Whole Exome Re-Sequencing Implicates CCDC38 and
... airflow obstruction. Although the main risk factor for COPD is smoking, some individuals are observed to have a high forced expired volume in 1 second (FEV1) despite many years of heavy smoking. We hypothesised that these ‘‘resistant smokers’’ may harbour variants which protect against lung function ...
... airflow obstruction. Although the main risk factor for COPD is smoking, some individuals are observed to have a high forced expired volume in 1 second (FEV1) despite many years of heavy smoking. We hypothesised that these ‘‘resistant smokers’’ may harbour variants which protect against lung function ...
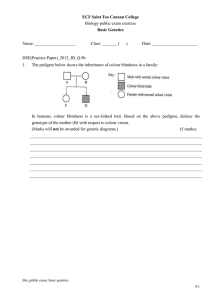
public exam_basic genetics_R1
... The parents of students 1 and 2 are tongue-rollers, so each of them must carry at least one allele for tongue rolling. Student 2 is a non-roller, so she must have received at least one allele for non-tongue ...
... The parents of students 1 and 2 are tongue-rollers, so each of them must carry at least one allele for tongue rolling. Student 2 is a non-roller, so she must have received at least one allele for non-tongue ...
The Units of Selection
... bility, and probability of fertilization of gametes that arises from their own haploid genotype, independent of the genotype of the parents which formed them. Thus, differences in germination of seeds or hatching of eggs arising from different amounts of nutritive material are not gametic selection ...
... bility, and probability of fertilization of gametes that arises from their own haploid genotype, independent of the genotype of the parents which formed them. Thus, differences in germination of seeds or hatching of eggs arising from different amounts of nutritive material are not gametic selection ...
Interplay between copy number, dosage compensation and
... median of values for one dose genes with the distribution of median values for the same number of two dose genes that were randomly sampled from each line (Fig 1A). For both sexes, we observed that one dose genes had significantly higher expression variability than two dose genes (P < 0.001). In ...
... median of values for one dose genes with the distribution of median values for the same number of two dose genes that were randomly sampled from each line (Fig 1A). For both sexes, we observed that one dose genes had significantly higher expression variability than two dose genes (P < 0.001). In ...
MGI-Guidelines for Nomenclature of Genes, Genetic Markers
... To aid interspecific comparison of genetic and other information, a gene that is identifiable as a homolog of an already named gene in another species can be named as "-like" "-homolog" or "related." (Note: this is not the same as "related sequence" which applies to related sequences within mouse or ...
... To aid interspecific comparison of genetic and other information, a gene that is identifiable as a homolog of an already named gene in another species can be named as "-like" "-homolog" or "related." (Note: this is not the same as "related sequence" which applies to related sequences within mouse or ...
slowly switching between environments facilitates reverse evolution
... Data Archived: Dryad doi:10.5061/dryad.0s96k Natural populations must constantly adapt to ever-changing environmental conditions. A particularly interesting question is whether such adaptations can be reversed by returning the population to an ancestral environment. Such evolutionary reversals have ...
... Data Archived: Dryad doi:10.5061/dryad.0s96k Natural populations must constantly adapt to ever-changing environmental conditions. A particularly interesting question is whether such adaptations can be reversed by returning the population to an ancestral environment. Such evolutionary reversals have ...
1 Genetic constitution of a population
... Several agencies affect gene and genotype frequencies in the process of transmission of genes from one generation to the next. To understand quantitative genetic variation fully we need to know how these factors, separately and together, influence genetic variation in populations over time, and what ...
... Several agencies affect gene and genotype frequencies in the process of transmission of genes from one generation to the next. To understand quantitative genetic variation fully we need to know how these factors, separately and together, influence genetic variation in populations over time, and what ...
One vitellogenin gene in an ocean of many: The molecular ecology
... sets of the teleost orthologs revealing a fourth group of orthologs (aqp8ba) in the older teleost lineages. To validate these observations, we re-examined the syntenic relationships of the teleost aqp8 genes in relation to the spotted gar loci (Figure S10). These new data confirmed the syntenic arra ...
... sets of the teleost orthologs revealing a fourth group of orthologs (aqp8ba) in the older teleost lineages. To validate these observations, we re-examined the syntenic relationships of the teleost aqp8 genes in relation to the spotted gar loci (Figure S10). These new data confirmed the syntenic arra ...
Handouts BIO301-Essentials of Genetics Virtual University of Pakistan
... Labrador retrievers one gene locus affects coat color by controlling pigment eumelanin deposited in the fur. Example A dominant allele B for black, recessive allele b brown coat, a second gene (e) locus controls eumelanin deposited in fur. Dogs homozygous recessive at this locus (ee) will have ...
... Labrador retrievers one gene locus affects coat color by controlling pigment eumelanin deposited in the fur. Example A dominant allele B for black, recessive allele b brown coat, a second gene (e) locus controls eumelanin deposited in fur. Dogs homozygous recessive at this locus (ee) will have ...
Integration of QTL Information with Traditional Animal Breeding
... and extent of LD is important. The main factors that create LD in a population are mutation, selection, drift (inbreeding), and migration or crossing (see below). The main factor that breaks down LD is the process of recombination that rearranges haplotypes that exist within a parent in every genera ...
... and extent of LD is important. The main factors that create LD in a population are mutation, selection, drift (inbreeding), and migration or crossing (see below). The main factor that breaks down LD is the process of recombination that rearranges haplotypes that exist within a parent in every genera ...
PDF version - GeneNetwork
... Variation in expression is purely due to differences among cell and organ systems rather than being due to genetic or environmental factors. The output tables and graphs are particularly useful when studying genes with minimal annotation or when testing the hypothesis that expression of two or more ...
... Variation in expression is purely due to differences among cell and organ systems rather than being due to genetic or environmental factors. The output tables and graphs are particularly useful when studying genes with minimal annotation or when testing the hypothesis that expression of two or more ...
PDF
... of them are restricted to populations under Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE; see, e.g., Falconer and MacKay, 1996), including a special case of gene frequency being one half (Mather and Jinks, 1982). Others also adequately account for Hardy–Weinberg disequilibrium (HWD; e.g., Cockerham, 1954; Yang, ...
... of them are restricted to populations under Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE; see, e.g., Falconer and MacKay, 1996), including a special case of gene frequency being one half (Mather and Jinks, 1982). Others also adequately account for Hardy–Weinberg disequilibrium (HWD; e.g., Cockerham, 1954; Yang, ...
PDF
... oligonucleotide array detected more transcripts that are less conserved compared to the known exons, especially those transcripts toward the end of the chromosome. ...
... oligonucleotide array detected more transcripts that are less conserved compared to the known exons, especially those transcripts toward the end of the chromosome. ...
Natural Selection and Genetic Drift: An Exploration of Allele
... An allele is one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome. Because each person’s genome contains two copies of each chromosome (one from his father and one from his mother), each individual has two alleles for each gene. These ...
... An allele is one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome. Because each person’s genome contains two copies of each chromosome (one from his father and one from his mother), each individual has two alleles for each gene. These ...
PATERNAL CARE: DIRECT AND INDIRECT GENETIC EFFECTS
... There is underlying genetic variation in all parental care behaviors for both sexes in N. vespilloides with moderate to strong intersexual genetic correlations (Walling et al. 2008). However, within the sexes, the pattern of genetic correlations between parental care behaviors differs for males and ...
... There is underlying genetic variation in all parental care behaviors for both sexes in N. vespilloides with moderate to strong intersexual genetic correlations (Walling et al. 2008). However, within the sexes, the pattern of genetic correlations between parental care behaviors differs for males and ...
From out of old fields comes all this new corn
... and epistatic components of variance indicate that the magnitude of epistatic variance is small compared to additive and dominance components. • Yet, the magnitude of epistatic variance is difficult to estimate, and may play a very important role in heterosis. ...
... and epistatic components of variance indicate that the magnitude of epistatic variance is small compared to additive and dominance components. • Yet, the magnitude of epistatic variance is difficult to estimate, and may play a very important role in heterosis. ...
Introduction to Paleoanthropology
... from the contents of one of these projects and the content was still licensed by the project under this license at the time of derivation this document has to be licensed under the same, a similar or a compatible license, as stated in section 4b of the license. The list of contributors is included i ...
... from the contents of one of these projects and the content was still licensed by the project under this license at the time of derivation this document has to be licensed under the same, a similar or a compatible license, as stated in section 4b of the license. The list of contributors is included i ...
Mutation at the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene (PAH) and its use
... of the region of North America called Quebec, where resides one of the best documented populations in the world.2–6 French settlers came before 1759; Loyalists from the United States and emigrants from the United Kingdom came after 1759; non-French, non-British settlers arrived in substantial number ...
... of the region of North America called Quebec, where resides one of the best documented populations in the world.2–6 French settlers came before 1759; Loyalists from the United States and emigrants from the United Kingdom came after 1759; non-French, non-British settlers arrived in substantial number ...
biojeopardy evolution
... What are Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain DNA, which encodes some of their proteins. Also…they are not connected physically or via transport vesicles to organelles of the endomembrane system. Continue ...
... What are Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain DNA, which encodes some of their proteins. Also…they are not connected physically or via transport vesicles to organelles of the endomembrane system. Continue ...
For those mutants where the enhancement bred true, if
... +/ +; Df(3R)p13, e, */ TM6B were selected by the presence of the ebony marker, and the absence of the p[w+] marker, and used to create independent stocks. Those mutants which segregated with the X chromosome were discarded. ...
... +/ +; Df(3R)p13, e, */ TM6B were selected by the presence of the ebony marker, and the absence of the p[w+] marker, and used to create independent stocks. Those mutants which segregated with the X chromosome were discarded. ...
Analysis of Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli O145 strains
... O145-associated illness were reported in a day care in Minnesota in 1999 (Luna and Mody, 2010). It was also responsible for a waterborne human illness in Oregon in 2005 (Yoder et al., 2008). In 2010, there was a multistate outbreak of E. coli O145 STEC infections associated with the consumption of r ...
... O145-associated illness were reported in a day care in Minnesota in 1999 (Luna and Mody, 2010). It was also responsible for a waterborne human illness in Oregon in 2005 (Yoder et al., 2008). In 2010, there was a multistate outbreak of E. coli O145 STEC infections associated with the consumption of r ...
Human Origins and Intelligent Design*
... orangutans are also non-existent.19, 21 In light of the fossil record, it seems likely that the first simians and early hominoids are members of basic types distinct from both lower primates and living apes. Modern apes may represent at least one basic type. Crossbreeding and genetic experiments cou ...
... orangutans are also non-existent.19, 21 In light of the fossil record, it seems likely that the first simians and early hominoids are members of basic types distinct from both lower primates and living apes. Modern apes may represent at least one basic type. Crossbreeding and genetic experiments cou ...
BioinformaIcs Journal Club
... species. Without this analysis, we would have concluded from the first mapping that this symbiont was absent (or at very low abundance) from all individuals. ...
... species. Without this analysis, we would have concluded from the first mapping that this symbiont was absent (or at very low abundance) from all individuals. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.