Biology 2002 - Spring Branch ISD
... 1. Recall the video and explain Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection and his “tree of life” idea. How does his theory explain the diversity of life on earth today? 2. In the theory of evolution, the term adaptation refers to random genetic changes in the DNA code of an organism, which i ...
... 1. Recall the video and explain Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection and his “tree of life” idea. How does his theory explain the diversity of life on earth today? 2. In the theory of evolution, the term adaptation refers to random genetic changes in the DNA code of an organism, which i ...
Final Exam Genetics Fall 2011
... 7) In small isolated populations, gene frequencies can fluctuate considerably. The term that applies to this circumstance is A) natural selection. B) stabilizing selection. C) genetic isolation. D) allelic separation. E) genetic drift. ...
... 7) In small isolated populations, gene frequencies can fluctuate considerably. The term that applies to this circumstance is A) natural selection. B) stabilizing selection. C) genetic isolation. D) allelic separation. E) genetic drift. ...
Medical Genomics and Electronic Health Records
... The patient asks about her risk of ovarian cancer as her aunt died from this disease The physician queries the database Her risk is found to be low based on: ○ The alleles she has inherited ○ Her exposure to epigenetic influences The patient is reassured ...
... The patient asks about her risk of ovarian cancer as her aunt died from this disease The physician queries the database Her risk is found to be low based on: ○ The alleles she has inherited ○ Her exposure to epigenetic influences The patient is reassured ...
Document
... Where humans change a species by breeding it for certain traits. Ex. Humans select traits that are favorable in plants and animals, then breed only those with the trait, producing more of that trait. ...
... Where humans change a species by breeding it for certain traits. Ex. Humans select traits that are favorable in plants and animals, then breed only those with the trait, producing more of that trait. ...
Genetic Variation Mutations
... Genetic Variation There are three primary sources of genetic variation, which we will learn more about: ...
... Genetic Variation There are three primary sources of genetic variation, which we will learn more about: ...
Document
... The reference sequence for each human chromosome provides the framework for understanding genome function, variation and evolution. Here we report the finished sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1. Chromosome 1 is gene-dense, with 3,141 genes and 991 pseudogenes, and many coding ...
... The reference sequence for each human chromosome provides the framework for understanding genome function, variation and evolution. Here we report the finished sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1. Chromosome 1 is gene-dense, with 3,141 genes and 991 pseudogenes, and many coding ...
Bio 30 Unit D1 Population GeneticsTAR
... • Distinguish between founder effect and the bottleneck effect on gene pools. • Explain how the process of natural selection is related to microevolution. • Explain the cause of heterozygote advantage and how it affects a gene pool. • Describe strategies used in captive breeding and population manag ...
... • Distinguish between founder effect and the bottleneck effect on gene pools. • Explain how the process of natural selection is related to microevolution. • Explain the cause of heterozygote advantage and how it affects a gene pool. • Describe strategies used in captive breeding and population manag ...
Gene Regulation in Cells
... translation. Proteins are the molecular machines that carry out the functions that cells need to perform, so the exact mix of proteins in a cell determines its cell fate (what kind of cell it is, for example making a neuron different from a skin cell). Therefore, gene regulation links genotype (gene ...
... translation. Proteins are the molecular machines that carry out the functions that cells need to perform, so the exact mix of proteins in a cell determines its cell fate (what kind of cell it is, for example making a neuron different from a skin cell). Therefore, gene regulation links genotype (gene ...
gene to protein webquest.indd
... transport of materials, energy transfer, protein building, waste disposal, information feedback, and even movement. In addition, most cells in multicellular organisms perform some special functions that others do not. • The Living Environment: Cells - the work of the cell is carried out by the many ...
... transport of materials, energy transfer, protein building, waste disposal, information feedback, and even movement. In addition, most cells in multicellular organisms perform some special functions that others do not. • The Living Environment: Cells - the work of the cell is carried out by the many ...
File
... source, or species, is known as recombinant DNA. Process of joining together fragments of DNA is called gene splicing. Why make recombinant DNA? To make plants resistant to disease To make bacteria produce certain proteins for humans that can’t, like insulin ...
... source, or species, is known as recombinant DNA. Process of joining together fragments of DNA is called gene splicing. Why make recombinant DNA? To make plants resistant to disease To make bacteria produce certain proteins for humans that can’t, like insulin ...
Level Guide Chapter 9
... with the same form of the trait as the parent plant. Mendel used cross-pollination to find out what would happen if he crossed two plants with different forms of a trait. When Mendel used ratios to compare the number of white flowers to the number of purple flowers produced in the second generation, ...
... with the same form of the trait as the parent plant. Mendel used cross-pollination to find out what would happen if he crossed two plants with different forms of a trait. When Mendel used ratios to compare the number of white flowers to the number of purple flowers produced in the second generation, ...
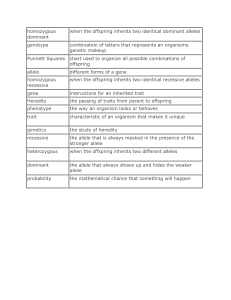
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
Reproduction in Plants - Amazing World of Science with Mr. Green
... Part of the cell which contains chromosomes Structures in the nucleus that are made from a chemical called DNA A chemical that contains the code for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what that organism will look like). The coded instructions contained in DNA which give the organism its inheri ...
... Part of the cell which contains chromosomes Structures in the nucleus that are made from a chemical called DNA A chemical that contains the code for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what that organism will look like). The coded instructions contained in DNA which give the organism its inheri ...
The principles and methods formulated by Gregor Mendel provide
... 1/4 AA, 2/4 Aa, 1/4 aa, which can also be expressed as a 1:2:1 ratio. 9. For the corresponding phenotypes, the fraction with normal pigmentation is ______ and the fraction with albinism is _____, so the corresponding ratio is ____________. Notice that the chart you completed on page 2 has been very ...
... 1/4 AA, 2/4 Aa, 1/4 aa, which can also be expressed as a 1:2:1 ratio. 9. For the corresponding phenotypes, the fraction with normal pigmentation is ______ and the fraction with albinism is _____, so the corresponding ratio is ____________. Notice that the chart you completed on page 2 has been very ...
Molecular Koch`s Postulates Applied to Microbial Pathogenicity
... hold within a specific host, to avoid normal host genic members of a genus or pathogenic strains of defense mechanisms, and, once established, to mula species. (2) Specific inactivation of the gene(s) astiply. To the microbial geneticist, the challenge issociated to with the suspected virulence trai ...
... hold within a specific host, to avoid normal host genic members of a genus or pathogenic strains of defense mechanisms, and, once established, to mula species. (2) Specific inactivation of the gene(s) astiply. To the microbial geneticist, the challenge issociated to with the suspected virulence trai ...
slides available - The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering
... Network of thousands of organizations around the world, 1200 of which are disease advocacy organizations. Working to accelerate development and access to interventions for all conditions driven by patients/participants/consumers ...
... Network of thousands of organizations around the world, 1200 of which are disease advocacy organizations. Working to accelerate development and access to interventions for all conditions driven by patients/participants/consumers ...
GENETICS
... Explain some mechanisms by which gene expression is regulated in prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. Explain current recombinant technologies. Explain some practical applications of nucleic acid technology. Explain the legal and ethical problems that may arise from technology applications. ...
... Explain some mechanisms by which gene expression is regulated in prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. Explain current recombinant technologies. Explain some practical applications of nucleic acid technology. Explain the legal and ethical problems that may arise from technology applications. ...
Name
... 4.1.11 Explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics. 4.1.12 Predict the possible offspring from a monoybrid and dihybrid crosses using Punnett squares. Derive the genotypic and phenotype ratios. 4.1.13 Distinguish between various complex inheritance patterns (incomplete ...
... 4.1.11 Explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics. 4.1.12 Predict the possible offspring from a monoybrid and dihybrid crosses using Punnett squares. Derive the genotypic and phenotype ratios. 4.1.13 Distinguish between various complex inheritance patterns (incomplete ...
Biotechnology Pre/PostTest Key (w/citations)
... Piecescan of DNA from twoown different organisms can be joined They produce their pesticides They can grow larger than unmodified crops Genescannot from complex such as animals can be inserted into simpler organisms They cause an organisms allergic reaction Theysuch can as contain extra nutrients ba ...
... Piecescan of DNA from twoown different organisms can be joined They produce their pesticides They can grow larger than unmodified crops Genescannot from complex such as animals can be inserted into simpler organisms They cause an organisms allergic reaction Theysuch can as contain extra nutrients ba ...
Genetics of Cancer
... 6. What is the role of telomeres and cancer? Telomere Length and Cancer- If they become short 2 chromosomes Can stick together and some of these cells would die due to this. In cancer you normally see long telomeres because cancer cells resemble stem cells, because they have high telomerase acti ...
... 6. What is the role of telomeres and cancer? Telomere Length and Cancer- If they become short 2 chromosomes Can stick together and some of these cells would die due to this. In cancer you normally see long telomeres because cancer cells resemble stem cells, because they have high telomerase acti ...
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON THE UCL CANCER INSTITUTE
... Project Background: Our view of the regulatory genome has changed dramatically in recent years. We have expanded beyond classical models of gene control to appreciate that the spatial organization of the genome and the manner in which genes and regulatory elements are embedded therein has a critical ...
... Project Background: Our view of the regulatory genome has changed dramatically in recent years. We have expanded beyond classical models of gene control to appreciate that the spatial organization of the genome and the manner in which genes and regulatory elements are embedded therein has a critical ...
Biology - Greenwood International School
... 74. Describe how Mendel’s results can be explained by scientific knowledge of genes and chromosomes. 75. Differentiate between genotype and phenotype of an organism. 76. Explain how probability is used to predict the results of genetic crosses. 77. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of mono ...
... 74. Describe how Mendel’s results can be explained by scientific knowledge of genes and chromosomes. 75. Differentiate between genotype and phenotype of an organism. 76. Explain how probability is used to predict the results of genetic crosses. 77. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of mono ...
Self Assessment: Natural Selection
... b. evolutionary processes have a final goal they are striving towards c. organisms can always find the resources they need in some way or another d. there are only so many natural resources and humans are under pressure to use them now 4. All individuals of a species that live in a defined area is c ...
... b. evolutionary processes have a final goal they are striving towards c. organisms can always find the resources they need in some way or another d. there are only so many natural resources and humans are under pressure to use them now 4. All individuals of a species that live in a defined area is c ...
test 1 2003
... B) divergence of populations C) increase in homozygosity D) homogenization of populations E) B and C. 20) A person who believes that living forms are fundamentally different from non-living matter is a: A) mechanist B) vitalist C) atheist D) materialist 21) The use of Populus models A) demonstrates ...
... B) divergence of populations C) increase in homozygosity D) homogenization of populations E) B and C. 20) A person who believes that living forms are fundamentally different from non-living matter is a: A) mechanist B) vitalist C) atheist D) materialist 21) The use of Populus models A) demonstrates ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.