Instrumental Methods of Analysis
... Detectors • Low flux of photons and low energy of infrared radiation make it more difficult to detect. • photon detector- based upon photoconductive effect that occurs in certain semiconductor materials. Absorption of light causes resistance to decrease. Voltage drop across load resistor measured: ...
... Detectors • Low flux of photons and low energy of infrared radiation make it more difficult to detect. • photon detector- based upon photoconductive effect that occurs in certain semiconductor materials. Absorption of light causes resistance to decrease. Voltage drop across load resistor measured: ...
Harmonic Motion, Waves, and Sound Wave Models
... • Describe the relationships pendulum to determine where in between potential energy and the swing the potential and kinetic kinetic energy in a system. energies are greatest and least, • Apply the law of conservation and then use this information to of energy to derive an equation predict the max ...
... • Describe the relationships pendulum to determine where in between potential energy and the swing the potential and kinetic kinetic energy in a system. energies are greatest and least, • Apply the law of conservation and then use this information to of energy to derive an equation predict the max ...
Solutions - Illinois State Chemistry
... From these results, we see that the population of the v=1 level is only about 8% that of the v=0 level, € and the population of the v=2 level is only 0.6% of the v=0 level. The intensity of a transition from an initial state to a final state is directly proportional to the population of the initial ...
... From these results, we see that the population of the v=1 level is only about 8% that of the v=0 level, € and the population of the v=2 level is only 0.6% of the v=0 level. The intensity of a transition from an initial state to a final state is directly proportional to the population of the initial ...
****** 1 - Weizmann Institute of Science
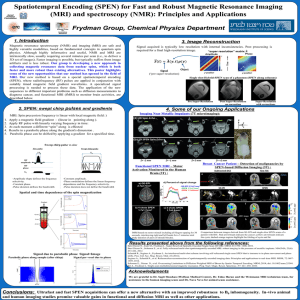
... Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and imaging (MRI) are safe and highly versatile modalities, based on fundamental concepts in quantum spin physics. Although highly informative and useful, NMR and MRI are intrinsically slow, usually requiring several minutes per scan (i.e., to deliver a 3D set o ...
... Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and imaging (MRI) are safe and highly versatile modalities, based on fundamental concepts in quantum spin physics. Although highly informative and useful, NMR and MRI are intrinsically slow, usually requiring several minutes per scan (i.e., to deliver a 3D set o ...
A quantum calculation of the higher order terms in the Bloch
... need to inverse equation (11). Taking Shirley’s notations ( b instead of &ol), we obtain : ...
... need to inverse equation (11). Taking Shirley’s notations ( b instead of &ol), we obtain : ...
Bloch Oscillations
... • Imagine a particle in a periodic potential acted on by a constant force. • Example: electrons in crystal lattice exposed to constant electric field • Classically, we expect Ohmic behavior ...
... • Imagine a particle in a periodic potential acted on by a constant force. • Example: electrons in crystal lattice exposed to constant electric field • Classically, we expect Ohmic behavior ...
1.3.5 Spectroscopy Name Symbol Definition SI unit Notes total term
... Ĥ hfs is the hyperfine coupling hamiltonian. The coupling constants a are usually quoted in MHz, but they are sometimes quoted in magnetic induction units (G or T) obtained by dividing by the conversion factor gµB/h, which has the SI unit Hz/T; geµB/h ≈ 28.025 ...
... Ĥ hfs is the hyperfine coupling hamiltonian. The coupling constants a are usually quoted in MHz, but they are sometimes quoted in magnetic induction units (G or T) obtained by dividing by the conversion factor gµB/h, which has the SI unit Hz/T; geµB/h ≈ 28.025 ...
Document
... of the resulting oscillations to fall to one-third of its initial value. (b) How many oscillations are made by the block in this time? 61. For x(t) = xm cos(dt+), suppose the amplitude xm is Fm given by xm 2 2 , where Fm is the [m ( d 2 ) 2 b 2 d2 ]1 / 2 ...
... of the resulting oscillations to fall to one-third of its initial value. (b) How many oscillations are made by the block in this time? 61. For x(t) = xm cos(dt+), suppose the amplitude xm is Fm given by xm 2 2 , where Fm is the [m ( d 2 ) 2 b 2 d2 ]1 / 2 ...
Resonance
In physics, resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when a given system is driven by another vibrating system or external force to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific preferential frequency.Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are known as the system's resonant frequencies, or resonance frequencies. At resonant frequencies, small periodic driving forces have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations. This is because the system stores vibrational energy.Resonance occurs when a system is able to store and easily transfer energy between two or more different storage modes (such as kinetic energy and potential energy in the case of a pendulum). However, there are some losses from cycle to cycle, called damping. When damping is small, the resonant frequency is approximately equal to the natural frequency of the system, which is a frequency of unforced vibrations. Some systems have multiple, distinct, resonant frequencies.Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and resonance of quantum wave functions. Resonant systems can be used to generate vibrations of a specific frequency (e.g., musical instruments), or pick out specific frequencies from a complex vibration containing many frequencies (e.g., filters).The term Resonance (from Latin resonantia, 'echo', from resonare, 'resound') originates from the field of acoustics, particularly observed in musical instruments, e.g. when strings started to vibrate and to produce sound without direct excitation by the player.