Giovanni Romeo
... the Tas1 family, identified 17 such pedigrees which showed a maximal HLOD score of 4.17 (a=0.80), and an NPL=4.99 (p=0.00002) at markers AFMa272zg9 and D2S2271 respectively. These results indicate the existence of a new major susceptibility locus for FNMTC on chromosome 2q21. In addition, six candid ...
... the Tas1 family, identified 17 such pedigrees which showed a maximal HLOD score of 4.17 (a=0.80), and an NPL=4.99 (p=0.00002) at markers AFMa272zg9 and D2S2271 respectively. These results indicate the existence of a new major susceptibility locus for FNMTC on chromosome 2q21. In addition, six candid ...
Name Date Ch 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles – Biology in
... Concept 10.3 Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid 11. In the following table – draw and explain what is happening in each stage of meiosis ...
... Concept 10.3 Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid 11. In the following table – draw and explain what is happening in each stage of meiosis ...
Genetics/Genetic Disorders, Evolution
... 3. mutation: random change in DNA sequence of a gene (can change amino acid sequence & protein coded for… can change the way the trait is expressed)… not all mutations matter in evolution, to matter they must be heritable (in gametes) 4. natural selection: organisms with variation best suited for en ...
... 3. mutation: random change in DNA sequence of a gene (can change amino acid sequence & protein coded for… can change the way the trait is expressed)… not all mutations matter in evolution, to matter they must be heritable (in gametes) 4. natural selection: organisms with variation best suited for en ...
F 6 Biology - Ch 9: Heredity and Genetics Name: ( ) 9.1.1 THE
... Under normal circumstances, all the linked genes remain together during cell division and so pass into the gamete, and hence the offspring, together. They do not therefore segregate in accordance with Mendel's Second Law of Independent Assortment. 9.4.1 Crossing Over and Recombination It is known th ...
... Under normal circumstances, all the linked genes remain together during cell division and so pass into the gamete, and hence the offspring, together. They do not therefore segregate in accordance with Mendel's Second Law of Independent Assortment. 9.4.1 Crossing Over and Recombination It is known th ...
Formalizing the gene centered view of evolution
... A standard first model of sexual reproduction assumes that recombination of the genes during sexual reproduction results in a complete mixing of the possible alleles not just in each pair of mating organisms but rather throughout the species—the group of organisms that is mating and reproducing. Offsp ...
... A standard first model of sexual reproduction assumes that recombination of the genes during sexual reproduction results in a complete mixing of the possible alleles not just in each pair of mating organisms but rather throughout the species—the group of organisms that is mating and reproducing. Offsp ...
Mackay, T. F. C. and R. R. H. Anholt (2007).
... measurements could be affected by significant genotype– environment (G ! E) interactions. Recently, Douglas Wahlsten and colleagues [3] performed a meta-analysis of behavioral data acquired by different laboratories on the same inbred mouse strains over a period of up to 50 years. Behavioral phenoty ...
... measurements could be affected by significant genotype– environment (G ! E) interactions. Recently, Douglas Wahlsten and colleagues [3] performed a meta-analysis of behavioral data acquired by different laboratories on the same inbred mouse strains over a period of up to 50 years. Behavioral phenoty ...
Conditions for extinction of some lethal alleles of X-linked
... are dominant, all the carriers die so they are rarely detected due to their rapid elimination from populations. However, recessive lethal alleles only cause death of carrier males and homozygous carrier females, though the last ones must be daughters of a carrier male, so they rarely exist. Heterozy ...
... are dominant, all the carriers die so they are rarely detected due to their rapid elimination from populations. However, recessive lethal alleles only cause death of carrier males and homozygous carrier females, though the last ones must be daughters of a carrier male, so they rarely exist. Heterozy ...
PDF - University of Florida
... Baer seeks answers to more fundamental questions about population diversity. “Why do different populations and different species have different amounts of genetic variation,” he asks. That’s an important question because genetic variation or mutation is the mechanism by which living things adapt to ...
... Baer seeks answers to more fundamental questions about population diversity. “Why do different populations and different species have different amounts of genetic variation,” he asks. That’s an important question because genetic variation or mutation is the mechanism by which living things adapt to ...
Microsoft Word - UWE Research Repository
... evaluation of food quality and food safety. One of the promising approaches is the development of genetic tests and genetic markers for selective breeding towards genotypes with desirable food quality characteristics. This presentation will give an overview of research on the development of genetic ...
... evaluation of food quality and food safety. One of the promising approaches is the development of genetic tests and genetic markers for selective breeding towards genotypes with desirable food quality characteristics. This presentation will give an overview of research on the development of genetic ...
Topic 5
... that might impair gene function). In most cases proof of a causative mutation requires finding different mutations (in different families) that affect the same gene, leading to similar phenotypes. All types of mutations can affect a gene’s function but particular genes often turn out to be altered i ...
... that might impair gene function). In most cases proof of a causative mutation requires finding different mutations (in different families) that affect the same gene, leading to similar phenotypes. All types of mutations can affect a gene’s function but particular genes often turn out to be altered i ...
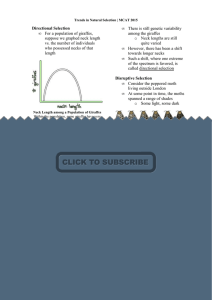
Directional Selection • For a population of giraffes, suppose we
... programmed to lay a given number of eggs might look like this: ...
... programmed to lay a given number of eggs might look like this: ...
Acquired Traits Revisited
... in progeny. Newborn rat pups that are licked and groomed by their mothers mature to be relatively calm and brave. Newborns that receive little or no maternal licking grow up to be nervous and seek darkness. The hippocampus of the brain of a well-licked rat is better developed and releases less of th ...
... in progeny. Newborn rat pups that are licked and groomed by their mothers mature to be relatively calm and brave. Newborns that receive little or no maternal licking grow up to be nervous and seek darkness. The hippocampus of the brain of a well-licked rat is better developed and releases less of th ...
Hardy Weinber AP Biology SSS Questions
... are homozygous for the Ic allele. Individuals with wavy hair are heterozygous (IsIc). In a population of 1,000 individuals, 245 were found to have straight hair, 393 had curly hair, and 362 had wavy hair. • (a) Calculate the allelic frequencies of the Is and Ic alleles. ...
... are homozygous for the Ic allele. Individuals with wavy hair are heterozygous (IsIc). In a population of 1,000 individuals, 245 were found to have straight hair, 393 had curly hair, and 362 had wavy hair. • (a) Calculate the allelic frequencies of the Is and Ic alleles. ...
FIT C Ch3 evolution
... • The three varieties may work in concert or in opposition to one another (consider drugs as reinforcers in ontogeny, but with deleterious effects at the other levels of selection). • Scenarios about human origins (including the evolution of verbal behavior) must take all three levels into account. ...
... • The three varieties may work in concert or in opposition to one another (consider drugs as reinforcers in ontogeny, but with deleterious effects at the other levels of selection). • Scenarios about human origins (including the evolution of verbal behavior) must take all three levels into account. ...
Genetics Review
... Mutation: damage to genetic material A mutation to genetic material is usually not beneficial. Mutagens are things that cause mutations, they include: 1. High Temperatures 2. Toxic Chemicals (pesticides, etc) 3. Radiation (nuclear and solar) Many common place items are capable of causing mutations: ...
... Mutation: damage to genetic material A mutation to genetic material is usually not beneficial. Mutagens are things that cause mutations, they include: 1. High Temperatures 2. Toxic Chemicals (pesticides, etc) 3. Radiation (nuclear and solar) Many common place items are capable of causing mutations: ...
As you explore Folder 4, fill in the data tables below, using a +
... mitochondria was used in this study along with DNA from other genes. Cytochrome b is an important substance for cell metabolism and has probably been around since the first prokaryotes. Changes in its nucleotide base sequence (A, T, C, and G) that do not disrupt the gene's function provide us with a ...
... mitochondria was used in this study along with DNA from other genes. Cytochrome b is an important substance for cell metabolism and has probably been around since the first prokaryotes. Changes in its nucleotide base sequence (A, T, C, and G) that do not disrupt the gene's function provide us with a ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 – Biol-1, C. Briggs, revised Fall 2015 Test
... 26. explain how these lines of evidence provide support for the idea of evolution: the fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and molecular biology. Some of these are not in textbook. 27. describe the observations that led Darwin to develop his theory for evolutio ...
... 26. explain how these lines of evidence provide support for the idea of evolution: the fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and molecular biology. Some of these are not in textbook. 27. describe the observations that led Darwin to develop his theory for evolutio ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 – Biol-1, C. Briggs, revised Fall 2015 Test
... 26. explain how these lines of evidence provide support for the idea of evolution: the fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and molecular biology. Some of these are not in textbook. 27. describe the observations that led Darwin to develop his theory for evolutio ...
... 26. explain how these lines of evidence provide support for the idea of evolution: the fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and molecular biology. Some of these are not in textbook. 27. describe the observations that led Darwin to develop his theory for evolutio ...
TAY-SACHS DISEASE AND OTHER CONDITIONS MORE
... infectious virus such as hepatitis where the hepatitis virus is carried in the body ...
... infectious virus such as hepatitis where the hepatitis virus is carried in the body ...
Classification and phylogeny – Chapter 2
... – Repeat sequences = 43.95% of total content of human chromosome 6 ...
... – Repeat sequences = 43.95% of total content of human chromosome 6 ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.