2016 January Research Review
... sperm, egg, and early embryo in which genes are passed on through generations. Earlier in 2015 a Chinese scientist was the first reported to edit the genome of a human embryo and sparked great controversy. The researchers found that of 86 embryos treated with CRISPR, only 28 survived and were succes ...
... sperm, egg, and early embryo in which genes are passed on through generations. Earlier in 2015 a Chinese scientist was the first reported to edit the genome of a human embryo and sparked great controversy. The researchers found that of 86 embryos treated with CRISPR, only 28 survived and were succes ...
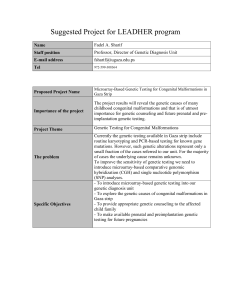
Suggested Project for LEADHER program Name Fadel A. Sharif
... The project results will reveal the genetic causes of many childhood congenital malformations and that is of utmost importance for genetic counseling and future prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing. ...
... The project results will reveal the genetic causes of many childhood congenital malformations and that is of utmost importance for genetic counseling and future prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing. ...
Chapter 9 DNA and the Molecular Structure of Chromosomes
... molecules of DNA segregated into about 50 domains. ...
... molecules of DNA segregated into about 50 domains. ...
Genetics Science Learning Center
... 4. The "twisted ladder" shape of the DNA molecule is called a _________________________________ 5. Name the four bases found in a DNA molecule: _____________________________________________ 6. A DNA strand is made of ________________________ which make up ___________________ which make up sentences. ...
... 4. The "twisted ladder" shape of the DNA molecule is called a _________________________________ 5. Name the four bases found in a DNA molecule: _____________________________________________ 6. A DNA strand is made of ________________________ which make up ___________________ which make up sentences. ...
Chapter 13 - Auburn CUSD 10
... Another method of genetic engineering is forced polyploidy. Scientists use drugs that prevent chromosomal separation to increase the normal number of chromosomes. In animals, this is usually fatal, but many plants benefit from this and produce larger crops. ...
... Another method of genetic engineering is forced polyploidy. Scientists use drugs that prevent chromosomal separation to increase the normal number of chromosomes. In animals, this is usually fatal, but many plants benefit from this and produce larger crops. ...
Ch 20 Reading Guide - Dublin City Schools
... 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hydrolytic enzyme in the plasmid. 4. Describe the role of an expression vector. 5. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. ...
... 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hydrolytic enzyme in the plasmid. 4. Describe the role of an expression vector. 5. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. ...
Citrus Breeding - Udayana University Official Website
... • Each progeny evaluated from each family ...
... • Each progeny evaluated from each family ...
Pre AP Biology Semester 2 exam Review Guide
... d) What condition will this karyotype cause? • Trisomy 21 also called ...
... d) What condition will this karyotype cause? • Trisomy 21 also called ...
7.1: Variations, Mutations, and Selective Advantage Learning Check:
... a gene. Mutations that occur in somatic cells can have significant effects on the individual, but will not be passed on to the next generation. Mutation can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial to an organism. Mutations that occur in gamete cells can be passed onto the next generation. Mutations resul ...
... a gene. Mutations that occur in somatic cells can have significant effects on the individual, but will not be passed on to the next generation. Mutation can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial to an organism. Mutations that occur in gamete cells can be passed onto the next generation. Mutations resul ...
Biology UNIT 2 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of traits Big Ideas
... How are different forms of a gene distributed to offspring? How can we use probability to predict traits? How do alleles segregate when more than one gene is involved? What did Mendel contribute to our understanding of genetics? What are some exceptions to Mendel’s principles? Does the environment h ...
... How are different forms of a gene distributed to offspring? How can we use probability to predict traits? How do alleles segregate when more than one gene is involved? What did Mendel contribute to our understanding of genetics? What are some exceptions to Mendel’s principles? Does the environment h ...
3 Basic Shapes
... • Many Heterotrophs – Feed on living and dead matter & return nutrients to soil (saprophytes) • Some autotrophs and perform photosynthesis – Cyanobacteria • Essential to healthy ecosystems ...
... • Many Heterotrophs – Feed on living and dead matter & return nutrients to soil (saprophytes) • Some autotrophs and perform photosynthesis – Cyanobacteria • Essential to healthy ecosystems ...
Gene Cloning And DNA vs - Mr. Lesiuk
... Gene Therapy is one example of biotechnology. The goal is to alter the phenotype in a human, by altering their genetic makeup. Ex. Child suffering from SCID, now has proper B and T lymphocytes with the proper gene placed into her stem cells. When genetic engineers alter genes of organisms other than ...
... Gene Therapy is one example of biotechnology. The goal is to alter the phenotype in a human, by altering their genetic makeup. Ex. Child suffering from SCID, now has proper B and T lymphocytes with the proper gene placed into her stem cells. When genetic engineers alter genes of organisms other than ...
Asexual reproduction
... Asexual reproduction only needs one parent, unlike sexual reproduction, which needs two parents. Since there is only one parent, there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information. As a result, the offspring are genetically identical to the parent and to each other. They are clones. ...
... Asexual reproduction only needs one parent, unlike sexual reproduction, which needs two parents. Since there is only one parent, there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information. As a result, the offspring are genetically identical to the parent and to each other. They are clones. ...
Document
... When you make new cells, your body is putting together different letters of the DNA alphabet. Even with just four letters, the DNA alphabet spells out all of the information you need to create new cells and to stay healthy. The order of the DNA bases is called the sequence. Just like the order of th ...
... When you make new cells, your body is putting together different letters of the DNA alphabet. Even with just four letters, the DNA alphabet spells out all of the information you need to create new cells and to stay healthy. The order of the DNA bases is called the sequence. Just like the order of th ...
4.1 Intro to Bioengineering
... into its cells. Scientists hope to be able to do the same thing to humans in the near future. What ...
... into its cells. Scientists hope to be able to do the same thing to humans in the near future. What ...
Biology Chp 1 Notes (The Science of Life)
... a. Cell Division: the formation of two new cells from one existing cell 1. all living things grow this way b. Development: the process by which an organism becomes a mature adult 1. achieved by cell division and differentiation 2. an adult organism is composed of many different cells 6. Reproductio ...
... a. Cell Division: the formation of two new cells from one existing cell 1. all living things grow this way b. Development: the process by which an organism becomes a mature adult 1. achieved by cell division and differentiation 2. an adult organism is composed of many different cells 6. Reproductio ...
Big Idea 3B Study Guide
... EK 3B1: Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. ...
... EK 3B1: Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. ...
genetic engineering: its prospects, facts or fiction?
... DNA can be duplicated in large quantities. The subsequently produced protein can then be removed from the host and used as a genetically engineered product in humans, other animals, plants, bacteria, or viruses. The donor DNA can be introduced directly into an organism by techniques such as injectio ...
... DNA can be duplicated in large quantities. The subsequently produced protein can then be removed from the host and used as a genetically engineered product in humans, other animals, plants, bacteria, or viruses. The donor DNA can be introduced directly into an organism by techniques such as injectio ...
File
... DNA was first discovered in 1869, but scientists didn’t really know much about it. After analyzing cells of may different organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals, scientists found DNA in all of them. In 1944 Avery confirmed that DNA was the material of inheritance. ...
... DNA was first discovered in 1869, but scientists didn’t really know much about it. After analyzing cells of may different organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals, scientists found DNA in all of them. In 1944 Avery confirmed that DNA was the material of inheritance. ...
Introduction to the biology and technology of DNA microarrays
... Proteins • Large molecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids. • Amino acids: Class of 20 different organic compounds containing a basic amino group (-NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH). • The order of the amino acids is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene c ...
... Proteins • Large molecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids. • Amino acids: Class of 20 different organic compounds containing a basic amino group (-NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH). • The order of the amino acids is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene c ...
TT2007 Lecture 8 HB
... Gregor Mendel- genes come in pairs, separate in gametes, and randomly come back together again as pairs during fertilization. This is explained in modern terms by reassortment during meiosis allele- any one of the alternative forms of a gene homozygous organism- organism having the same allele of a ...
... Gregor Mendel- genes come in pairs, separate in gametes, and randomly come back together again as pairs during fertilization. This is explained in modern terms by reassortment during meiosis allele- any one of the alternative forms of a gene homozygous organism- organism having the same allele of a ...
Review: Final Life Science Assessment
... concentration to an area where they are in a lower concentration is called diffusion. 21. Water diffuses through a cell membrane by a special process called osmosis. 22. A method of cell transport that requires a cell to use energy to move materials from one area to another is called active transpor ...
... concentration to an area where they are in a lower concentration is called diffusion. 21. Water diffuses through a cell membrane by a special process called osmosis. 22. A method of cell transport that requires a cell to use energy to move materials from one area to another is called active transpor ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.