nucleic acids 3115
... DNA divides, separates, and attracts new nucleotides to replace the strand that split away. Interesting Scientific Fact: DNA and RNA work together to make protein. Protein, as you recall, is the type of molecule of which most living things are made. Here is how it works. The first part of the proces ...
... DNA divides, separates, and attracts new nucleotides to replace the strand that split away. Interesting Scientific Fact: DNA and RNA work together to make protein. Protein, as you recall, is the type of molecule of which most living things are made. Here is how it works. The first part of the proces ...
Gen660_Lecture1B_sequencing_2014
... Use a ‘super matrix’ of variable sequence characters 2. Construct many separate trees, one for each gene, and then compare Often construct a ‘super tree’ that is built from all single trees 3. Incorporate non-sequence characters like synteny, intron structure, etc. ...
... Use a ‘super matrix’ of variable sequence characters 2. Construct many separate trees, one for each gene, and then compare Often construct a ‘super tree’ that is built from all single trees 3. Incorporate non-sequence characters like synteny, intron structure, etc. ...
Chapter 11 – What is DNA and how does it work?
... So when a cell splits, each cell has identical DNA in each cell. 19.) How is it possible that new DNA and original DNA are identical? The bases are complementary so they always pair with the same exact base. ...
... So when a cell splits, each cell has identical DNA in each cell. 19.) How is it possible that new DNA and original DNA are identical? The bases are complementary so they always pair with the same exact base. ...
Learning outcomes
... I can explain the terms co-dominance and polygenic inheritance. I know that Genetic and Environmental Factors determine the final phenotype of an organism, and can give examples. I can explain the importance of natural selection in the evolution of a species. I can explain the difference between sel ...
... I can explain the terms co-dominance and polygenic inheritance. I know that Genetic and Environmental Factors determine the final phenotype of an organism, and can give examples. I can explain the importance of natural selection in the evolution of a species. I can explain the difference between sel ...
B1 Revision Mind Maps
... Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is i ...
... Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is i ...
Mendel's Laws of Heredity - West-MEC
... Meiosis :The cell division that produces sex cells. Mutation : A change in the type or order of the bases in an organism DNA: deletion, insertion or substitution. Natural Selection : The process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at a higher rate than organisms with ...
... Meiosis :The cell division that produces sex cells. Mutation : A change in the type or order of the bases in an organism DNA: deletion, insertion or substitution. Natural Selection : The process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at a higher rate than organisms with ...
Appendix A - Rodent Breeding
... 1. Colony managers are required to report health concerns related to the breeding colony to the LAR veterinary staff as soon as possible. Health concerns include but not limited to increased pup mortality, decreased reproductive efficiency, decreased pup growth rate or negatively altered parental or ...
... 1. Colony managers are required to report health concerns related to the breeding colony to the LAR veterinary staff as soon as possible. Health concerns include but not limited to increased pup mortality, decreased reproductive efficiency, decreased pup growth rate or negatively altered parental or ...
Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA
... mixture of chains terminating with T at their 3' end but aJI having the same 5' end (the 5' end of the primer). Similar incubations are c a r r i e d out in the p r e s e n c e of e a c h of the o t h e r t h r e e dideoxy derivatives, giving mixtures terminating at the positions of C, A, and G resp ...
... mixture of chains terminating with T at their 3' end but aJI having the same 5' end (the 5' end of the primer). Similar incubations are c a r r i e d out in the p r e s e n c e of e a c h of the o t h e r t h r e e dideoxy derivatives, giving mixtures terminating at the positions of C, A, and G resp ...
Genetic Problem Worksheet
... What is the probability that they have a child with type A blood? With type B blood? With type O blood? 10. Hemophilia is an X linked trait. If a mother is heterozygous for hemophilia and father does not have hemophilia, what is the probability that they have a child with hemophilia? ...
... What is the probability that they have a child with type A blood? With type B blood? With type O blood? 10. Hemophilia is an X linked trait. If a mother is heterozygous for hemophilia and father does not have hemophilia, what is the probability that they have a child with hemophilia? ...
Glossary - Red Angus Association of America
... --A measure of how two traits vary together. A correlation of +1.00 means that as one trait increases the other also increases – a perfect positive relationship. A correlation of –1.00 means that as one trait increases the other decreases—a perfect negative, or inverse, relationship. A correlation ...
... --A measure of how two traits vary together. A correlation of +1.00 means that as one trait increases the other also increases – a perfect positive relationship. A correlation of –1.00 means that as one trait increases the other decreases—a perfect negative, or inverse, relationship. A correlation ...
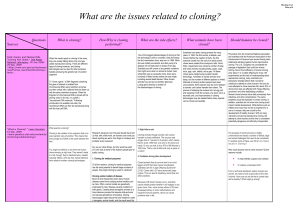
Human cloning - 10EssentialScience
... Much of what researchers learn about human disease comes from studying animal models such as mice. Often, animal models are genetically engineered to carry disease-causing mutations in their genes. Creating these transgenic animals is a time-intensive process that requires trial-and-error and severa ...
... Much of what researchers learn about human disease comes from studying animal models such as mice. Often, animal models are genetically engineered to carry disease-causing mutations in their genes. Creating these transgenic animals is a time-intensive process that requires trial-and-error and severa ...
AA - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... A biological species is: a grouping of organisms that can interbreed and are reproductively isolated from other such groups. Species are recognized on the basis of their morphology (size, shape, and appearance) and, more recently, by genetic analysis. For example, there are up to 20 000 species of b ...
... A biological species is: a grouping of organisms that can interbreed and are reproductively isolated from other such groups. Species are recognized on the basis of their morphology (size, shape, and appearance) and, more recently, by genetic analysis. For example, there are up to 20 000 species of b ...
this PDF file - Undergraduate Science Journals
... phenotypic changes, we will attempt to order to gauge the overall fertility of the identify the genomic changes responsible for generation. Selected plants have been the phenotypic changes using the examined for morphological changes and polymerase chain reaction technique, or photographed with a ca ...
... phenotypic changes, we will attempt to order to gauge the overall fertility of the identify the genomic changes responsible for generation. Selected plants have been the phenotypic changes using the examined for morphological changes and polymerase chain reaction technique, or photographed with a ca ...
Marcy-and-Silvia-for-posting
... The next slide is a sketch of pre-implantation genetic diagnosis or PGD. The embryo, shown as an oval, was created outside the body by combining egg and sperm in a petri dish, and allowed to grow and divide for 3 days until what as a singlecelled zygote became an 8-celled embryo. One of the 8 cells ...
... The next slide is a sketch of pre-implantation genetic diagnosis or PGD. The embryo, shown as an oval, was created outside the body by combining egg and sperm in a petri dish, and allowed to grow and divide for 3 days until what as a singlecelled zygote became an 8-celled embryo. One of the 8 cells ...
Document
... than are at lower temperatures, indicating that the fungus is under heat stress. 2. More putative virulence genes (ex. those coding for the proteins responsive to oxidative stress and host immune system and for toxin production) are highly expressed at 37˚C, although there is no contact with host ce ...
... than are at lower temperatures, indicating that the fungus is under heat stress. 2. More putative virulence genes (ex. those coding for the proteins responsive to oxidative stress and host immune system and for toxin production) are highly expressed at 37˚C, although there is no contact with host ce ...
presentation - Harlem Children Society
... transgenic mice C57B/6 vulnerable in developing melanoma comparable to human melanoma patients with mutated Hbraf gene. • The C57B/6 mice will be tested for the presence of mutBraf gene. • The mice that test out positive for the gene will be followed to see if they develop melanoma. • The melanomas ...
... transgenic mice C57B/6 vulnerable in developing melanoma comparable to human melanoma patients with mutated Hbraf gene. • The C57B/6 mice will be tested for the presence of mutBraf gene. • The mice that test out positive for the gene will be followed to see if they develop melanoma. • The melanomas ...
PLEIOTROPIC EFFECT OF Rht3 DWARFING GENE ON SOME
... and Rht1S are prevalentin Southern European cultivars (W ORLAND and LAW 1986). There were trials of using some other Rht dwarfing genes, but without significant success (W ORLAND et al. 1980). For now, only strong dwarfing allel Rht3 (known as 'Tom Thumb' or 'Minister dwarf' gene) shows some breedin ...
... and Rht1S are prevalentin Southern European cultivars (W ORLAND and LAW 1986). There were trials of using some other Rht dwarfing genes, but without significant success (W ORLAND et al. 1980). For now, only strong dwarfing allel Rht3 (known as 'Tom Thumb' or 'Minister dwarf' gene) shows some breedin ...
Inheritence of Quantitative Traits
... Genetic correlation if traits have a non-zero genetic correlation selection for one trait yields change in the other trait. ...
... Genetic correlation if traits have a non-zero genetic correlation selection for one trait yields change in the other trait. ...
Chapter 13 Guided Notes - Meiosis and Life Cycles
... ○ The sister chromatids are closely associated all along their length. This association is called _______________________________________________________. (Recall this from Chapter 12!) ...
... ○ The sister chromatids are closely associated all along their length. This association is called _______________________________________________________. (Recall this from Chapter 12!) ...
Genome duplication, divergent resolution and
... improve the image, but the original Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90, 7431–7435 and RNAi for genes encoding proteins picture, for the metazoa, will have been 10 Jansen, G. et al. (1997) Reverse genetics by involved in DNA replication caused a generated with broad-cast, dsRNAchemical mutagenesis in Caeno ...
... improve the image, but the original Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90, 7431–7435 and RNAi for genes encoding proteins picture, for the metazoa, will have been 10 Jansen, G. et al. (1997) Reverse genetics by involved in DNA replication caused a generated with broad-cast, dsRNAchemical mutagenesis in Caeno ...
Preparation of SCRATCHY Hybrid Protein Libraries
... of hybrid enzymes (ITCHY) technology (1) and DNA shuffling (2). It generates combinatorial libraries of hybrid proteins consisting of multiple fragments from two or more parental DNA sequences with no restriction to DNA sequence identity between the original sequences (3). Such multi-crossover hybri ...
... of hybrid enzymes (ITCHY) technology (1) and DNA shuffling (2). It generates combinatorial libraries of hybrid proteins consisting of multiple fragments from two or more parental DNA sequences with no restriction to DNA sequence identity between the original sequences (3). Such multi-crossover hybri ...
blood12618insidebloodcombined 2075..2083
... a poorer prognosis with regard to progressionfree and overall survival (OS). In fact, the patients with .1 mutation in the 9 genes (groups 3 and 4 in Guièze et al) had a significantly poorer outcome, with a median OS of 28.2 and 27.1 months, respectively. With the limited sample size of this study, ...
... a poorer prognosis with regard to progressionfree and overall survival (OS). In fact, the patients with .1 mutation in the 9 genes (groups 3 and 4 in Guièze et al) had a significantly poorer outcome, with a median OS of 28.2 and 27.1 months, respectively. With the limited sample size of this study, ...
BLA Biology
... for this problem with blood tests). • The ABO and RH genes are only two of many blood antigens that are present on human red cells and must be matched up for successful blood transfusions. ...
... for this problem with blood tests). • The ABO and RH genes are only two of many blood antigens that are present on human red cells and must be matched up for successful blood transfusions. ...
Bio 30 Complete Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can explain the meaning of haploidy, diploidy, and polyploidy _____ I can explain the steps of the cell cycle including interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase / cytokinesis _____ I can differentiate and compare the processes of mitosis and meiosis in terms of their purpose, ...
... _____ I can explain the meaning of haploidy, diploidy, and polyploidy _____ I can explain the steps of the cell cycle including interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase / cytokinesis _____ I can differentiate and compare the processes of mitosis and meiosis in terms of their purpose, ...
CACAO_remote_training_UW_Parkside
... different article. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=2677606 ...
... different article. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=2677606 ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.