organisms do not evolve, species do”. ...
... Summary Questions: 1) The driving force behind evolution is the interaction between the individual organisms and the __________. 2) In your own words, define what an adaptive variation is? 3) Explain what the following statement means, “Individual organisms do not evolve, species do”. ...
MOLECULAR MARKERS APPLICATION FOR GENETIC RESOURCES CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFERENT PLANT SPECIES
... mutants. Possible application of molecular markers in germplasm collections are: identification and verification of old and new collected genotypes; detection of duplicates; genetic purity analysis; genetic diversity analysis; construction of „core collection“ and selection of interesting, gene reso ...
... mutants. Possible application of molecular markers in germplasm collections are: identification and verification of old and new collected genotypes; detection of duplicates; genetic purity analysis; genetic diversity analysis; construction of „core collection“ and selection of interesting, gene reso ...
File
... For example, a test cross between two organisms with same genotype, Tt will result in offspring with genotypes: TT, Tt, and tt. In this example, the predicted genotypic ratio is 1:2:1. ...
... For example, a test cross between two organisms with same genotype, Tt will result in offspring with genotypes: TT, Tt, and tt. In this example, the predicted genotypic ratio is 1:2:1. ...
bio 11 genetics sep 15
... Hardy-Weinberg principle Explains when no change takes place over time Allele frequency in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change The situation in which allele frequency stays the same is called genetic equilibrium 5 conditions Random mating P ...
... Hardy-Weinberg principle Explains when no change takes place over time Allele frequency in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change The situation in which allele frequency stays the same is called genetic equilibrium 5 conditions Random mating P ...
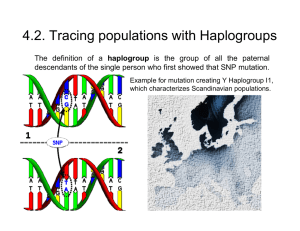
4.2. Tracing populations with Haplogroups
... Mitochondrial Haplogroups mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is defined by differences in human mitochondrial DNA. This allows to trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the spread across the globe. ...
... Mitochondrial Haplogroups mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is defined by differences in human mitochondrial DNA. This allows to trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the spread across the globe. ...
Genetic Models
... Multifactorial/polygenic: Complex Traits Multifactorial (many factors) polygenic (many genes) Generally assumed that each of the factors and genes contribute a small amount to phenotypic variability ...
... Multifactorial/polygenic: Complex Traits Multifactorial (many factors) polygenic (many genes) Generally assumed that each of the factors and genes contribute a small amount to phenotypic variability ...
Document
... Mutational loads are found in essentially ALL species, including several threatened & endangered. Deleterious alleles are normally found only at low frequencies, typically much less than 1% at any locus. Deleterious alleles are found at many loci. ...
... Mutational loads are found in essentially ALL species, including several threatened & endangered. Deleterious alleles are normally found only at low frequencies, typically much less than 1% at any locus. Deleterious alleles are found at many loci. ...
Multiple choice questions BIO1130FF
... FF.1 Which of the following conditions is not one of those under which a population of diploid organisms will achieve genetic equilibrium? a. X the mutation rate is increasing b. no immigration from other populations c. the population is infinite in size d. individuals mate randomly FF.2 Because of ...
... FF.1 Which of the following conditions is not one of those under which a population of diploid organisms will achieve genetic equilibrium? a. X the mutation rate is increasing b. no immigration from other populations c. the population is infinite in size d. individuals mate randomly FF.2 Because of ...
1 - jfriel
... when an allele is fixed? What is a genetic bottleneck. Give an example of one. What is founder effect? How does this the resulting population? Page 1 of 5 ...
... when an allele is fixed? What is a genetic bottleneck. Give an example of one. What is founder effect? How does this the resulting population? Page 1 of 5 ...
Agenda - UCLA Human Genetics
... We will describe network analysis methods widely used in systems biologic and systems genetic applications. The goal is to familiarize researchers with network methods and software for integrating genomic data sets with complex phenotype data. Participants will learn how to integrate disparate data ...
... We will describe network analysis methods widely used in systems biologic and systems genetic applications. The goal is to familiarize researchers with network methods and software for integrating genomic data sets with complex phenotype data. Participants will learn how to integrate disparate data ...
Evolution as Genetic Change
... Evolution as Genetic Change • Natural selection acts on phenotypes, survival and reproduction determine which alleles are inherited, changing relative frequencies of alleles in a population over time. • Thus evolution is any change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a population’s gene pool ...
... Evolution as Genetic Change • Natural selection acts on phenotypes, survival and reproduction determine which alleles are inherited, changing relative frequencies of alleles in a population over time. • Thus evolution is any change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a population’s gene pool ...
How to Feed a Hungry World
... • Will we have the resources to continue developing new varieties? • Seed banks may help but who owns the genes? ...
... • Will we have the resources to continue developing new varieties? • Seed banks may help but who owns the genes? ...
Making sense of genetic variation!
... •!infer the evolutionary mechanisms responsible for the origins and maintenance of genetic variation Mutation is the source of variation that stochastic and deterministic factors can upon. ...
... •!infer the evolutionary mechanisms responsible for the origins and maintenance of genetic variation Mutation is the source of variation that stochastic and deterministic factors can upon. ...
Chapter 10.3 Notes The Theory of Natural Selection **Key Concept
... a. Darwin noticed a lot of variation in domesticated plants and animals b. Artificial selection is the process by which humans select traits through breeding ...
... a. Darwin noticed a lot of variation in domesticated plants and animals b. Artificial selection is the process by which humans select traits through breeding ...
Conservation of Farm Animal Genetic Resources
... (FAnGR are a source of income for poor rural communities, losing them will be detrimental to their livelihoods). ...
... (FAnGR are a source of income for poor rural communities, losing them will be detrimental to their livelihoods). ...
Mechanisms in variability
... plants in a common garden. This was the approach of Clausen, Keck and Hiesey (1948) in studying variation in yarrow from the Pacific coast near Stanford University up the Sierra Nevada mountains. In their native environments the plants varied in size and stature. All grown in a common garden at Stan ...
... plants in a common garden. This was the approach of Clausen, Keck and Hiesey (1948) in studying variation in yarrow from the Pacific coast near Stanford University up the Sierra Nevada mountains. In their native environments the plants varied in size and stature. All grown in a common garden at Stan ...
Class Project: Online Research for a Genetic Disorder
... continued refinement of the data brings us ever closer to a complete human genome reference sequence. This will be a fundamental resource in future biomedical research. The 46 human chromosomes between them house almost 3 billion base pairs of DNA that contains about 30,000 - 40,000 protein-coding g ...
... continued refinement of the data brings us ever closer to a complete human genome reference sequence. This will be a fundamental resource in future biomedical research. The 46 human chromosomes between them house almost 3 billion base pairs of DNA that contains about 30,000 - 40,000 protein-coding g ...
Population Genetics
... 1. Genetic Drift: This represents random changes in small gene pools due to sampling errors in propagation of alleles. The bottleneck effect and founder effect are prime examples of genetic drift. In either case the number of individuals in a population is drastically reduced distorting the original ...
... 1. Genetic Drift: This represents random changes in small gene pools due to sampling errors in propagation of alleles. The bottleneck effect and founder effect are prime examples of genetic drift. In either case the number of individuals in a population is drastically reduced distorting the original ...
Section B: Causes of Microevolution CHAPTER 23 THE
... • Genetic drift occurs when changes in gene frequencies from one generation to another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. • For example, one would not be too surprised if a coin produced seven heads and three tails in ten tosses, but you ...
... • Genetic drift occurs when changes in gene frequencies from one generation to another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. • For example, one would not be too surprised if a coin produced seven heads and three tails in ten tosses, but you ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.