9. Mechanical oscillations and resonances R
... acoustics, or oscillating electric and magnetic fields in optics. The mathematical treatment always yields to similar generic equations. Using the rotary oscillation of a disk as an example, we will learn about the general properties of (harmonic) oscillators in this experiment. In particular, we wi ...
... acoustics, or oscillating electric and magnetic fields in optics. The mathematical treatment always yields to similar generic equations. Using the rotary oscillation of a disk as an example, we will learn about the general properties of (harmonic) oscillators in this experiment. In particular, we wi ...
MRI SIMPLIFIED Parth Patel MIV, USC SOM
... Resonance relates to the transfer/exchange of energies between two systems at a specific frequency. It is analogous to talking to someone on your cell phone. In magnetic resonance, only protons with the same frequency as the RF pulse will respond. ...
... Resonance relates to the transfer/exchange of energies between two systems at a specific frequency. It is analogous to talking to someone on your cell phone. In magnetic resonance, only protons with the same frequency as the RF pulse will respond. ...
ch10_shm_16slides
... oscillating system at all times, the result is driven harmonic motion. Here, the driving force has the same frequency as the spring system and always points in the direction of the object’s velocity. ...
... oscillating system at all times, the result is driven harmonic motion. Here, the driving force has the same frequency as the spring system and always points in the direction of the object’s velocity. ...
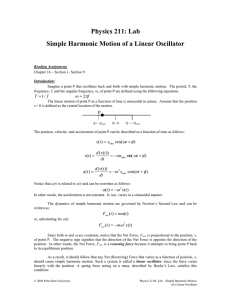
Lab #11: Simple Harmonic Motion of a Linear Oscillator
... simple pendulums, and physical pendulums.) Damping: In the real world, most oscillations are eventually “damped” due to friction or viscous forces. A damping force causes the amplitude (and therefore, energy) of a given system to decrease over time. In the position equation, x(t), for a damped simpl ...
... simple pendulums, and physical pendulums.) Damping: In the real world, most oscillations are eventually “damped” due to friction or viscous forces. A damping force causes the amplitude (and therefore, energy) of a given system to decrease over time. In the position equation, x(t), for a damped simpl ...
Diamond Quantum Magnetomets
... brightness. The application of a microwave field with resonant frequency drives from the |0> to the |±1> spin sublevels, and leads therefore to a drop of the luminescence intensity. Microwave energy ms = +-1 ...
... brightness. The application of a microwave field with resonant frequency drives from the |0> to the |±1> spin sublevels, and leads therefore to a drop of the luminescence intensity. Microwave energy ms = +-1 ...
Document
... d) The classical HO may have zero energy, but the quantum HO may not. e) The classical HO does allow the bond to break, whereas the quantum ...
... d) The classical HO may have zero energy, but the quantum HO may not. e) The classical HO does allow the bond to break, whereas the quantum ...
(x = 0 ).
... If the spring is hung vertically, the only change is in the equilibrium position, which is at the point where the spring force equals the gravitational force. ...
... If the spring is hung vertically, the only change is in the equilibrium position, which is at the point where the spring force equals the gravitational force. ...
Optical Pumping
... momentum states of the atomic ground state, which are populated when light is absorbed and emitted. This experiment reveals many phenomena of quantum mechanics including angular momentum selection rules, the density matrix, and resonance. Optical pumping is important to a wide variety of application ...
... momentum states of the atomic ground state, which are populated when light is absorbed and emitted. This experiment reveals many phenomena of quantum mechanics including angular momentum selection rules, the density matrix, and resonance. Optical pumping is important to a wide variety of application ...
Resonance
In physics, resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when a given system is driven by another vibrating system or external force to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific preferential frequency.Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are known as the system's resonant frequencies, or resonance frequencies. At resonant frequencies, small periodic driving forces have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations. This is because the system stores vibrational energy.Resonance occurs when a system is able to store and easily transfer energy between two or more different storage modes (such as kinetic energy and potential energy in the case of a pendulum). However, there are some losses from cycle to cycle, called damping. When damping is small, the resonant frequency is approximately equal to the natural frequency of the system, which is a frequency of unforced vibrations. Some systems have multiple, distinct, resonant frequencies.Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and resonance of quantum wave functions. Resonant systems can be used to generate vibrations of a specific frequency (e.g., musical instruments), or pick out specific frequencies from a complex vibration containing many frequencies (e.g., filters).The term Resonance (from Latin resonantia, 'echo', from resonare, 'resound') originates from the field of acoustics, particularly observed in musical instruments, e.g. when strings started to vibrate and to produce sound without direct excitation by the player.