univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... into a number of sub-populations and that gene frequencies fluctuate randomly between these sub-populations or neighbourhoods. Such processes may have the following practical effects: a) the performance of progenies originating from different neighbourhoods within one particular stand may vary from ...
... into a number of sub-populations and that gene frequencies fluctuate randomly between these sub-populations or neighbourhoods. Such processes may have the following practical effects: a) the performance of progenies originating from different neighbourhoods within one particular stand may vary from ...
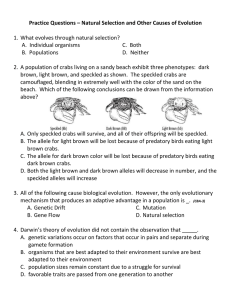
Evolution Practice Questions
... Practice Questions – Common Descent and Evidences 12. Birds and reptiles are similar in that they are vertebrates and lay eggs. They differ in that reptiles have teeth, and birds have beaks. Some birds do possess teeth; however, these teeth are present only in the embryonic stage. What conclusion i ...
... Practice Questions – Common Descent and Evidences 12. Birds and reptiles are similar in that they are vertebrates and lay eggs. They differ in that reptiles have teeth, and birds have beaks. Some birds do possess teeth; however, these teeth are present only in the embryonic stage. What conclusion i ...
Evolution at Multiple Loci
... (between sister alleles on other chromosome). • The effect of an allele depends upon what it is paired with. • Because of this dependence, the outcome of dominance variation is not entirely predictable - it is context dependent. • This context disappears every generation because of meiosis. The pair ...
... (between sister alleles on other chromosome). • The effect of an allele depends upon what it is paired with. • Because of this dependence, the outcome of dominance variation is not entirely predictable - it is context dependent. • This context disappears every generation because of meiosis. The pair ...
Introduction to Psychology
... - Eye color, blood type Predominantly environmental - Language, religion ...
... - Eye color, blood type Predominantly environmental - Language, religion ...
What is Evolution?
... Change must be genetic Modern, genetic definition: “evolution is change in gene frequencies between generations” ...
... Change must be genetic Modern, genetic definition: “evolution is change in gene frequencies between generations” ...
Human Growth and Development Genetics
... Self-esteem, approval Desire to live up to one’s potential ...
... Self-esteem, approval Desire to live up to one’s potential ...
Genetic algorithms for neural networks
... exp(-1/T), only one can be included – Prevents unphysical input sets being found ...
... exp(-1/T), only one can be included – Prevents unphysical input sets being found ...
Exercise 4.2: Improving on nature
... Lawson is a high yielding wheat variety bred for high rainfall areas. This self pollinating plant was produced by a traditional breeding program. Outline the steps you think the CSIRO followed to breed this plant. ________________________________________________ _____________________________________ ...
... Lawson is a high yielding wheat variety bred for high rainfall areas. This self pollinating plant was produced by a traditional breeding program. Outline the steps you think the CSIRO followed to breed this plant. ________________________________________________ _____________________________________ ...
Genetic algorithms for neural networks
... exp(-1/T), only one can be included – Prevents unphysical input sets being found ...
... exp(-1/T), only one can be included – Prevents unphysical input sets being found ...
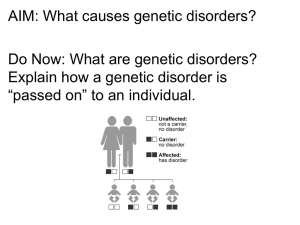
Inheritance and Genetic Diseases
... METASTASIS(spread of disease from part to another non-adjacent part.) occurs when cancer cells spread through body Somatic mutation dies when cells die/ tumour cells are killed Occurs after conception/ will not be passed down ...
... METASTASIS(spread of disease from part to another non-adjacent part.) occurs when cancer cells spread through body Somatic mutation dies when cells die/ tumour cells are killed Occurs after conception/ will not be passed down ...
Vocab Puzzle
... 5. deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. 6. A diagram of the genetic history of an individual: can show how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. ...
... 5. deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. 6. A diagram of the genetic history of an individual: can show how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. ...
Komaei presentation
... we need both phenotypic data and genotypic data. Inoculation with spores of fungi Using genetic marker Molecular markers are genetic loci that can be easily tracked and quantified in a population and may be associated with a particular gene or trait of interest ...
... we need both phenotypic data and genotypic data. Inoculation with spores of fungi Using genetic marker Molecular markers are genetic loci that can be easily tracked and quantified in a population and may be associated with a particular gene or trait of interest ...
Hardy-Weinberg updated 9
... + q = 1 can be expanded to describe the relationships of allele frequencies to genotype frequencies in a population ...
... + q = 1 can be expanded to describe the relationships of allele frequencies to genotype frequencies in a population ...
Inheritance and Genetics
... • studied height, flower color, seed coat color, and seed shape over many generations • he chose 1 or 2 traits per generation to watch • crossed plants with different traits and learned that offspring usually had dominate trait ...
... • studied height, flower color, seed coat color, and seed shape over many generations • he chose 1 or 2 traits per generation to watch • crossed plants with different traits and learned that offspring usually had dominate trait ...
SBI3UI Name: Evolution Review Questions Answer the following
... 3. How might Lamarck have explained an elephant’s long trunk? 4. An athlete breaks her leg. Years later she has a child who walks with a limp. Is this evolution? Explain. 5. How is the work of Malthus related to the concept of survival of the fittest? 6. A scientist finds a rare fossil – a whale wit ...
... 3. How might Lamarck have explained an elephant’s long trunk? 4. An athlete breaks her leg. Years later she has a child who walks with a limp. Is this evolution? Explain. 5. How is the work of Malthus related to the concept of survival of the fittest? 6. A scientist finds a rare fossil – a whale wit ...
Evolution - Effingham County Schools
... – Natural selection is the cause of adaptive evolution – 99% of all species that ever lived are extinct ...
... – Natural selection is the cause of adaptive evolution – 99% of all species that ever lived are extinct ...
Here
... (d) What advantage might naked mole rats gain by being eusocial (only a few individuals reproduce)?They may be more altruistic and thus able to cooperate better to dig tunnels and exploit rare, large food sources. What disadvantage might they face? Small Ne makes them vulnerable to drift fixing bad ...
... (d) What advantage might naked mole rats gain by being eusocial (only a few individuals reproduce)?They may be more altruistic and thus able to cooperate better to dig tunnels and exploit rare, large food sources. What disadvantage might they face? Small Ne makes them vulnerable to drift fixing bad ...
Variation Hardy
... The range of genetic variation within a population of interbreeding organisms is the gene pool. The proportions of alleles tend to remain constant from generation to generation. This is the Hardy– Weinberg Principle and can be used to predict the frequency of genotypes within a population if the fol ...
... The range of genetic variation within a population of interbreeding organisms is the gene pool. The proportions of alleles tend to remain constant from generation to generation. This is the Hardy– Weinberg Principle and can be used to predict the frequency of genotypes within a population if the fol ...
Processes of Evolution
... entire collection of alleles for a given trait throughout a given population. • The word for all genes for all traits in an individual or population is genome. ...
... entire collection of alleles for a given trait throughout a given population. • The word for all genes for all traits in an individual or population is genome. ...
Populations
... hence lowest variation of diversity among species Just explaining the mean level of diversity is challenging ...
... hence lowest variation of diversity among species Just explaining the mean level of diversity is challenging ...
Chromosome Mutation - Hicksville Public Schools
... 17. Sickle Cell Anemia - blood disorder causing sickling of the red blood cells 18. Tay-Sachs Disease - damage of the nerve cells in brain and spinal cord 19. Turner Syndrome - lack of either one whole or a part of an X chromosome 20. Wilson’s Disease - body’s inability to get rid of excess copper i ...
... 17. Sickle Cell Anemia - blood disorder causing sickling of the red blood cells 18. Tay-Sachs Disease - damage of the nerve cells in brain and spinal cord 19. Turner Syndrome - lack of either one whole or a part of an X chromosome 20. Wilson’s Disease - body’s inability to get rid of excess copper i ...
My Slides - people.vcu.edu
... • Are traits for offspring ‘in-between’ or outside the range of parent values? • How often do several loci influence a trait in a natural population? – How hard will it be to find these loci? ...
... • Are traits for offspring ‘in-between’ or outside the range of parent values? • How often do several loci influence a trait in a natural population? – How hard will it be to find these loci? ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.