Freeman, Evolutionary Analysis 4th ed
... 14. What is blending inheritance, and why did it pose a problem for Darwin's theory? Why is it not considered a problem today? Blending inheritance was the theory that offspring inherit traits by "blending" two components inherited from each parent, such that each original component is irrevocably a ...
... 14. What is blending inheritance, and why did it pose a problem for Darwin's theory? Why is it not considered a problem today? Blending inheritance was the theory that offspring inherit traits by "blending" two components inherited from each parent, such that each original component is irrevocably a ...
12 Cons Bio 2010
... 1 Geographic range 2 Habitat specificity 3Local abundance Classic rare = narrow range, endemic in restricted habitat, small pop. B. Vulnerability to anthropogenic extinction and conservation plans 561-2 Small species due to small range size and human population densities must protect threatened ha ...
... 1 Geographic range 2 Habitat specificity 3Local abundance Classic rare = narrow range, endemic in restricted habitat, small pop. B. Vulnerability to anthropogenic extinction and conservation plans 561-2 Small species due to small range size and human population densities must protect threatened ha ...
1. Determining the Gene and Genotypic Array
... drift. There will be selection for those resistant to the disease (and correlated selection for genes close to the genes conferring resistance), but there will also be drift at other loci simply by reducing the size of the breeding population. ...
... drift. There will be selection for those resistant to the disease (and correlated selection for genes close to the genes conferring resistance), but there will also be drift at other loci simply by reducing the size of the breeding population. ...
SINGLE GENE DISORDER
... Its a phenomenon whereby the symptoms of a genetic disorder become apparent at an earlier age as it is passed on to the next generation. In most cases, an increase of severity of symptoms is also noted. Anticipation is common in trinucleotide repeat disorders such as Huntington's disease and myotoni ...
... Its a phenomenon whereby the symptoms of a genetic disorder become apparent at an earlier age as it is passed on to the next generation. In most cases, an increase of severity of symptoms is also noted. Anticipation is common in trinucleotide repeat disorders such as Huntington's disease and myotoni ...
Jeopardy - Ms. Lee`s Classes @ JICHS
... insects for Pollination from flowers; fruits hold seeds ...
... insects for Pollination from flowers; fruits hold seeds ...
2 How Genes Vary in Fish Populations
... most purposes. In the gene pool of a population, we look at every individual and count the types of alleles that exist at a locus. For simplicity, we examine one locus at a time. We quantify and describe populations in terms of their allele frequencies, which are the relative proportions of each typ ...
... most purposes. In the gene pool of a population, we look at every individual and count the types of alleles that exist at a locus. For simplicity, we examine one locus at a time. We quantify and describe populations in terms of their allele frequencies, which are the relative proportions of each typ ...
Biological Psychology CH1
... Basis of what we know today all stems from the work of Gregor Mendel in the 1800’s Pertinent vocabulary: genes, chromosomes, DNA, RNA, proteins, enzymes, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, recessive. Some traits are sex-linked, all others are autosomal Sex limited genes = both sexes have the gene, ...
... Basis of what we know today all stems from the work of Gregor Mendel in the 1800’s Pertinent vocabulary: genes, chromosomes, DNA, RNA, proteins, enzymes, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, recessive. Some traits are sex-linked, all others are autosomal Sex limited genes = both sexes have the gene, ...
2 + pn
... established before East Asian populations. East Asian populations were established from later migrations out of the Middle East. With each migration, a reduction in population size would lead to bottlenecks and a greater influence from drift, which would lower heterozygosity. Those populations estab ...
... established before East Asian populations. East Asian populations were established from later migrations out of the Middle East. With each migration, a reduction in population size would lead to bottlenecks and a greater influence from drift, which would lower heterozygosity. Those populations estab ...
ppt - Language Log
... origins and development of life on the planet, as well as modern human variation and adaptation. Let us briefly explore what underlies the mechanism of Natural Selection, and then turn our attention to the genetic processes that produce variation. ...
... origins and development of life on the planet, as well as modern human variation and adaptation. Let us briefly explore what underlies the mechanism of Natural Selection, and then turn our attention to the genetic processes that produce variation. ...
Chapter 4 section 2
... A pesticide sprayed on corn to kill grasshoppers, for example, may kill most of the grasshoppers, but those that survive happen to have a gene that protects them from the pesticide. These surviving insects pass on this resistant gene to their offspring. Each time the corn is sprayed, more resist ...
... A pesticide sprayed on corn to kill grasshoppers, for example, may kill most of the grasshoppers, but those that survive happen to have a gene that protects them from the pesticide. These surviving insects pass on this resistant gene to their offspring. Each time the corn is sprayed, more resist ...
Student handout - Avida-ED
... Understanding the Introduction of Genetic Variations by Random Mutation ...
... Understanding the Introduction of Genetic Variations by Random Mutation ...
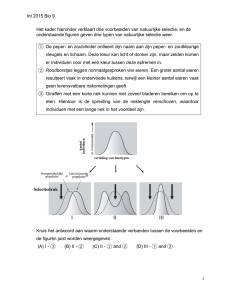
int_2015_Bio_9
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
Adaptation, natural selection and speciation
... Adaptation, natural selection and speciation homework 2 1. Complete the following sentences: Natural selection is the process by which members of a population _______ adapted to the environment_________, reproduce and pass their _______onto the next generation. An example of natural selection is the ...
... Adaptation, natural selection and speciation homework 2 1. Complete the following sentences: Natural selection is the process by which members of a population _______ adapted to the environment_________, reproduce and pass their _______onto the next generation. An example of natural selection is the ...
Mechanisms of Evolution Key Concepts
... – Is the only deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg that leads to adaptation (of the population to the environment) ...
... – Is the only deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg that leads to adaptation (of the population to the environment) ...
File
... for the presence of homologous structures. Multiple species of organisms descended from the same common ancestor at some point in the past. • Convergent Evolution - Method of evolution accounting for the presence of analogous structures. Organisms of different species often live in similar environme ...
... for the presence of homologous structures. Multiple species of organisms descended from the same common ancestor at some point in the past. • Convergent Evolution - Method of evolution accounting for the presence of analogous structures. Organisms of different species often live in similar environme ...
1 Study questions: Part 1 (popgen and QG). First Exam. Evolution
... the _______________ equilibrium (fill in the blank). If the population is perturbed away from the equilibrium, will the population return to the starting point? Why or why not? ...
... the _______________ equilibrium (fill in the blank). If the population is perturbed away from the equilibrium, will the population return to the starting point? Why or why not? ...
Genetic Disorders in Culture and Art
... monk whose work on pea plants in the mid-1800s provided the foundations for the science of genetics. Humans had been breeding plants and animals for centuries before Mendel, but he was the first to record his experiments then think and write about them scientifically. ...
... monk whose work on pea plants in the mid-1800s provided the foundations for the science of genetics. Humans had been breeding plants and animals for centuries before Mendel, but he was the first to record his experiments then think and write about them scientifically. ...
A Perspective on Human Genetics
... monk whose work on pea plants in the mid-1800s provided the foundations for the science of genetics. Humans had been breeding plants and animals for centuries before Mendel, but he was the first to record his experiments then think and write about them scientifically. ...
... monk whose work on pea plants in the mid-1800s provided the foundations for the science of genetics. Humans had been breeding plants and animals for centuries before Mendel, but he was the first to record his experiments then think and write about them scientifically. ...
Genetic Variation
... • Everything (living) is made of cells and that is where the information describing “you” resides. • Cells have many smaller structures called organelles, that perform functions essential to life. • The nucleus of our cells contains our genetic information. ...
... • Everything (living) is made of cells and that is where the information describing “you” resides. • Cells have many smaller structures called organelles, that perform functions essential to life. • The nucleus of our cells contains our genetic information. ...
Evolution Test Review
... ___________________________ Producing many offspring, some of which may not survive. ___________________________ Heritable differences that make an individual unique ___________________________ An advantageous trait; one well-suited for the environment ___________________________ The ability of an o ...
... ___________________________ Producing many offspring, some of which may not survive. ___________________________ Heritable differences that make an individual unique ___________________________ An advantageous trait; one well-suited for the environment ___________________________ The ability of an o ...
Chapter 3-1 • Definitions: - Genetics: the scientific study of heredity
... - Heredity: the passing of traits from parent to offspring - Trait: different physical characteristics - Purebred: an organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent - Gene: factor that controls traits - Allele: different forms of a gene - Dominant Allele: its tra ...
... - Heredity: the passing of traits from parent to offspring - Trait: different physical characteristics - Purebred: an organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent - Gene: factor that controls traits - Allele: different forms of a gene - Dominant Allele: its tra ...
(lectures 5-7) - Felsenstein/Kuhner lab
... overall gene frequency of A among all the populations will not change, but the gene frequency in any one population will change dramatically. (In effect, what has happened is that genetic drift converts variability within populations into differences between populations). 9. Mutation and migration c ...
... overall gene frequency of A among all the populations will not change, but the gene frequency in any one population will change dramatically. (In effect, what has happened is that genetic drift converts variability within populations into differences between populations). 9. Mutation and migration c ...
File
... D.________________________involves _____________________ 1. Mendel also conducted dihybrid crosses- wondered if both traits would always appear together or if they would be expressed independently of each other 2. Mendel discovered phenotypic ratio in F2 generation as always____________regardless of ...
... D.________________________involves _____________________ 1. Mendel also conducted dihybrid crosses- wondered if both traits would always appear together or if they would be expressed independently of each other 2. Mendel discovered phenotypic ratio in F2 generation as always____________regardless of ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.