One-loop divergencies in the theory of gravitation
... The recent advances in the understanding of gauge theories make a fresh approach to the quantum theory of gravitation possible. First, we now know precisely how to obtain Feynman rules for a gauge theory [7]; secondly, the dimensional regularization scheme provides a powerful tool to handle divergen ...
... The recent advances in the understanding of gauge theories make a fresh approach to the quantum theory of gravitation possible. First, we now know precisely how to obtain Feynman rules for a gauge theory [7]; secondly, the dimensional regularization scheme provides a powerful tool to handle divergen ...
Fine Structure Constant Variation from a Late Phase Transition
... vacuum expectation value (0, 0, 0, τ2, τ2 ) where τ s are the Pauli matrices [16, 17]. This pattern of vevs breaks SO(10) down to SU(4) × SU(2)L × U(1)I3R , where the U(1) is the diagonal generator of SU(2)R . The superpotential of the theory necessarily contains a Planck suppressed operator of the ...
... vacuum expectation value (0, 0, 0, τ2, τ2 ) where τ s are the Pauli matrices [16, 17]. This pattern of vevs breaks SO(10) down to SU(4) × SU(2)L × U(1)I3R , where the U(1) is the diagonal generator of SU(2)R . The superpotential of the theory necessarily contains a Planck suppressed operator of the ...
The Psychophysical Matrix and Group Analysis
... that reversing the spin of the one particle instantaneously reversed the spin of the other (Dossey, 1982). In 1982, Alain Aspect showed that this synchronicity, which transcends the speed of light, even holds between distant regions of space-time (Coveney and Highfield, 1991). This discovery links t ...
... that reversing the spin of the one particle instantaneously reversed the spin of the other (Dossey, 1982). In 1982, Alain Aspect showed that this synchronicity, which transcends the speed of light, even holds between distant regions of space-time (Coveney and Highfield, 1991). This discovery links t ...
PowerPoint - Physics - University of Florida
... •The zeroth order Hamiltonian (Ĥ0D) includes the exchange bias. •The zeroth order wavefunctions may be labeled according to the spin projections (m1 and m2) of the two monomers within a dimer, i.e. ...
... •The zeroth order Hamiltonian (Ĥ0D) includes the exchange bias. •The zeroth order wavefunctions may be labeled according to the spin projections (m1 and m2) of the two monomers within a dimer, i.e. ...
488-390 - Wseas.us
... Bernoulli equation for incompressible potential flow. Following Heisenberg, a temporal uncertainty relation is introduced as p k . Key-Words: - Quantum mechanics. Space-time physics. Invariant statistical theory of fields. TOE Similarly, the invariant definition of the peculiar and diffusion ...
... Bernoulli equation for incompressible potential flow. Following Heisenberg, a temporal uncertainty relation is introduced as p k . Key-Words: - Quantum mechanics. Space-time physics. Invariant statistical theory of fields. TOE Similarly, the invariant definition of the peculiar and diffusion ...
3,2,1 1 1 2 = −= −= nn E n ekm E Only memorize the second form.
... For the quizzes and tests, you should know all the concepts and equations in this summary. Section 28.3: The Bohr Atom The Bohr model of the atom is successful in describing the spectra of atomic hydrogen and hydrogen-like ions. One of the basic assumptions of the model is that the electron can exis ...
... For the quizzes and tests, you should know all the concepts and equations in this summary. Section 28.3: The Bohr Atom The Bohr model of the atom is successful in describing the spectra of atomic hydrogen and hydrogen-like ions. One of the basic assumptions of the model is that the electron can exis ...
Path Integrals in Quantum Field Theory
... can happen, will happen. Each distinct history can be thought of as a path through the configuration space that describes the state of the system at any given time. For quantum field theory, the configuration space is a Fock space where each vector represents the number of each type of particle with ...
... can happen, will happen. Each distinct history can be thought of as a path through the configuration space that describes the state of the system at any given time. For quantum field theory, the configuration space is a Fock space where each vector represents the number of each type of particle with ...
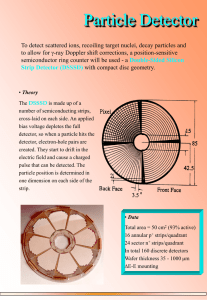
particle detector
... semiconductor ring counter will be used - a Double-Sided Silicon Strip Detector (DSSSD) with compact disc geometry. ...
... semiconductor ring counter will be used - a Double-Sided Silicon Strip Detector (DSSSD) with compact disc geometry. ...
on the behaviour of atoms in an electromagnetic wa ve field
... exhibit in many respects a great similarity with the properties which, on the classical theory, systems consisting of small · electrically charged particles would possess. One of the main problems in the modern theory of atoms is therefore to find to what extent and in what manner the conceptions an ...
... exhibit in many respects a great similarity with the properties which, on the classical theory, systems consisting of small · electrically charged particles would possess. One of the main problems in the modern theory of atoms is therefore to find to what extent and in what manner the conceptions an ...