Document
... a product, I wondered why it is blue or not another colour. Interested, I began researching this issue and found that the solutions of not only copper, but whole d-block(transition) elements are coloured. After my research, I found that the solutions of metals are called metal complexes, or coordina ...
... a product, I wondered why it is blue or not another colour. Interested, I began researching this issue and found that the solutions of not only copper, but whole d-block(transition) elements are coloured. After my research, I found that the solutions of metals are called metal complexes, or coordina ...
Introduction to Fluorescence Spectroscopies I. Theory
... In the case of infrared absorption, the low energy infrared radiation is absorbed by the molecule causing a transition normally from its ground vibrational state to an excited vibrational state. In the case of scattering measurements, much higher energy radiation is used, usually in the visible or ...
... In the case of infrared absorption, the low energy infrared radiation is absorbed by the molecule causing a transition normally from its ground vibrational state to an excited vibrational state. In the case of scattering measurements, much higher energy radiation is used, usually in the visible or ...
Foreign molecules and ions in beryl obtained by infrared and visible
... The infrared (IR) and visible spectra (VIS) of two natural beryl samples indicate the presence of two types of water molecule, Fe2+, Fe3+ ions and CO3 . The spectra of two types of water molecules can be recognized with molecular fundamental vibrations at 3687 cm-1 (asymmetric stretching) for type I ...
... The infrared (IR) and visible spectra (VIS) of two natural beryl samples indicate the presence of two types of water molecule, Fe2+, Fe3+ ions and CO3 . The spectra of two types of water molecules can be recognized with molecular fundamental vibrations at 3687 cm-1 (asymmetric stretching) for type I ...
Crystallization of hydroxide cobalt carbonate Co2CO3(OH)2
... hydroxide carbonate Co2CO3(OH)2 and its hydrated phases Co2CO3(OH)2•nH2O have been subject of interest in the scientific literature because they can be precursors of the socalled low-dimensional cobalt oxide-based nanomaterials. Various cobalt salts can be precursors of Co3O4, but carbonates and hyd ...
... hydroxide carbonate Co2CO3(OH)2 and its hydrated phases Co2CO3(OH)2•nH2O have been subject of interest in the scientific literature because they can be precursors of the socalled low-dimensional cobalt oxide-based nanomaterials. Various cobalt salts can be precursors of Co3O4, but carbonates and hyd ...
Molecular Term Symbols
... Excitations between molecular electronic states provide information about properties of molecules. As noted in Engel and Reid, molecular electronic transitions are induced by UV/VIS radiation, and so these transitions involve much more energy compared to the vibrational-rotational spectroscopies tha ...
... Excitations between molecular electronic states provide information about properties of molecules. As noted in Engel and Reid, molecular electronic transitions are induced by UV/VIS radiation, and so these transitions involve much more energy compared to the vibrational-rotational spectroscopies tha ...
Time of flight-photoemission electron microscope for ultrahigh
... The experimental realization of an attosecond nanoplasmonic field microscope, which will measure the time evolution of excited optical fields on plasmonic nanostructures with nanometer spatial and attosecond time resolution, is based on probing the response of photoelectrons excited by an isolated a ...
... The experimental realization of an attosecond nanoplasmonic field microscope, which will measure the time evolution of excited optical fields on plasmonic nanostructures with nanometer spatial and attosecond time resolution, is based on probing the response of photoelectrons excited by an isolated a ...
J - Laboratory of Molecular Interactions
... systems with multiple bonds. They are small in the case of 1 H shielding, but large for example for 17 O shielding. This phemonenon is connected with the relative magnitude of diaand paramagnetic parts: 1 H shielding is dominated by the diamagnetic part, which is less sensitive than the paramagnetic ...
... systems with multiple bonds. They are small in the case of 1 H shielding, but large for example for 17 O shielding. This phemonenon is connected with the relative magnitude of diaand paramagnetic parts: 1 H shielding is dominated by the diamagnetic part, which is less sensitive than the paramagnetic ...
File - GENERAL DEPARTMENT
... We call this process spontaneous emission – spontaneous because the event was not triggered by any outside influence. The direction and phase of each of such photons is random. The light from a sodium or mercury lamp is generated in this manner. [Normally, the mean – life of excited atoms before spo ...
... We call this process spontaneous emission – spontaneous because the event was not triggered by any outside influence. The direction and phase of each of such photons is random. The light from a sodium or mercury lamp is generated in this manner. [Normally, the mean – life of excited atoms before spo ...
2.2.3.- X-ray diffraction
... a) The x-ray generator is based on the impacts between source electrons and metal atoms, which result in the emission of electrons of the metal, leaving a large number of holes inside the inner electronic shells. These holes become immediately occupied by electrons from more external shells and the ...
... a) The x-ray generator is based on the impacts between source electrons and metal atoms, which result in the emission of electrons of the metal, leaving a large number of holes inside the inner electronic shells. These holes become immediately occupied by electrons from more external shells and the ...
***** 1
... With this approach, many heavy-ion capture reactions at energies above and well below the Coulomb barrier have been successfully described. ...
... With this approach, many heavy-ion capture reactions at energies above and well below the Coulomb barrier have been successfully described. ...
UNIT III - Photochemistry
... However, the absorbed radiation does not necessarily cause a chemical reaction. When the conditions are not favourable for the molecules to react, the light energy may be reemitted as heat or light or it remains unused. Stark-Einstein Law of Photochemical Equivalence (or) Principle of Quantum Activa ...
... However, the absorbed radiation does not necessarily cause a chemical reaction. When the conditions are not favourable for the molecules to react, the light energy may be reemitted as heat or light or it remains unused. Stark-Einstein Law of Photochemical Equivalence (or) Principle of Quantum Activa ...
Title Near-ultraviolet inverse photoemission spectroscopy using ultra
... Although the Fermi edge of Ag is not accessible with other filters having lower center energies, the overall energy resolution can reasonably be estimated from Eq. (2). For example, the filter centered at 3.71 eV with w = 0.11 eV gives overall resolution of 0.27 eV in FWHM. Since the values are clos ...
... Although the Fermi edge of Ag is not accessible with other filters having lower center energies, the overall energy resolution can reasonably be estimated from Eq. (2). For example, the filter centered at 3.71 eV with w = 0.11 eV gives overall resolution of 0.27 eV in FWHM. Since the values are clos ...
Lab 2: Spectroscopy of Atoms and Ions
... occur at exactly the same wavelengths as emission from those elements. Since an atom’s energy levels are fixed, the amounts of energy it can gain from white light are exactly the same as those it can lose when excited in a discharge or flame. You may have noticed the difficulty of seeing lines at th ...
... occur at exactly the same wavelengths as emission from those elements. Since an atom’s energy levels are fixed, the amounts of energy it can gain from white light are exactly the same as those it can lose when excited in a discharge or flame. You may have noticed the difficulty of seeing lines at th ...
Photoelectric Effect
... 1. Cut strips of poster board with an approximate 4” width. 2. You could build an example setup at the teacher station prior to them starting the lab. Background info: The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation falls on an object. It was first theorized by a ...
... 1. Cut strips of poster board with an approximate 4” width. 2. You could build an example setup at the teacher station prior to them starting the lab. Background info: The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation falls on an object. It was first theorized by a ...
Physics of the Interaction of Charged Particles with Nuclei
... a consequence of the complexity of the nucleus as a physical object. Even in case the nucleon-nucleon interaction force would be known, and it would be possible to assume that this interaction does not depend on the presence of other nucleons, the many body problem of nuclear structure could hardly ...
... a consequence of the complexity of the nucleus as a physical object. Even in case the nucleon-nucleon interaction force would be known, and it would be possible to assume that this interaction does not depend on the presence of other nucleons, the many body problem of nuclear structure could hardly ...
Chemistry Handout 08 - (Redox)
... Questions 20 and 21 refer to the following: Two chemistry students each combine a different metal with hydrochloric acid. Student A uses zinc, and hydrogen gas is readily produced. Student B uses copper, and no hydrogen gas is produced. ...
... Questions 20 and 21 refer to the following: Two chemistry students each combine a different metal with hydrochloric acid. Student A uses zinc, and hydrogen gas is readily produced. Student B uses copper, and no hydrogen gas is produced. ...
Monday, Oct. 2, 2006
... • Orbits and energy levels an electron can occupy are labeled by – Principle quantum number: n • n can only be integer ...
... • Orbits and energy levels an electron can occupy are labeled by – Principle quantum number: n • n can only be integer ...
Example 4: A one-electron atom is irradiated with visible light. The
... Question 3.4: The emission spectrum of a one-electron atom showed 6 lines: 90000 cm-1, 75000 cm-1, 50000 cm-1, 40000 cm-1, 25000 cm-1 and 15000 cm-1. How many lines would you expect to see in the absorption spectrum and at what energies? Express your answer in cm-1. Question 2.5: An atom has three ...
... Question 3.4: The emission spectrum of a one-electron atom showed 6 lines: 90000 cm-1, 75000 cm-1, 50000 cm-1, 40000 cm-1, 25000 cm-1 and 15000 cm-1. How many lines would you expect to see in the absorption spectrum and at what energies? Express your answer in cm-1. Question 2.5: An atom has three ...
Atomic Spectra - Rutgers Physics
... The shift clearly falls off rapidly with increasing n. For our data involving different n values, approximating the difference between initial and final state relativistic shifts by that for the final state (smaller n) only gives a result approximately in the range of fit error for the experimental ...
... The shift clearly falls off rapidly with increasing n. For our data involving different n values, approximating the difference between initial and final state relativistic shifts by that for the final state (smaller n) only gives a result approximately in the range of fit error for the experimental ...
Nugget
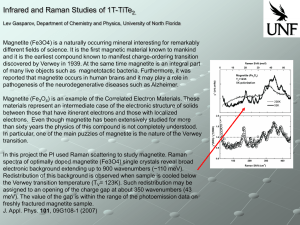
... Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a naturally occurring mineral interesting for remarkably different fields of science. It is the first magnetic material known to mankind and it is the earliest compound known to manifest charge-ordering transition discovered by Verwey in 1939. At the same time magnetite is an in ...
... Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a naturally occurring mineral interesting for remarkably different fields of science. It is the first magnetic material known to mankind and it is the earliest compound known to manifest charge-ordering transition discovered by Verwey in 1939. At the same time magnetite is an in ...
1 Indentifying Unknown #M20 via Infrared Spectroscopy, Mass
... formula was discovered. When looking at the mass spectra (Figure 2) the molecular ion peak (A in Figure 2), which was determined to be an even numbered value because the unknown was determined to have no nitrogen atoms, appears at approximately 98 g/mol. To calculate the molecular formula, the molec ...
... formula was discovered. When looking at the mass spectra (Figure 2) the molecular ion peak (A in Figure 2), which was determined to be an even numbered value because the unknown was determined to have no nitrogen atoms, appears at approximately 98 g/mol. To calculate the molecular formula, the molec ...
Two-Center Gaussian potential well for studying light nucleus in
... In the light nucleus, deformation plays an important role in determining nuclear structure. This deviations from spherical structures are found in the axial deformations and the clustering because numerous experimental studies have revealed a clustering phenomena in them [1], [2]. Freer and Merchant ...
... In the light nucleus, deformation plays an important role in determining nuclear structure. This deviations from spherical structures are found in the axial deformations and the clustering because numerous experimental studies have revealed a clustering phenomena in them [1], [2]. Freer and Merchant ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.