Satiable Curiosity - Journal of Genetic Genealogy
... not merely backup copies scattered along the length of the chromosome. The DNA sequences formed palindromes, with one copy reading the same as the other copy backward. By forming a hairpin turn, the copies could interact with each other during duplication of the Y chromosome, much like the paired au ...
... not merely backup copies scattered along the length of the chromosome. The DNA sequences formed palindromes, with one copy reading the same as the other copy backward. By forming a hairpin turn, the copies could interact with each other during duplication of the Y chromosome, much like the paired au ...
the whole slide set
... b. The gene pool of this population never experienced mutation or gene flow. c. A very small number of mink may have colonized this island, and this founder effect and subsequent genetic drift fixed many alleles. d. The colonizing population may have had much more genetic diversity, but in the last ...
... b. The gene pool of this population never experienced mutation or gene flow. c. A very small number of mink may have colonized this island, and this founder effect and subsequent genetic drift fixed many alleles. d. The colonizing population may have had much more genetic diversity, but in the last ...
Diagnostic perspective in general practice
... in the exciting and rapidly expanding world of medical genetics. The role includes routine diagnosis, early detection, and community and ethical guidance. Virtually all of the three billion nucleotides of the human genome have been sequenced and the knowledge of their organisation into the known 30 ...
... in the exciting and rapidly expanding world of medical genetics. The role includes routine diagnosis, early detection, and community and ethical guidance. Virtually all of the three billion nucleotides of the human genome have been sequenced and the knowledge of their organisation into the known 30 ...
Introduction to Genetics
... gametogenesis (the formation of new gametes) and then independently assort. What this means is that while genes are in pairs, when they are passed on to offspring it is random as to which one the offspring gets, and each different trait is passed on independently of each other. This is what allows u ...
... gametogenesis (the formation of new gametes) and then independently assort. What this means is that while genes are in pairs, when they are passed on to offspring it is random as to which one the offspring gets, and each different trait is passed on independently of each other. This is what allows u ...
PPT file - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... for each of the genotypes, as there may be allele effects on viability. Instead, get expected values from the data: ...
... for each of the genotypes, as there may be allele effects on viability. Instead, get expected values from the data: ...
Chapter 15 ppt - Burgos Bio Blog
... individuals that will be added to a population as it grows, multiply the size of the current population (N) by the rate of growth (r). • Normally, as we learned last chapter, populations do not always grow unchecked (ie death). The population size that a given environment can sustain is called the c ...
... individuals that will be added to a population as it grows, multiply the size of the current population (N) by the rate of growth (r). • Normally, as we learned last chapter, populations do not always grow unchecked (ie death). The population size that a given environment can sustain is called the c ...
Hardy Weinberg Practice
... Directions: Read the preceding information about a specific population. Assume the population is in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, and answer the following questions. Be sure to SHOW ALL your calculations work in order to get FULL credit. Questions 1 and2: In a given population of 200 humans on a remot ...
... Directions: Read the preceding information about a specific population. Assume the population is in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, and answer the following questions. Be sure to SHOW ALL your calculations work in order to get FULL credit. Questions 1 and2: In a given population of 200 humans on a remot ...
Evolution
... Example: The short-nosed echidna of Australia and Tasmania is well adapted to its diet of ants and termites. It has powerful claws to break into ant nests and termite mounds, and a long, sticky tongue to collect its prey. The short-nosed echidna also has spines to protect itself. It cannot roll up l ...
... Example: The short-nosed echidna of Australia and Tasmania is well adapted to its diet of ants and termites. It has powerful claws to break into ant nests and termite mounds, and a long, sticky tongue to collect its prey. The short-nosed echidna also has spines to protect itself. It cannot roll up l ...
RichardDurbin_CSI2011
... gives long tips to the tree • In “big” populations, tips are hundreds of generations long, so tens of thousands of private variants per sample, hundreds functional ...
... gives long tips to the tree • In “big” populations, tips are hundreds of generations long, so tens of thousands of private variants per sample, hundreds functional ...
IS THE POPULATION SIZE OF A SPECIES RELEVANT TO ITS
... the dynamics of a closely linked locus. Of particular interest is the role of population size on genetic draft. Remarkably, the rate of substitution of weakly selected advantageous mutations decreases with increasing population size, whereas that for deleterious mutations increases with population s ...
... the dynamics of a closely linked locus. Of particular interest is the role of population size on genetic draft. Remarkably, the rate of substitution of weakly selected advantageous mutations decreases with increasing population size, whereas that for deleterious mutations increases with population s ...
Magic Square
... Match each term to its definition. Put the number of the term in the proper square marked by the letter of its definition. If your answers are correct, the numerical total will be the same across each row and down each column. Definitions: A. A variation of a trait or gene. B. Two alleles that are t ...
... Match each term to its definition. Put the number of the term in the proper square marked by the letter of its definition. If your answers are correct, the numerical total will be the same across each row and down each column. Definitions: A. A variation of a trait or gene. B. Two alleles that are t ...
Genetic factors in aggression
... factors and not their rearing environment. However, the link is not as simple. This is because studies have shown that the highest rates of violence in adopted children occurs when both the biological AND adoptive parents are aggressive. This supports the idea of a gene-environment interaction. Furt ...
... factors and not their rearing environment. However, the link is not as simple. This is because studies have shown that the highest rates of violence in adopted children occurs when both the biological AND adoptive parents are aggressive. This supports the idea of a gene-environment interaction. Furt ...
Section 7.2 Reinforcement
... separately expressed, and both phenotypes are also completely expressed. Human blood type is an example of both codominance and a multiple allele trait. The alleles for blood types A and B are codominant, which can be expressed as an AB blood type. The allele for type O blood is recessive to the oth ...
... separately expressed, and both phenotypes are also completely expressed. Human blood type is an example of both codominance and a multiple allele trait. The alleles for blood types A and B are codominant, which can be expressed as an AB blood type. The allele for type O blood is recessive to the oth ...
Unit D Review
... Traits can be determined by one ___________ or several __________. Traits can also be affected by __________________. Nature vs. nurture (______________ vs. _________________) – genes and environment affect traits. ...
... Traits can be determined by one ___________ or several __________. Traits can also be affected by __________________. Nature vs. nurture (______________ vs. _________________) – genes and environment affect traits. ...
Lesson 2- environmental inheritance and dominant recessive alleles
... recessive gene for blue eyes from dad then you will have brown eyes. • However, you would still carry a recessive gene for blue eyes which can be passed on to their offspring. ...
... recessive gene for blue eyes from dad then you will have brown eyes. • However, you would still carry a recessive gene for blue eyes which can be passed on to their offspring. ...
Changes in Traits
... successive generations of a population of reproducing organisms, and unfavorable traits that are heritable become less common. Acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, such as individuals with favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce than those ...
... successive generations of a population of reproducing organisms, and unfavorable traits that are heritable become less common. Acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, such as individuals with favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce than those ...
IB Biology 11 SL (H) - Anoka
... ● How genetic information is transmitted from parents to offspring through the processes of meiosis and translation, using the example of sickle-cell anemia fertilization as they relate to chromosome recombination and sexual reproduction ● State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucl ...
... ● How genetic information is transmitted from parents to offspring through the processes of meiosis and translation, using the example of sickle-cell anemia fertilization as they relate to chromosome recombination and sexual reproduction ● State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucl ...
Men Women - iiap.res.in
... …one special difficulty, which at first appeared to me insuperable, and actually fatal to my whole theory. I allude to the neuters or sterile females in insect-communities…from being sterile, they cannot propagate their kind. ...
... …one special difficulty, which at first appeared to me insuperable, and actually fatal to my whole theory. I allude to the neuters or sterile females in insect-communities…from being sterile, they cannot propagate their kind. ...
two ald “mutations”
... “Mutation” of a gene might be due to changes elsewhere! •ald is Drosophila mps1 homolog; isolated four mutations (all rescued by ald+ transgene) •two ald alleles cause meiotic and mitotic defects (ald sequence changes) •two ald “mutations” cause only meiotic defects (normal ald sequence) •both cont ...
... “Mutation” of a gene might be due to changes elsewhere! •ald is Drosophila mps1 homolog; isolated four mutations (all rescued by ald+ transgene) •two ald alleles cause meiotic and mitotic defects (ald sequence changes) •two ald “mutations” cause only meiotic defects (normal ald sequence) •both cont ...
Practice Problems for Genetics Test
... Assume that a red nosed male reindeer is crossed with a heterozygous black nosed female reindeer. Indicate the different phenotypes of the offspring and the ratio that they will appear. 3. Incomplete Dominance ...
... Assume that a red nosed male reindeer is crossed with a heterozygous black nosed female reindeer. Indicate the different phenotypes of the offspring and the ratio that they will appear. 3. Incomplete Dominance ...
Name: Date - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... 26) Be prepared to group an organism into a kingdom based on certain characteristics given. For example, to which kingdom does the following organism belong? Organism: “I am a multicellular heterotroph that eats by ingesting grass. I have eukaryotic cells” ...
... 26) Be prepared to group an organism into a kingdom based on certain characteristics given. For example, to which kingdom does the following organism belong? Organism: “I am a multicellular heterotroph that eats by ingesting grass. I have eukaryotic cells” ...
is the population size of a species relevant to its evolution?
... the dynamics of a closely linked locus. Of particular interest is the role of population size on genetic draft. Remarkably, the rate of substitution of weakly selected advantageous mutations decreases with increasing population size, whereas that for deleterious mutations increases with population s ...
... the dynamics of a closely linked locus. Of particular interest is the role of population size on genetic draft. Remarkably, the rate of substitution of weakly selected advantageous mutations decreases with increasing population size, whereas that for deleterious mutations increases with population s ...
Objectives for Lab Quiz 5
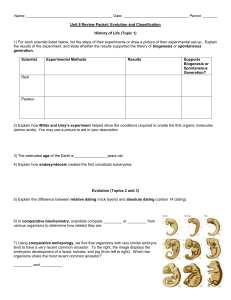
... 2-cell and 4-cell blastomere morula blastocyst (blastula) with inner cell mass gastrula with embryonic disk primary germ layers ectoderm mesoderm endoderm ...
... 2-cell and 4-cell blastomere morula blastocyst (blastula) with inner cell mass gastrula with embryonic disk primary germ layers ectoderm mesoderm endoderm ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.