Chapter 1 The Kondo screening cloud: what it is and
... length one-dimensional quantum wire. In the first case, (Subsection 1.3.1) this wire is closed into a ring and we consider the persistent current through it as a function of the ring length and magnetic flux. In the second case, (Subsection 1.3.2) the ring is straight with the quantum dot coupled to ...
... length one-dimensional quantum wire. In the first case, (Subsection 1.3.1) this wire is closed into a ring and we consider the persistent current through it as a function of the ring length and magnetic flux. In the second case, (Subsection 1.3.2) the ring is straight with the quantum dot coupled to ...
Newsletter 102 - Psi-k
... The aim of this workshop was to bring together two different communities who share a welldefined common interest, namely the ab-initio calculation of electron correlation problems (principally total energies, but touching other properties such magnetism, excitations, forces etc), using classes of me ...
... The aim of this workshop was to bring together two different communities who share a welldefined common interest, namely the ab-initio calculation of electron correlation problems (principally total energies, but touching other properties such magnetism, excitations, forces etc), using classes of me ...
Quantum Stein`s lemma revisited, inequalities for quantum entropies
... Given states ρ, σ ∈ S(H) the probabilities for obtaining the outcome 0 for the observable E are given by tr(ρ⊗n a) and tr(σ ⊗n a) with a := E(0) given that the n-partite system is prepared either in state ρ⊗n or in state σ ⊗n . Suppose that we use the observable E as a decision rule, meaning that wh ...
... Given states ρ, σ ∈ S(H) the probabilities for obtaining the outcome 0 for the observable E are given by tr(ρ⊗n a) and tr(σ ⊗n a) with a := E(0) given that the n-partite system is prepared either in state ρ⊗n or in state σ ⊗n . Suppose that we use the observable E as a decision rule, meaning that wh ...
Density Functional Theory for Systems with Electronic Edges
... ... |Ψ(r1 , r2 , ..., rN )| dr2 dr3 ...drN . ...
... ... |Ψ(r1 , r2 , ..., rN )| dr2 dr3 ...drN . ...
Quantum Mechanics (Part II)
... predictions, yet also deeply perplexing, challenging deeply-held convictions of objectivity, causality, determinism, and continuity at the core of classical physics and everyday experience. We have expectations and intuitions about how macroscopic objects should act, but things on the atomic-scale j ...
... predictions, yet also deeply perplexing, challenging deeply-held convictions of objectivity, causality, determinism, and continuity at the core of classical physics and everyday experience. We have expectations and intuitions about how macroscopic objects should act, but things on the atomic-scale j ...
Quantum computing: An IBM perspective
... the number 15 using a seven-spin molecule). These demonstrations, together with those of other groups, helped transform experimental quantum computing into a growing field of research. By the early 2000s, the liquid-state NMRQC had been pushed close to some natural limits to the ability to distinguis ...
... the number 15 using a seven-spin molecule). These demonstrations, together with those of other groups, helped transform experimental quantum computing into a growing field of research. By the early 2000s, the liquid-state NMRQC had been pushed close to some natural limits to the ability to distinguis ...
The Standard Model and its Simple Extensions
... (In practise the three best measured parameters are used: α(0), GF, mZ) Can test the model if more than three observables are measured Expect one-loop correction to be of order α ∼ 1% ➟ have to be taken into account of precision better than that • quantities get sensitive to other parameters (mt, mH ...
... (In practise the three best measured parameters are used: α(0), GF, mZ) Can test the model if more than three observables are measured Expect one-loop correction to be of order α ∼ 1% ➟ have to be taken into account of precision better than that • quantities get sensitive to other parameters (mt, mH ...
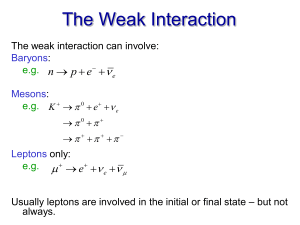
The Weak Interaction
... Strong Interaction Since the gluon is massless the range of the gluon is infinite. But we have said that all real particles are colour singlets (colour charge zero). Therefore if a gluon is to be exchanged between two particles (e.g. a neutron and a proton) the gluon must be also be a colour single ...
... Strong Interaction Since the gluon is massless the range of the gluon is infinite. But we have said that all real particles are colour singlets (colour charge zero). Therefore if a gluon is to be exchanged between two particles (e.g. a neutron and a proton) the gluon must be also be a colour single ...
P. LeClair
... 1. A spherical volume of radius a is filled with charge of uniform density ρ. We want to know the potential energy U of this sphere of charge, that is, the work done in assembling it. Calculate it by building up the sphere up layer by layer, making use of the fact that the field outside a spherical ...
... 1. A spherical volume of radius a is filled with charge of uniform density ρ. We want to know the potential energy U of this sphere of charge, that is, the work done in assembling it. Calculate it by building up the sphere up layer by layer, making use of the fact that the field outside a spherical ...