PPT format - Columbia University
... Element: An element is a substance which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical processes. Examples: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen. Atomic interpretation: An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. Hydrogen (H) atoms, carbon atoms (C), oxygen atoms (O). Compound: A c ...
... Element: An element is a substance which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical processes. Examples: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen. Atomic interpretation: An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. Hydrogen (H) atoms, carbon atoms (C), oxygen atoms (O). Compound: A c ...
Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
... Two chemical are mixed together and a gas is produce. ...
... Two chemical are mixed together and a gas is produce. ...
Ch 9 Cellular Respiration
... 9.1 CHEMICAL PATHWAYS Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain make up a process called the ...
... 9.1 CHEMICAL PATHWAYS Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain make up a process called the ...
7.5.9 Compare physical properties of matter to the chemical property
... substance, along with other properties Color cannot be used by itself to identify a substance An absence of color is also a physical property ...
... substance, along with other properties Color cannot be used by itself to identify a substance An absence of color is also a physical property ...
matter
... • Chemical reaction (also known as a chemical change) is a change in a substance or substances that results in a totally new substance – Ex: 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) Notice that the reactants (the substances you start with) combine to form a new substance (the product) ...
... • Chemical reaction (also known as a chemical change) is a change in a substance or substances that results in a totally new substance – Ex: 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) Notice that the reactants (the substances you start with) combine to form a new substance (the product) ...
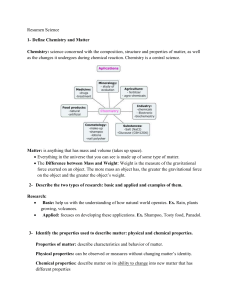
Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter A. How do chemists describe
... So far, none of the models you have drawn or interpreted are of metals. How can you visualize solid metals? The following picture shows a common use of aluminum foil. Although we use the chemical symbol "Al" to represent aluminum, what we visualize is actually a large collection of aluminum atoms. L ...
... So far, none of the models you have drawn or interpreted are of metals. How can you visualize solid metals? The following picture shows a common use of aluminum foil. Although we use the chemical symbol "Al" to represent aluminum, what we visualize is actually a large collection of aluminum atoms. L ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
Elements Combine to Form Compounds
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
Naming Compounds
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... specific ratio by mass according to the law of definite proportions. In a mixture, the components are not present in a specific ratio by mass. ...
... specific ratio by mass according to the law of definite proportions. In a mixture, the components are not present in a specific ratio by mass. ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... describe what chemical change can happen to the substance. * Chemical bond: force of attraction between two atoms that hold them together, H2O. Any change in a substance that involves a rearrangement of the way atoms are bonded is a chemical change. Material undergoing a chemical change is said to b ...
... describe what chemical change can happen to the substance. * Chemical bond: force of attraction between two atoms that hold them together, H2O. Any change in a substance that involves a rearrangement of the way atoms are bonded is a chemical change. Material undergoing a chemical change is said to b ...
Chapter 9 Balancing Equations
... formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole ...
... formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole ...
File
... Entropy- a measure of disorder of a system The more ordered a system is, the more entropy it has – for example a clean, organized room has less entropy than a messy room. ...
... Entropy- a measure of disorder of a system The more ordered a system is, the more entropy it has – for example a clean, organized room has less entropy than a messy room. ...
Types of Chemical Reactions Name_________________________
... Note: Access to some of the websites may not be possible dependent upon your computer system and or the network connection. You are still required to work through each main type of reaction providing balanced chemical equations based on the word descriptions. I. How can I tell if a chemical reaction ...
... Note: Access to some of the websites may not be possible dependent upon your computer system and or the network connection. You are still required to work through each main type of reaction providing balanced chemical equations based on the word descriptions. I. How can I tell if a chemical reaction ...
File
... chemical changes are less obvious. In a chemical reaction, two or more substances undergo a reorganization of atoms to form other substances. The substances that go into a chemical reaction are the reactants. The substances produced by a chemical reaction are the products. The properties of the prod ...
... chemical changes are less obvious. In a chemical reaction, two or more substances undergo a reorganization of atoms to form other substances. The substances that go into a chemical reaction are the reactants. The substances produced by a chemical reaction are the products. The properties of the prod ...
8.5DF: Chemical Formulas and Equations
... while cooking. Interestingly, there are many different ways that chemical reactions and chemical equations are used in cooking. For example, when you bake a cake, one of the chemical reactions that occurs is the baking soda reacting with water to produce carbon dioxide gas. This gas produces the “ho ...
... while cooking. Interestingly, there are many different ways that chemical reactions and chemical equations are used in cooking. For example, when you bake a cake, one of the chemical reactions that occurs is the baking soda reacting with water to produce carbon dioxide gas. This gas produces the “ho ...
Unit 2 matter - Kowenscience.com
... physical & chemical properties a) Physical Properties: Properties that can be observed and measured without changing the chemical composition of a substance ...
... physical & chemical properties a) Physical Properties: Properties that can be observed and measured without changing the chemical composition of a substance ...
Chemistry Midterm Review Sheet
... 1) Balance the following chemical equations and name each product and reactant: a) Ca(OH)2 + HCl CaCl2 + H2O b) Fe2O3 + C Fe + CO2 c) P4O10 + H2O H3PO4 d) Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that may occur when each of the following pairs is mixed. ...
... 1) Balance the following chemical equations and name each product and reactant: a) Ca(OH)2 + HCl CaCl2 + H2O b) Fe2O3 + C Fe + CO2 c) P4O10 + H2O H3PO4 d) Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that may occur when each of the following pairs is mixed. ...
Week 6 Review 2014-15
... States of Matter Solid Density Viscosity Compressibility Structure Shape Volume Movement Draw a PictureNanoscopic Eyes ...
... States of Matter Solid Density Viscosity Compressibility Structure Shape Volume Movement Draw a PictureNanoscopic Eyes ...
exo and endo experiments
... changes form. For that reason, if you had a certain number of atoms of a certain element on the left side of a chemical reaction equation, then you would have to have the same number of atoms of that element on the right side of the equation. This entails that mass can also be conserved during a che ...
... changes form. For that reason, if you had a certain number of atoms of a certain element on the left side of a chemical reaction equation, then you would have to have the same number of atoms of that element on the right side of the equation. This entails that mass can also be conserved during a che ...
Honors Chapter 2
... Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
... Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids have no shape, but they do have a volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and volume. ...
Writing Chemical Equations - Mrs. Procee's Online Classroom
... At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Translate chemical word equations into formula ...
... At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Translate chemical word equations into formula ...
Chemical weapon

A chemical weapon (CW) is a munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on human beings. The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) states: The term chemical weapon may also be applied to any toxic chemical or its precursor that can cause death, injury, temporary incapacitation or sensory irritation through its chemical action. Munitions or other delivery devices designed to deliver chemical weapons, whether filled or unfilled, are also considered weapons themselves.They are classified as weapons of mass destruction (WMDs), though they are distinct from nuclear weapons, biological weapons (diseases), and radiological weapons (which use radioactive decay of elements). All may be used in warfare known by the military acronym NBC, for nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare. Weapons of mass destruction are distinct from conventional weapons, which are primarily effective due to their explosive, kinetic, or incendiary potential. Chemical weapons can be widely dispersed in gas, liquid and solid forms, and may easily afflict others than the intended targets. Nerve gas, tear gas and pepper spray are three modern examples.Lethal, unitary, chemical agents and munitions are extremely volatile and they constitute a class of hazardous chemical weapons that are now being stockpiled by many nations. (Unitary agents are effective on their own and require no mixing with other agents.) The most dangerous of these are nerve agents GA, GB, GD, and VX, and vesicant (blister) agents which are formulations of sulfur mustard such as H, HT, and HD. All are liquids at normal room temperature, but become gaseous when released. Widely used during the First World War, the effects of so-called mustard gas, phosgene gas and others caused lung searing, blindness, death and maiming.Pepper spray is of common use today. It is potentially lethal. There are no recent records of pepper spray being used in war, despite the fact that it inflicts fewer injuries and side-effects compared with impact and explosive weapons.Under the Chemical Weapons Convention (1993), there is a legally binding, world-wide ban on the production, stockpiling, and use of chemical weapons and their precursors. Notwithstanding, large stockpiles thereof continue to exist, usually justified as only a precaution against putative use by an aggressor.