Natural Selection is not an Invisible Hand
... by animal and plant breeders, of particularly desirable individuals. Breeders literally select who gets to be the parents of a new generation. In this way, they often directly cause evolution of domesticate ...
... by animal and plant breeders, of particularly desirable individuals. Breeders literally select who gets to be the parents of a new generation. In this way, they often directly cause evolution of domesticate ...
23_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... • Selection can favor whichever phenotype is less common in a population • For example, frequency-dependent selection selects for approximately equal numbers of “right-mouthed” and “left-mouthed” scale-eating ...
... • Selection can favor whichever phenotype is less common in a population • For example, frequency-dependent selection selects for approximately equal numbers of “right-mouthed” and “left-mouthed” scale-eating ...
Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment
... additively so that there are fairly equal contributions from all the genes involved. They affect traits such as skin color and height. A dominant gene is the member of an interacting pair of alleles whose influence is more evident in the phenotype. A recessive gene is the member of an interacting pa ...
... additively so that there are fairly equal contributions from all the genes involved. They affect traits such as skin color and height. A dominant gene is the member of an interacting pair of alleles whose influence is more evident in the phenotype. A recessive gene is the member of an interacting pa ...
Complications to the relationship between genotype to phenotype
... • Human genome sequencing will reveal thousands of genetic variations among individuals that many will assume are associated with disease or phenotypic variation • But translating such genotypic differences into phenotypic states is prone to pitfalls • for example, genetic abnormalities differ in th ...
... • Human genome sequencing will reveal thousands of genetic variations among individuals that many will assume are associated with disease or phenotypic variation • But translating such genotypic differences into phenotypic states is prone to pitfalls • for example, genetic abnormalities differ in th ...
higher fitness
... • Natural selection never acts on a gene – It acts on the organism as a whole (the entire collection of genes) – It can only affect which individuals survive and reproduce and which do not ...
... • Natural selection never acts on a gene – It acts on the organism as a whole (the entire collection of genes) – It can only affect which individuals survive and reproduce and which do not ...
Document
... Impacts, Issues: The Color of Skin Skin color comes from the pigment melanin • Produced by melanocytes in skin cells • More than 100 genes directly or indirectly influence amount of melanin in an individual’s skin • Lead to many variations in skin color ...
... Impacts, Issues: The Color of Skin Skin color comes from the pigment melanin • Produced by melanocytes in skin cells • More than 100 genes directly or indirectly influence amount of melanin in an individual’s skin • Lead to many variations in skin color ...
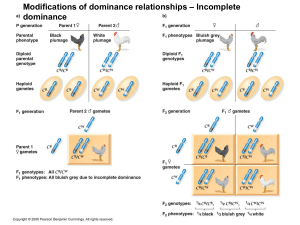
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... product 1. Threshold effect – the phenomenon that “50% of the protein is enough” is fairly common among many genes Example: Tay- Sachs disease At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown ...
... product 1. Threshold effect – the phenomenon that “50% of the protein is enough” is fairly common among many genes Example: Tay- Sachs disease At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown ...
LEQ: What did Mendel discover about the patterns of inheritance?
... idea that acquired traits are inherited Lamark thought that organisms adapted to changes in their environment through altered behaviors. The behaviors lead to selective use or disuse of given structures causing them to increase or decrease in size. ...
... idea that acquired traits are inherited Lamark thought that organisms adapted to changes in their environment through altered behaviors. The behaviors lead to selective use or disuse of given structures causing them to increase or decrease in size. ...
LEQ: What did Mendel discover about the patterns of inheritance?
... idea that acquired traits are inherited Lamark thought that organisms adapted to changes in their environment through altered behaviors. The behaviors lead to selective use or disuse of given structures causing them to increase or decrease in size. ...
... idea that acquired traits are inherited Lamark thought that organisms adapted to changes in their environment through altered behaviors. The behaviors lead to selective use or disuse of given structures causing them to increase or decrease in size. ...
Validity of transferring the footprint sites identified in lab
... Are the CRM sequences in the reference genome different from those in the Raleigh, N.C. sample? A concern was raised that laboratory lines might be subject to conditions that may have led to the loss of functional binding sites, either by selection or by genetic drift. If so, the footprint site data ...
... Are the CRM sequences in the reference genome different from those in the Raleigh, N.C. sample? A concern was raised that laboratory lines might be subject to conditions that may have led to the loss of functional binding sites, either by selection or by genetic drift. If so, the footprint site data ...
Biology 4.24 Evolution Within a Species
... • mtDNA passes unchanged from a female parent to all of her offspring (i.e.: no recombination as can occur during meiosis). ...
... • mtDNA passes unchanged from a female parent to all of her offspring (i.e.: no recombination as can occur during meiosis). ...
Adaptation and Inheritance
... mother and half from your father. This is why you share some of your _________________________________ with your mother and some with your father. Egg and sperm cells are the only cells to have ______ chromosomes. During fertilisation, the egg and sperm cells join together to produce an ____________ ...
... mother and half from your father. This is why you share some of your _________________________________ with your mother and some with your father. Egg and sperm cells are the only cells to have ______ chromosomes. During fertilisation, the egg and sperm cells join together to produce an ____________ ...
Genetics 314 – Spring, 2004
... 1. You have become intrigued with aquaculture, the ‘farming’ of fish for food. You decide to become a fish breeder and breed designer trout for restaurants. You discover most of the traits you are interested in are under quantitative control and have a heritability (h2) of less than .4. a) What is m ...
... 1. You have become intrigued with aquaculture, the ‘farming’ of fish for food. You decide to become a fish breeder and breed designer trout for restaurants. You discover most of the traits you are interested in are under quantitative control and have a heritability (h2) of less than .4. a) What is m ...
Notes
... Any change in a _____________________________________________. Mutations occur at ________________________. The Genetic Code Chromosomes are made of ____________. Each chromosome contains thousands of ___________________. The sequence of ______________ in a gene forms a code that tells the ...
... Any change in a _____________________________________________. Mutations occur at ________________________. The Genetic Code Chromosomes are made of ____________. Each chromosome contains thousands of ___________________. The sequence of ______________ in a gene forms a code that tells the ...
5.2- Studying Genetic Crosses
... Analyzing the phenotype should provide insight into the unknown genotype. ...
... Analyzing the phenotype should provide insight into the unknown genotype. ...
Gregor Mendel
... More Terms that will help you A LOT… D. Law of Segregation: An egg and sperm only carry one allele each for inherited character because the two members of an allele pair separate from each other during the production of gametes. E. Homozygous: An organism that has two identical alleles for a gene. ...
... More Terms that will help you A LOT… D. Law of Segregation: An egg and sperm only carry one allele each for inherited character because the two members of an allele pair separate from each other during the production of gametes. E. Homozygous: An organism that has two identical alleles for a gene. ...
Blueprint of Life
... of a seal or whale and that of a bat, compare and contrast their limb structure and function. What selection pressures might have helped the development of the ‘flipper’? 11. Outline some specific biochemical similarities which provide evidence for evolution and indicate what evidence they provide. ...
... of a seal or whale and that of a bat, compare and contrast their limb structure and function. What selection pressures might have helped the development of the ‘flipper’? 11. Outline some specific biochemical similarities which provide evidence for evolution and indicate what evidence they provide. ...
acta 20 - Pontifical Academy of Sciences
... that mutations are rare: they are chiefly very small errors in copying the hereditary patrimony, which is chemically a substance called DNA and is essentially a book of instructions on how to build a new organism, almost identical to the parent/s, a copy of which is transmitted by the parent/s to th ...
... that mutations are rare: they are chiefly very small errors in copying the hereditary patrimony, which is chemically a substance called DNA and is essentially a book of instructions on how to build a new organism, almost identical to the parent/s, a copy of which is transmitted by the parent/s to th ...
Biology/Life Science CST - Standardized Testing and Reporting (CA
... g. mitochondria make energy Chapter 7-2 and Chapter 9 by the breakdown of 24. What is the function of the Mitochondria?(179) glucose to carbon 25. What is cellular respiration? (221-222) ...
... g. mitochondria make energy Chapter 7-2 and Chapter 9 by the breakdown of 24. What is the function of the Mitochondria?(179) glucose to carbon 25. What is cellular respiration? (221-222) ...
Quantitative Genetics: Traits controlled my many loci Quantitative
... Sir Ronald Fisher (1890-1962): Linking quantitative traits variation and Mendelian genetics • In 1918, Fisher showed that a large number of Mendelian factors (genes) influencing a trait would cause a nearly continuous distribution of trait values. Therefore, mendelian genetics can lead to an approxi ...
... Sir Ronald Fisher (1890-1962): Linking quantitative traits variation and Mendelian genetics • In 1918, Fisher showed that a large number of Mendelian factors (genes) influencing a trait would cause a nearly continuous distribution of trait values. Therefore, mendelian genetics can lead to an approxi ...
Introduction vs Rationale, Writing
... Measuring genetic diversity in wild populations: molecular and adaptive genetic variation in Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata) A fundamental and yet unresolved problem in evolutionary biology is the extent to which variability in molecular genetic markers such as allozyme and DNA polymorphi ...
... Measuring genetic diversity in wild populations: molecular and adaptive genetic variation in Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata) A fundamental and yet unresolved problem in evolutionary biology is the extent to which variability in molecular genetic markers such as allozyme and DNA polymorphi ...
Fire came with costs
... says that it was crucial to tap into the knowledge of toxicologists and geneticists to test the hypothesis that ‘…during human evolution, selection pressure towards increased resistance against fire-related toxicants was generated once humans started to use fire on a routine basis. This hypothesis i ...
... says that it was crucial to tap into the knowledge of toxicologists and geneticists to test the hypothesis that ‘…during human evolution, selection pressure towards increased resistance against fire-related toxicants was generated once humans started to use fire on a routine basis. This hypothesis i ...
Larsen Chapter Guide 5
... 4. What are the two opposing selective pressures involved in the evolution of human skin color? 5. What does it mean that human skin color has a clinal distribution? 6. Why do biological anthropologists use the term “lactase persistence” instead of “lactose intolerance”? Which condition is normal in ...
... 4. What are the two opposing selective pressures involved in the evolution of human skin color? 5. What does it mean that human skin color has a clinal distribution? 6. Why do biological anthropologists use the term “lactase persistence” instead of “lactose intolerance”? Which condition is normal in ...
onset is two to five years. Around 5,000 people in... UK have ALS at any time and 10 per cent...
... St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust to translate discoveries into tests and procedures, including ‘preimplantation genetic diagnosis’ (PGD) for ALS caused by a mutation on the SOD1 gene. ‘PGD gives people who carry a mutated gene the opportunity to avoid passing it on to their children,’ says Professor ...
... St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust to translate discoveries into tests and procedures, including ‘preimplantation genetic diagnosis’ (PGD) for ALS caused by a mutation on the SOD1 gene. ‘PGD gives people who carry a mutated gene the opportunity to avoid passing it on to their children,’ says Professor ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.