File
... Imagine that you observe an increase in the frequency of brown coloration genes and a decrease in the frequency of green coloration genes in a beetle population. Any combination of the mechanisms of microevolution might be responsible for the pattern, and part of the scientist's job is to figure out ...
... Imagine that you observe an increase in the frequency of brown coloration genes and a decrease in the frequency of green coloration genes in a beetle population. Any combination of the mechanisms of microevolution might be responsible for the pattern, and part of the scientist's job is to figure out ...
Organismal Biology/23B-CausesOfMicroevolution
... • Genetic drift occurs when changes in gene frequencies from one generation to another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. • For example, one would not be too surprised if a coin produced seven heads and three tails in ten tosses, but you ...
... • Genetic drift occurs when changes in gene frequencies from one generation to another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. • For example, one would not be too surprised if a coin produced seven heads and three tails in ten tosses, but you ...
Lecture 5 Mutation and Genetic Variation
... 2. One of the best documented examples of how new genes can originate concerns the evolution of the gene that codes for the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh). = enzyme that breaks down alcohol (found in rotting fruit). F. Changes in the number of chromosomes. Anueuploid variation – changes in the n ...
... 2. One of the best documented examples of how new genes can originate concerns the evolution of the gene that codes for the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh). = enzyme that breaks down alcohol (found in rotting fruit). F. Changes in the number of chromosomes. Anueuploid variation – changes in the n ...
Lecture series on “The Human Genome”
... rearrangements, the first identification of behavioural mutants, and the elucidation of gene regulatory networks controlling cell-cell communication and development of the body plan and organ systems. The genetic control of all of these processes has been remarkably conserved during the course of ev ...
... rearrangements, the first identification of behavioural mutants, and the elucidation of gene regulatory networks controlling cell-cell communication and development of the body plan and organ systems. The genetic control of all of these processes has been remarkably conserved during the course of ev ...
GENETICS OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
... prevention of CAD will require treating genetic and environmental risk factors. Polygenic diseases are due to multiple genes each contributing only minimally or moderately to the phenotype. The genome wide association study, initiated only 2 years ago has been extremely productive. The first common ...
... prevention of CAD will require treating genetic and environmental risk factors. Polygenic diseases are due to multiple genes each contributing only minimally or moderately to the phenotype. The genome wide association study, initiated only 2 years ago has been extremely productive. The first common ...
Psych8_Lecture_Ch02use
... • It is important to avoid the naturalistic fallacy, however—it does not follow that evolution somehow improves organisms or that anything natural is good. • This means the genotypes and phenotypes that are passed on to survive allow the organisms to survive. It does not necessarily mean this is goo ...
... • It is important to avoid the naturalistic fallacy, however—it does not follow that evolution somehow improves organisms or that anything natural is good. • This means the genotypes and phenotypes that are passed on to survive allow the organisms to survive. It does not necessarily mean this is goo ...
Is socialism against human nature?
... patent genes for profit and thus not someone to be suspected of anti-capitalist or pro-socialist leanings) declared in the official press release issued by the journal Science [1] which published his firms results in its 16 February issue: "There are many surprises from this first look at our geneti ...
... patent genes for profit and thus not someone to be suspected of anti-capitalist or pro-socialist leanings) declared in the official press release issued by the journal Science [1] which published his firms results in its 16 February issue: "There are many surprises from this first look at our geneti ...
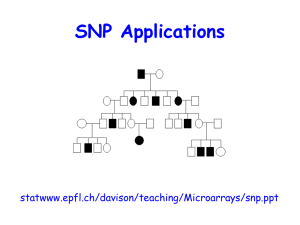
SNP Applications
... alleles shared identical by descent (IBD) of related individuals • Can be done either assuming (likelihood-based) or not assuming (nonparametric) a genetic mode of inheritance for a trait ...
... alleles shared identical by descent (IBD) of related individuals • Can be done either assuming (likelihood-based) or not assuming (nonparametric) a genetic mode of inheritance for a trait ...
My Slides - people.vcu.edu
... • What kinds of sequence changes cause effects? • Are most genetic changes affecting nearby genes or distal genes? • How much variation is there? • How robust is regulation overall? ...
... • What kinds of sequence changes cause effects? • Are most genetic changes affecting nearby genes or distal genes? • How much variation is there? • How robust is regulation overall? ...
Name: Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics Exam Matching: Match
... 11. Many genes have more than two alleles and are therefore said to have . This does not mean that an individual can have more than two alleles. It only means that more than two possible alleles exist in a population. 12. Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes. Traits controlle ...
... 11. Many genes have more than two alleles and are therefore said to have . This does not mean that an individual can have more than two alleles. It only means that more than two possible alleles exist in a population. 12. Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes. Traits controlle ...
Genes Within Populations
... • selection—the only form that produced adaptive evolutionary changes • Selection is the only agent that depends on the nature of the environment. The other 4 are independent of the environment. ...
... • selection—the only form that produced adaptive evolutionary changes • Selection is the only agent that depends on the nature of the environment. The other 4 are independent of the environment. ...
Human Genetic Disease Research Project
... What is the long-term prognosis (outlook) for an individual with this disease? Are there any treatments or cures? Could this disorder have been prevented? Can this individual have children in the future? Will their children be affected? What is the current status of research on this disord ...
... What is the long-term prognosis (outlook) for an individual with this disease? Are there any treatments or cures? Could this disorder have been prevented? Can this individual have children in the future? Will their children be affected? What is the current status of research on this disord ...
PGS: 454 – 458
... B. Populations evolve; not individuals. (You do not evolve; you get older, larger, and smarter!) 1. This is because we “are” what we “are” because of the genes that we inherit from our parents. You cannot change the DNA you were given from your biological parents but genetic mutations can occur rand ...
... B. Populations evolve; not individuals. (You do not evolve; you get older, larger, and smarter!) 1. This is because we “are” what we “are” because of the genes that we inherit from our parents. You cannot change the DNA you were given from your biological parents but genetic mutations can occur rand ...
The brain and spinal cord comprise the central nervous system
... • Describe how the cell cycle is believed to be controlled, and relate this mechanism to the development of cancer. • Draw a series of diagrams illustrating the phases of mitosis in animal cells, and tell what happens during each phase; describe cytokinesis in animal cells. • State differences betwe ...
... • Describe how the cell cycle is believed to be controlled, and relate this mechanism to the development of cancer. • Draw a series of diagrams illustrating the phases of mitosis in animal cells, and tell what happens during each phase; describe cytokinesis in animal cells. • State differences betwe ...
L9 genetic engineering
... whose bodies have been deep-frozen. Most people would be opposed to cloning a human from a deep-frozen, long-dead relative. Give one reason why. ...
... whose bodies have been deep-frozen. Most people would be opposed to cloning a human from a deep-frozen, long-dead relative. Give one reason why. ...
Applied Genetics
... • Genes are now known to control more than one trait • By altering/changing a single gene, multiple traits may be changed in ways we can’t predict • Human genes are only a small percentage of the information contained in DNA (5% or less)…we don’t know what most of the rest does ...
... • Genes are now known to control more than one trait • By altering/changing a single gene, multiple traits may be changed in ways we can’t predict • Human genes are only a small percentage of the information contained in DNA (5% or less)…we don’t know what most of the rest does ...
AR/AD/X-linked - REACh Families
... autosomal chromosomes Dominant: a change on one of the chromosomes is enough to cause disease Affects every generation Affects males and females equally ...
... autosomal chromosomes Dominant: a change on one of the chromosomes is enough to cause disease Affects every generation Affects males and females equally ...
Models, predictions, and the fossil record of modern human origins
... and that both African replacement and multiregional models can explain observed patterns of genetic variation.1,2 Consider, for example, the finding that many traits show higher genetic diversity within sub-Saharan African populations. While this finding can be interpreted as indicating a greater ag ...
... and that both African replacement and multiregional models can explain observed patterns of genetic variation.1,2 Consider, for example, the finding that many traits show higher genetic diversity within sub-Saharan African populations. While this finding can be interpreted as indicating a greater ag ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... Mutation – creating a new allele Gene flow – transferring alleles form one population to ...
... Mutation – creating a new allele Gene flow – transferring alleles form one population to ...
The Human Genome
... “very delicate.” Leading the life of a normal youngster was impossible because any cut or bump could lead to death. It was necessary to keep him always under strict surveillance. In spite of all the protection, he died at the age of 31 as the result of a minor fall. ...
... “very delicate.” Leading the life of a normal youngster was impossible because any cut or bump could lead to death. It was necessary to keep him always under strict surveillance. In spite of all the protection, he died at the age of 31 as the result of a minor fall. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.