Document
... One interesting phenomenon of the effect of temperature on resistance is superconductivity. In 1911, H. Kammerlingh Onnes found that mercury loses all its resistance abruptly at a critical temperature of 4.1 K. When a material attains zero resistance at some critical temperature, it is called a supe ...
... One interesting phenomenon of the effect of temperature on resistance is superconductivity. In 1911, H. Kammerlingh Onnes found that mercury loses all its resistance abruptly at a critical temperature of 4.1 K. When a material attains zero resistance at some critical temperature, it is called a supe ...
design of coplanar power amplifiers for mm-wave system
... backside process usually contributing significantly to heat removal in microstrip circuits. However, due to its technical and technological advantages, the coplanar GaAs MMICs have demonstrated to be cost effective for volume production [2]. Besides, with the emerging mounting solutions like the fli ...
... backside process usually contributing significantly to heat removal in microstrip circuits. However, due to its technical and technological advantages, the coplanar GaAs MMICs have demonstrated to be cost effective for volume production [2]. Besides, with the emerging mounting solutions like the fli ...
III.5. THE THERMISTOR 1. Work purpose To check the law
... substance has a large amount of conduction electrons. This kind of substances is called a semimetal. Both metals and semimetals are conductors. Conversely, when Eg is very great, the transition is much less probable and the substance is “poor” in conduction electrons. The current is vanishingly smal ...
... substance has a large amount of conduction electrons. This kind of substances is called a semimetal. Both metals and semimetals are conductors. Conversely, when Eg is very great, the transition is much less probable and the substance is “poor” in conduction electrons. The current is vanishingly smal ...
605-00010 Datasheet - Mouser Electronics
... Cathodic reaction:2Li + + CO2 + 1/2O2 + 2e - = Li2CO3 Anodic reaction:2Na+ + 1/2O2 + 2e- = Na2O Overall chemical reaction:Li2CO3 + 2Na + = Na2O + 2Li + + CO2 The Electromotive force(EMF) result from the above electrode reaction, accord with according to Nernst’s equation:: EMF = Ec - (R x T) / (2F) ...
... Cathodic reaction:2Li + + CO2 + 1/2O2 + 2e - = Li2CO3 Anodic reaction:2Na+ + 1/2O2 + 2e- = Na2O Overall chemical reaction:Li2CO3 + 2Na + = Na2O + 2Li + + CO2 The Electromotive force(EMF) result from the above electrode reaction, accord with according to Nernst’s equation:: EMF = Ec - (R x T) / (2F) ...
Elecrtonics_L1
... connected across a 6 V battery, calculate the voltage at B if the variable resistor is set to (i) 5 kΩ (ii) 40 k Ω A ...
... connected across a 6 V battery, calculate the voltage at B if the variable resistor is set to (i) 5 kΩ (ii) 40 k Ω A ...
LM384 5W Audio Power Amplifier
... Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments Sa ...
... Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments Sa ...
the franck-hertz experiment - University of Toronto Physics
... on the temperature of the oven. If the tube has been overheated, the emission current is small, and maxima and minima can hardly be recognized or seen at all. For checking purposes, remove the tube from the oven for approximately 30 seconds. Then, if the tube was overheated before, maxima can be fou ...
... on the temperature of the oven. If the tube has been overheated, the emission current is small, and maxima and minima can hardly be recognized or seen at all. For checking purposes, remove the tube from the oven for approximately 30 seconds. Then, if the tube was overheated before, maxima can be fou ...
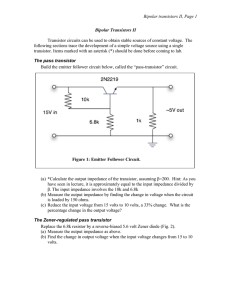
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
Electrical Principles Wk 1B
... Resistance (R) is the opposition to current flow. Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ώ). Resistance limits the flow of current in an electrical circuit. Conductors are made of materials that have very little resistance and permits electrons to move through it easily. ...
... Resistance (R) is the opposition to current flow. Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ώ). Resistance limits the flow of current in an electrical circuit. Conductors are made of materials that have very little resistance and permits electrons to move through it easily. ...
Ohm`s law
... Ohms law, defines the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. These basic electrical units apply to direct current, or alternating current. Ohm’s Law is the foundation of electronics and electricity. ...
... Ohms law, defines the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. These basic electrical units apply to direct current, or alternating current. Ohm’s Law is the foundation of electronics and electricity. ...
Thermal runaway

Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback.In other words, ""thermal runaway"" describes a process which is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), this risk is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation, although exothermic chemical reactions can be of concern here too. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar mass stars, the ""helium flash"".There are also concerns regarding global warming that a global average increase of 3-4 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial baseline could lead to a further unchecked increase in surface temperatures. For example, releases of methane, a greenhouse gas more potent than CO2, from wetlands, melting permafrost and continental margin seabed clathrate deposits could be subject to positive feedback.