Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as
... Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as one pair from each of our parents, which means that the sperm and egg receive 23 chromosomes through a complex process of cell division called as the meiosis. 2. Where is DNA found? Ans. Most of the DNA in a human cell is found in ...
... Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as one pair from each of our parents, which means that the sperm and egg receive 23 chromosomes through a complex process of cell division called as the meiosis. 2. Where is DNA found? Ans. Most of the DNA in a human cell is found in ...
Name________________ Where does variation come from
... Where does variation come from? - Guided Notes _____________ are controlled by genes. Individuals within a population are not _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits best suited to the envir ...
... Where does variation come from? - Guided Notes _____________ are controlled by genes. Individuals within a population are not _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits best suited to the envir ...
Genetic Algorithms
... In nature the evolution of species is a successful and robust method for ensuring that biological systems survive in their environment It can be seen as a search problem, in which the survival of solutions is determined by a form of natural selection ...
... In nature the evolution of species is a successful and robust method for ensuring that biological systems survive in their environment It can be seen as a search problem, in which the survival of solutions is determined by a form of natural selection ...
Natural Selection introduction
... Overproduction leads to competition within a species. In many cases, chance determines which members of a species survive. Chance alone in not the only factor which determines an individual’s survival. Changing environmental conditions, disease, parasites and predators all remove individuals from th ...
... Overproduction leads to competition within a species. In many cases, chance determines which members of a species survive. Chance alone in not the only factor which determines an individual’s survival. Changing environmental conditions, disease, parasites and predators all remove individuals from th ...
Population Genetics and Evolution File - Moodle
... Each of the four evolutionary mechanisms has different consequences. Only natural selection produces adaptation. Genetic drift causes random fluctuations in allele frequencies. Gene flow equalizes allele frequencies between populations. Mutation introduces new alleles. Inbreeding changes genotype fr ...
... Each of the four evolutionary mechanisms has different consequences. Only natural selection produces adaptation. Genetic drift causes random fluctuations in allele frequencies. Gene flow equalizes allele frequencies between populations. Mutation introduces new alleles. Inbreeding changes genotype fr ...
AP Biology
... Write the general HW equation and use it to calculate allele and genotype frequencies. Explain the consequences of HW equilibrium. Demonstrate that a population requires only one generation of random mating to establish HW equilibrium. Describe the usefulness of the HW model to population ge ...
... Write the general HW equation and use it to calculate allele and genotype frequencies. Explain the consequences of HW equilibrium. Demonstrate that a population requires only one generation of random mating to establish HW equilibrium. Describe the usefulness of the HW model to population ge ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... Mutations can create new alleles (1) Gene flow can introduce new alleles into the population (1) ...
... Mutations can create new alleles (1) Gene flow can introduce new alleles into the population (1) ...
Natural Selection introduction
... Overproduction leads to competition within a species. In many cases, chance determines which members of a species survive. Chance alone in not the only factor which determines an individual’s survival. Changing environmental conditions, disease, parasites and predators all remove individuals from th ...
... Overproduction leads to competition within a species. In many cases, chance determines which members of a species survive. Chance alone in not the only factor which determines an individual’s survival. Changing environmental conditions, disease, parasites and predators all remove individuals from th ...
GKEvolution
... lower ends of the curve have the greatest fitness ► Selection eliminates those with the average trait ► Natural selection is not the only cause of change ► In small populations, there can be a change in allele frequencies simply by chance & probability ► Ex: Some individuals might have lots of offsp ...
... lower ends of the curve have the greatest fitness ► Selection eliminates those with the average trait ► Natural selection is not the only cause of change ► In small populations, there can be a change in allele frequencies simply by chance & probability ► Ex: Some individuals might have lots of offsp ...
Unit 6
... evolutionary escalators were the most complex plants and animals. Evolution was driven by an innate tendency toward the greater and greater complexity, which Lamarck seemed to equate with perfection. 11. Explain what evidence convinced Darwin that species change over time. Each generation, environme ...
... evolutionary escalators were the most complex plants and animals. Evolution was driven by an innate tendency toward the greater and greater complexity, which Lamarck seemed to equate with perfection. 11. Explain what evidence convinced Darwin that species change over time. Each generation, environme ...
File - Bunse Biology
... Gene flow – movement of genes from one population to another (migration) Mutation – any change in a sequence of DNAMain Source Some mutations can affect an organism’s fitness while others have no effect on fitness. Recombination –(occurs during meiosis) Main Source ...
... Gene flow – movement of genes from one population to another (migration) Mutation – any change in a sequence of DNAMain Source Some mutations can affect an organism’s fitness while others have no effect on fitness. Recombination –(occurs during meiosis) Main Source ...
Evolution by natural selection is a major aspect
... The Definition: Biological evolution, simply put, is descent with modification. This definition encompasses small-scale evolution (changes in gene frequency in a population from one generation to the next) and large-scale evolution (the descent of different species from a common ancestor over many ...
... The Definition: Biological evolution, simply put, is descent with modification. This definition encompasses small-scale evolution (changes in gene frequency in a population from one generation to the next) and large-scale evolution (the descent of different species from a common ancestor over many ...
Evidence Supporting The Theory of Evolution
... population. (This variation is caused by organisms having different genes.) ...
... population. (This variation is caused by organisms having different genes.) ...
Advanced search and optimization techniques
... • Population is therefore a “cloud” of points, moving on the landscape over time as it evolves - adaptation ...
... • Population is therefore a “cloud” of points, moving on the landscape over time as it evolves - adaptation ...
Evolution for Bio. I Powerpoint
... What is gradual vs. quick? What is missing from the fossil record? Do different mechanisms work at different ...
... What is gradual vs. quick? What is missing from the fossil record? Do different mechanisms work at different ...
What IS a population???
... measured across generations using this approach. If p and q do not change freq from one generation to the next then the population is in equilibrium – neither of the alleles is being selected for or against A change in gene freq is an indicator of natural selection at work! A change in gene freq can ...
... measured across generations using this approach. If p and q do not change freq from one generation to the next then the population is in equilibrium – neither of the alleles is being selected for or against A change in gene freq is an indicator of natural selection at work! A change in gene freq can ...
GENETICS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN FAMILIES
... Premature coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs most commonly in families with multiple affected members. Such families are enriched with genetic variants that contribute to CAD, and therefore represent an ideal population for identification of susceptibility genes that might contribute to better ris ...
... Premature coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs most commonly in families with multiple affected members. Such families are enriched with genetic variants that contribute to CAD, and therefore represent an ideal population for identification of susceptibility genes that might contribute to better ris ...
Mechanism of Natural Selection
... It includes the process of natural selection, changes in allele frequencies, and changes in populations that result over time. Development of antibiotic resistant bacteria is an example of microevolution. ...
... It includes the process of natural selection, changes in allele frequencies, and changes in populations that result over time. Development of antibiotic resistant bacteria is an example of microevolution. ...
High throughput gene sequencing to identify new genes that cause
... human genetics within the past 25 years led to the identification of the molecular basis for 50% of these pathologies. However, the causative mutations in half of patients are still unknown. This is mainly due to genetic heterogeneity (mutation in several genes causing the same or very similar disea ...
... human genetics within the past 25 years led to the identification of the molecular basis for 50% of these pathologies. However, the causative mutations in half of patients are still unknown. This is mainly due to genetic heterogeneity (mutation in several genes causing the same or very similar disea ...
what should i know about evolution
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? 22. What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? 23. Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? (Directional, Stabilizing, Disru ...
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? 22. What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? 23. Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? (Directional, Stabilizing, Disru ...
Chapter 15: Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Populations
... genetic uniformity at a variety of loci previously screened to measure population genetic diversity. It has been hypothesized that a demographic crash or population bottleneck in the recent history of the species is causal to the observed monomorphic profiles for nuclear coding loci. The timing of a ...
... genetic uniformity at a variety of loci previously screened to measure population genetic diversity. It has been hypothesized that a demographic crash or population bottleneck in the recent history of the species is causal to the observed monomorphic profiles for nuclear coding loci. The timing of a ...
Population Genetics
... inheritance (population genetics) was crucial to the acceptance of Darwin’s hypothesis that natural selection played a significant role in evolution and thus in generating the diversity of life. The early population geneticists, R.A. Fisher, J.B.S. Haldane, and Sewall Wright, used primarily single-l ...
... inheritance (population genetics) was crucial to the acceptance of Darwin’s hypothesis that natural selection played a significant role in evolution and thus in generating the diversity of life. The early population geneticists, R.A. Fisher, J.B.S. Haldane, and Sewall Wright, used primarily single-l ...
CH3L2
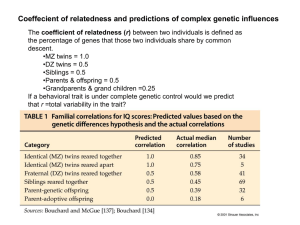
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.