Support worksheet – Chapter 4 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... the description applies to the process or a cross () if it does not. ...
... the description applies to the process or a cross () if it does not. ...
Key Area 6 Genetic Engineering
... Problem with that . . . 1. It was a slow and expensive process 2. Some people were allergic to the animal insulin 3. Some people did not like the idea of injecting a substance that came from animals ...
... Problem with that . . . 1. It was a slow and expensive process 2. Some people were allergic to the animal insulin 3. Some people did not like the idea of injecting a substance that came from animals ...
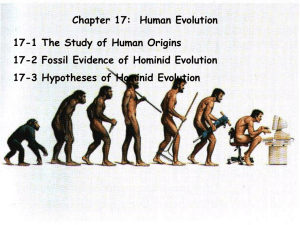
Chapter 17-Human Evolution
... Cro-Magnons later flourished would constitute evidence that the Neanderthals were killed off by Cro-Magnons. Fossil evidence of a body type representing a blend of Neanderthals and Cro-Magnon features would support the hypothesis that the two groups interbred. (4) It is not inevitable that descendan ...
... Cro-Magnons later flourished would constitute evidence that the Neanderthals were killed off by Cro-Magnons. Fossil evidence of a body type representing a blend of Neanderthals and Cro-Magnon features would support the hypothesis that the two groups interbred. (4) It is not inevitable that descendan ...
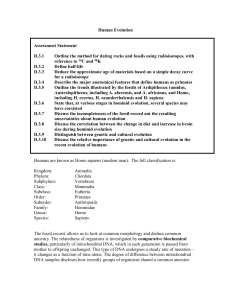
Human Evolution
... with a tendency for bipedalism will have had a better chance of replication in future generations. This would have been particularly effective in male–female pairs, rather than in troops of primates where males invested time and energy maintaining dominance over the females. On this account, hominid ...
... with a tendency for bipedalism will have had a better chance of replication in future generations. This would have been particularly effective in male–female pairs, rather than in troops of primates where males invested time and energy maintaining dominance over the females. On this account, hominid ...
Evolution Review 1. Define: homologous structures, analogous
... Define: homologous structures, analogous structures, cladogram/cladistics, common ancestor, natural selection, evolution, binomial nomenclature, taxonomy, species, adaptation, extinct, genetic variation ...
... Define: homologous structures, analogous structures, cladogram/cladistics, common ancestor, natural selection, evolution, binomial nomenclature, taxonomy, species, adaptation, extinct, genetic variation ...
Fundamentals of Genetics
... for each physical trait, and these alleles separate randomly during the formation of gametes ...
... for each physical trait, and these alleles separate randomly during the formation of gametes ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Variegation is a term that describes a leaf or flower that has two or more colors in a distinct alternating pattern. In some cases, variegation is caused by a mutation in the meristem that results in a chimera. Other sources of variegation include: Pattern variegation Transposons ...
... Variegation is a term that describes a leaf or flower that has two or more colors in a distinct alternating pattern. In some cases, variegation is caused by a mutation in the meristem that results in a chimera. Other sources of variegation include: Pattern variegation Transposons ...
File
... mechanism for evolution). This will help to illustrate your understanding of how natural selection works. We will be presenting these projects briefly ( a few minutes apiece). Natural Selection is the central theme in evolution and explains how organisms adapt to their environments and how variation ...
... mechanism for evolution). This will help to illustrate your understanding of how natural selection works. We will be presenting these projects briefly ( a few minutes apiece). Natural Selection is the central theme in evolution and explains how organisms adapt to their environments and how variation ...
Running head: A RESEARCH GUIDE TO THE GENETIC
... two different languages at once to succeed. Genres: There are a multitude of genres that correspond with this discourse community. There are simple methods of communication, but also more medical related forums needed. For example, encounters, medical forms filled out by the genetic counselor, are u ...
... two different languages at once to succeed. Genres: There are a multitude of genres that correspond with this discourse community. There are simple methods of communication, but also more medical related forums needed. For example, encounters, medical forms filled out by the genetic counselor, are u ...
Mendelian Genetics Student Objectives
... Essential knowledge 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding of the pattern of passage (transmission) of genes from parent to offspring. a. Rules of probability can be applied to analyze passage of single gene traits from parent to offspring. b. Segregation and independe ...
... Essential knowledge 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding of the pattern of passage (transmission) of genes from parent to offspring. a. Rules of probability can be applied to analyze passage of single gene traits from parent to offspring. b. Segregation and independe ...
genetics, health and disease
... single protein but can have drastic consequences. For example, a change to a single base can lead to the formation of a nonMutations in reproductive cells are passed on functional protein. Mutations outside the coding regions of to all of the offspring's body cells. genes can still affect protein pr ...
... single protein but can have drastic consequences. For example, a change to a single base can lead to the formation of a nonMutations in reproductive cells are passed on functional protein. Mutations outside the coding regions of to all of the offspring's body cells. genes can still affect protein pr ...
Introduction to Genetics and Genomics
... identical pairs matched homologous pairs match up (called a bivalent) crossing over can now occur as chromatids shorten, and thicken, they are called “tetrads” ...
... identical pairs matched homologous pairs match up (called a bivalent) crossing over can now occur as chromatids shorten, and thicken, they are called “tetrads” ...
Human Biology
... Some of this variation is due to our parents, but some of it is due to our upbringing and the environment in which we live – this is called “Environmental variation”. Variation due to inheritance only ...
... Some of this variation is due to our parents, but some of it is due to our upbringing and the environment in which we live – this is called “Environmental variation”. Variation due to inheritance only ...
Ethical issues in personalized genomics
... back to the start of technological time: the gradual replacement of luck with control. Once upon a time, we were dealt a hand by Fate, God, or the Unreliable Narrator, and the task of life was to deal with that hand. Now the task is to improve the deal. – Richard Powers ...
... back to the start of technological time: the gradual replacement of luck with control. Once upon a time, we were dealt a hand by Fate, God, or the Unreliable Narrator, and the task of life was to deal with that hand. Now the task is to improve the deal. – Richard Powers ...
B1 You and your genes
... Some of this variation is due to our parents, but some of it is due to our upbringing and the environment in which we live – this is called “Environmental variation”. Variation due to inheritance only ...
... Some of this variation is due to our parents, but some of it is due to our upbringing and the environment in which we live – this is called “Environmental variation”. Variation due to inheritance only ...
Agents of Change Lab Activity In this investigation, you will design
... Part II: Genetic Drift 10. Run at least 4 generations in which you examine the influence of population size on the degree and rate of genetic drift. Choose two or more starting populations of different sizes. As an option, you may also wish to model a founder effect. Part III: Natural Selection 11. ...
... Part II: Genetic Drift 10. Run at least 4 generations in which you examine the influence of population size on the degree and rate of genetic drift. Choose two or more starting populations of different sizes. As an option, you may also wish to model a founder effect. Part III: Natural Selection 11. ...
www.bioecon-network.org
... • benchmark with no externalities – modest extent of conservation due to non-rivalry and homogeneous parcels. • when externalities prevail – the higher the relative value of genetic information the more natural areas are allocated to conservation. • when externalities and thresholds prevail – it is ...
... • benchmark with no externalities – modest extent of conservation due to non-rivalry and homogeneous parcels. • when externalities prevail – the higher the relative value of genetic information the more natural areas are allocated to conservation. • when externalities and thresholds prevail – it is ...
Document
... Homologous autosomes are identical in length, size, shape, and gene sequence Sex chromosomes are nonidentical but still homologous Homologous chromosomes interact, then segregate from one another during meiosis ...
... Homologous autosomes are identical in length, size, shape, and gene sequence Sex chromosomes are nonidentical but still homologous Homologous chromosomes interact, then segregate from one another during meiosis ...
Chapter 15 How Organisms Evolve
... population to another – Immigration adds alleles to a population – Emigration removes alleles from a population ...
... population to another – Immigration adds alleles to a population – Emigration removes alleles from a population ...
CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES The Basis of
... 1. Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction. The Role of Meiosis in Sexual Life Cycles 2. Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: a. somatic cell and gamete b. autosome and sex chromosome c. haploid and diploid 3. Describe a karyotype and the types of information one can gain fr ...
... 1. Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction. The Role of Meiosis in Sexual Life Cycles 2. Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: a. somatic cell and gamete b. autosome and sex chromosome c. haploid and diploid 3. Describe a karyotype and the types of information one can gain fr ...
BIO 1102 - Makerere University Courses
... Outline the significance of nucleic acids, autosomal inheritance, epistasis, linkage, gene cloning, population genetics and ecological genetics. ...
... Outline the significance of nucleic acids, autosomal inheritance, epistasis, linkage, gene cloning, population genetics and ecological genetics. ...
Becoming Human Viewers Guide
... 2. “Hominds such as Lucy serve as a touchstone for discussing human origins.” 3. “In some ways, homo erectus was the evolutionary parent of our own species.” ...
... 2. “Hominds such as Lucy serve as a touchstone for discussing human origins.” 3. “In some ways, homo erectus was the evolutionary parent of our own species.” ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.