Chapter 10: Muslim Civilizations 622 – 1629
... founding of Islam? • What are some important beliefs of Muslims? • What’s the difference between Sunni and Shiite Muslims? • What were some social and economic advances brought about by Muslim empires? • Why is it significant that the Ottomans conquered Constantinople in 1453? ...
... founding of Islam? • What are some important beliefs of Muslims? • What’s the difference between Sunni and Shiite Muslims? • What were some social and economic advances brought about by Muslim empires? • Why is it significant that the Ottomans conquered Constantinople in 1453? ...
Slide 1
... • People were attracted to the economic benefit for Muslims not having to pay a poll tax ...
... • People were attracted to the economic benefit for Muslims not having to pay a poll tax ...
BE AN ALLY - VCU Global Education Office
... Fact: Although Islam began as a religion in the Middle East and its holiest sites are located there, the region is home to only about 20% of the world’s Muslims. The bulk of the world’s Muslim population–62%–is located in Asia. The four largest Muslim populations are in Indonesia, Pakistan, India an ...
... Fact: Although Islam began as a religion in the Middle East and its holiest sites are located there, the region is home to only about 20% of the world’s Muslims. The bulk of the world’s Muslim population–62%–is located in Asia. The four largest Muslim populations are in Indonesia, Pakistan, India an ...
Expansion of Islam Presentation
... successor of Muhammad, was meant to unite all Muslim – In the tradition of Muhammad, the Caliph is the temporal (worldly, secular) leader as well as the spiritual leader – Practically, this dual system died out with the destruction of the Abbasid Caliphate by the Mongols, and temporal and spiritual ...
... successor of Muhammad, was meant to unite all Muslim – In the tradition of Muhammad, the Caliph is the temporal (worldly, secular) leader as well as the spiritual leader – Practically, this dual system died out with the destruction of the Abbasid Caliphate by the Mongols, and temporal and spiritual ...
622 AD - Global Impacts
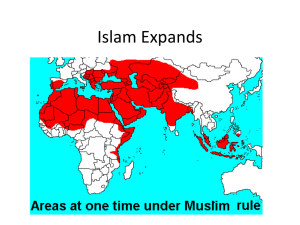
... • Between 632 AD, and 661 AD, the Islamic religion had spread to Egypt, Palestine, Syria, Mesopotamia, Iran, west to Tripoli (Libya), north to the Taurus and Caucasus Mts (Turkey and Georgia) and east to Pakistan. ...
... • Between 632 AD, and 661 AD, the Islamic religion had spread to Egypt, Palestine, Syria, Mesopotamia, Iran, west to Tripoli (Libya), north to the Taurus and Caucasus Mts (Turkey and Georgia) and east to Pakistan. ...
Unit 4 - River Mill Academy
... fasting, rituals; pious, miraculous power? Help spread Islam by traveling, preaching, examples Sunni ...
... fasting, rituals; pious, miraculous power? Help spread Islam by traveling, preaching, examples Sunni ...
Describe the physical features and climate of the Arabian Peninsula
... a. The geography and climate greatly impacted the lives of those who lived there. Bedouins were a nomadic group that traveled from oasis to oasis in order to survive. The climate affected their diet as they relied on dried fruit and nuts. 3. Who was Muhammad? Describe his early life. How did he beco ...
... a. The geography and climate greatly impacted the lives of those who lived there. Bedouins were a nomadic group that traveled from oasis to oasis in order to survive. The climate affected their diet as they relied on dried fruit and nuts. 3. Who was Muhammad? Describe his early life. How did he beco ...
Means
... Islam allows everything to be eaten except what it forbids. …It forbids pork and its by-products, alcohol and any narcotics. ** Halal meat comes from animals which have been slaughtered according to Muslim traditions. ...
... Islam allows everything to be eaten except what it forbids. …It forbids pork and its by-products, alcohol and any narcotics. ** Halal meat comes from animals which have been slaughtered according to Muslim traditions. ...
Muslim Civilizations (pg 32-33)
... Muhammad – military campaign to conquer across Byzantine and Persian empires - - belief in holiness in faith and paradise for those who die in battle Led Islam to Atlantic to Indus Valley (India) – Abbasid dynasty moves capital of Islam to Baghdad – rule until 1258 – Largest empire at time – baghdad ...
... Muhammad – military campaign to conquer across Byzantine and Persian empires - - belief in holiness in faith and paradise for those who die in battle Led Islam to Atlantic to Indus Valley (India) – Abbasid dynasty moves capital of Islam to Baghdad – rule until 1258 – Largest empire at time – baghdad ...
Sect. 3 The Golden Age of Muslim Civilization
... One group of Muslims used poetry to teach their ideas and beliefs. This group, called the Sufis, was mystics who believed that they could draw close to God through prayer, fasting, and a simple life. They taught that the world will reveal its mysteries to careful observers. They also helped spread I ...
... One group of Muslims used poetry to teach their ideas and beliefs. This group, called the Sufis, was mystics who believed that they could draw close to God through prayer, fasting, and a simple life. They taught that the world will reveal its mysteries to careful observers. They also helped spread I ...
Mr. Burton
... After Muhammad’s death, Abu Bakr became the first caliph, the title that Muslims use for the highest leader of Islam. ...
... After Muhammad’s death, Abu Bakr became the first caliph, the title that Muslims use for the highest leader of Islam. ...
Guided Reading Unit 2 - Islamamic Golden Age
... manufactured goods for trade.Social mobility, or the ability to move up in society, was possible through religious, scholarly, or military achievements.Although slavery was common, Islamic law taught that freeing slaves was a charitable act. ...
... manufactured goods for trade.Social mobility, or the ability to move up in society, was possible through religious, scholarly, or military achievements.Although slavery was common, Islamic law taught that freeing slaves was a charitable act. ...
Muslim Civilizations
... a strong leader. • During Shah Jahan’s (Akbar’s grandson) reign, it was the highest point of Mughal art, literature, and architecture. • When his wife died, he was so distraught that he built the Taj Mahal as a tomb for her. ...
... a strong leader. • During Shah Jahan’s (Akbar’s grandson) reign, it was the highest point of Mughal art, literature, and architecture. • When his wife died, he was so distraught that he built the Taj Mahal as a tomb for her. ...
Islam ppt.
... Non-Muslims, who were “Peoples of the Book,” were allowed religious freedom, but paid additional taxes. ...
... Non-Muslims, who were “Peoples of the Book,” were allowed religious freedom, but paid additional taxes. ...
Islam
... •The Qur’an Prohibits Muslims from forcing others to accept their religion •Muslim rulers were tolerant of other religions •Why did people convert to Islam? –It was appealing –They wouldn’t have to pay the non-muslim tax –You would be treated better ...
... •The Qur’an Prohibits Muslims from forcing others to accept their religion •Muslim rulers were tolerant of other religions •Why did people convert to Islam? –It was appealing –They wouldn’t have to pay the non-muslim tax –You would be treated better ...
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Islam Study Guide Section 1
... 39. Every mosque has a ________________ at which worshipers can wash their faces, arms, hands, and feet to show respect for God. 40. Arab merchants transported goods across the desert in ______________________. 41. Muslim traders were successful because they provided merchants with _________________ ...
... 39. Every mosque has a ________________ at which worshipers can wash their faces, arms, hands, and feet to show respect for God. 40. Arab merchants transported goods across the desert in ______________________. 41. Muslim traders were successful because they provided merchants with _________________ ...
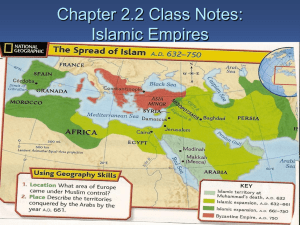
Chapter 2.2 Notes Islamic Empires
... 5. The Abbasids devoted their energy to trade, learning, and the arts. This time was the Golden Age of Islam. ...
... 5. The Abbasids devoted their energy to trade, learning, and the arts. This time was the Golden Age of Islam. ...
Islam in Europe
Islam gained its first foothold in continental Europe in 711 with the Umayyad conquest of Hispania. They advanced into France but in 732, were defeated by the Franks at the Battle of Tours. Over the centuries the Umayyads were gradually driven south and in 1492 the Moorish Emirate of Granada surrendered to Ferdinand V and Isabella. Muslim civilians were expelled from Spain and by 1614 none remained in Spain.Islam entered Eastern and Southeastern Europe in what are now parts of Russia and Bulgaria in the 13th century. The Ottoman Empire expanded into Europe taking huge portions of the Byzantine Empire in the 14th and 15th centuries. Over the centuries, the Ottoman Empire also gradually lost almost all of its European territories, until the empire collapsed in 1922. However, parts of the Balkans (such as Albania, Kosovo, Macedonia, Bulgaria, Sandzak (Serbia and Montenegro) and Bosnia) continue to have large populations of native, European Muslims. This is also the case in a number of regions within the Russian Federation such as the Northern Caucasus (Chechnya, Dagestan, Ingushetia, Kabardino-Balkaria, Karachay-Cherkessia, Stavropol Krai, Adygea), Crimea, Tatarstan, Bashkortostan and the Astrakhan Oblast. Transcontinental countries, such as Turkey, Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan have large Muslim populations.In the late 20th and early 21st centuries substantial numbers of non-native Muslims immigrated to Western Europe. By 2010 an estimated 44 million Muslims were living in Europe, including an estimated 19 million in the EU.