The French Revolution - World History Period 5
... Britain and France became involved in wars with several countries and against the counterrevolutionaries inside France. • The Committee of Public Safety was instituted in order to judge the counter revolutionaries ...
... Britain and France became involved in wars with several countries and against the counterrevolutionaries inside France. • The Committee of Public Safety was instituted in order to judge the counter revolutionaries ...
The French Revoluton Begins
... where there was still a king, but a Legislative Assembly would make the laws. • 6. During the French Revolution, many radical members of the Paris Commune wore long trousers instead of knee-length breeches and called themselves ...
... where there was still a king, but a Legislative Assembly would make the laws. • 6. During the French Revolution, many radical members of the Paris Commune wore long trousers instead of knee-length breeches and called themselves ...
Chapter 6 notes Sections 1 - 2
... • In a weakened state, France was threatened by other European powers. • This brought out radicals. The revolution was about to turn nasty. ...
... • In a weakened state, France was threatened by other European powers. • This brought out radicals. The revolution was about to turn nasty. ...
Western Civilization II HIS-102
... until the constitution of the realm is drawn up and fixed upon solid foundations.” It was passed 576-1 by the members ...
... until the constitution of the realm is drawn up and fixed upon solid foundations.” It was passed 576-1 by the members ...
Chapter 7-The French RevolutionWhole Chapter
... Economic hardship-high taxes, crop failures in the 1780s, which led to the price of bread doubling, and the country was in debt due to the Louis XVI. A weak leader-Louis XVI could not make decisions and he married a member of the Austrian royal family, Marie Antoinette, who was hated by the public. ...
... Economic hardship-high taxes, crop failures in the 1780s, which led to the price of bread doubling, and the country was in debt due to the Louis XVI. A weak leader-Louis XVI could not make decisions and he married a member of the Austrian royal family, Marie Antoinette, who was hated by the public. ...
Key Individuals - This area is password protected
... Court Oath- under Bailly’s leadership. – Remain until the nation is given a constitution ...
... Court Oath- under Bailly’s leadership. – Remain until the nation is given a constitution ...
The French Revolution
... merchants and business managers. They made up the largest part of the Third Estate Committee of Public Safety- Agency created to direct the war effort. Conscription- compulsory military service, also known as the draft. Coup d’état- quick seizure of power or sudden overthrow of government leaders by ...
... merchants and business managers. They made up the largest part of the Third Estate Committee of Public Safety- Agency created to direct the war effort. Conscription- compulsory military service, also known as the draft. Coup d’état- quick seizure of power or sudden overthrow of government leaders by ...
Concerto The French Revolution
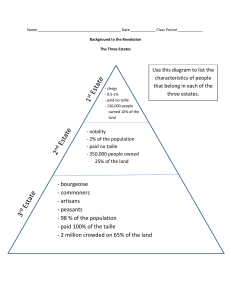
... B. Clergy or First Estate, numbered about 130,000 in a nation of 28 million C. Church owned about 10 percent of the land and extracted wealth in tithes D. Members of the hereditary nobility held almost all upper positions in church E. Second Estate consisted of 300,000 members of nobility and contro ...
... B. Clergy or First Estate, numbered about 130,000 in a nation of 28 million C. Church owned about 10 percent of the land and extracted wealth in tithes D. Members of the hereditary nobility held almost all upper positions in church E. Second Estate consisted of 300,000 members of nobility and contro ...
UNIT 9
... Young (PR) – Travels in France: Signs of Revolution Sieyes (PR) – What is the Third Estate? (PR) – The Declaration of Independence Lefebvre (S) – The Coming of the French Revolution Sutherland (S) – The Revolution of the Notables Sherman 161-162, 163-164 The Cahiers: Discontents of the Third Estate ...
... Young (PR) – Travels in France: Signs of Revolution Sieyes (PR) – What is the Third Estate? (PR) – The Declaration of Independence Lefebvre (S) – The Coming of the French Revolution Sutherland (S) – The Revolution of the Notables Sherman 161-162, 163-164 The Cahiers: Discontents of the Third Estate ...
File
... The assignats began to be used as currency. The Assembly decided to produce more in order to liquidate the national debt and to create a large body of new property owners with a direct stake in the revolution. The plan backfired as the value of assignats dropped and inflation increased, puttin ...
... The assignats began to be used as currency. The Assembly decided to produce more in order to liquidate the national debt and to create a large body of new property owners with a direct stake in the revolution. The plan backfired as the value of assignats dropped and inflation increased, puttin ...
wh unit 5 and semester review 13 worksheet
... ____________________C The Christians of Lalibela build stone-hewn churches in the shape of a cross hidden within rock enclosures of the highlands. ____________________T English Puritan led the Civil War against Charles I and became Lord Protector of England. ____________________A Matrilineal societi ...
... ____________________C The Christians of Lalibela build stone-hewn churches in the shape of a cross hidden within rock enclosures of the highlands. ____________________T English Puritan led the Civil War against Charles I and became Lord Protector of England. ____________________A Matrilineal societi ...
the french revolution
... was called the napoleonic code. it made France a legally uniform country. The napoleonic code also marked a trend to centralize and organize power on a national level.• This had begun with Richelieu, Mazarin, and Louis XIV, but was interrupted by This had begun with Richelieu, Mazarin, and Louis XIV ...
... was called the napoleonic code. it made France a legally uniform country. The napoleonic code also marked a trend to centralize and organize power on a national level.• This had begun with Richelieu, Mazarin, and Louis XIV, but was interrupted by This had begun with Richelieu, Mazarin, and Louis XIV ...
Name: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION: Video Questions Please
... 8. At first, it seemed that King Louis XVI would cooperate with some of the demands of the Third Estate. Why do you think he ultimately reacted so violently against them? ...
... 8. At first, it seemed that King Louis XVI would cooperate with some of the demands of the Third Estate. Why do you think he ultimately reacted so violently against them? ...
french rev timeline - Get Well Kathleen Davey
... exemptions, founded and directed new industries, established overseas colonies, and exerted control over trade and finance. To pay for these policies, collectively called mercantilism, they built standing armies. The ultimate purpose of this activity was to achieve what the French called gloire. Glo ...
... exemptions, founded and directed new industries, established overseas colonies, and exerted control over trade and finance. To pay for these policies, collectively called mercantilism, they built standing armies. The ultimate purpose of this activity was to achieve what the French called gloire. Glo ...
CHAPTER 20 The French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era, 1789
... toppled. In America, the 13 British colonies attained their independence from England. B. Political and Fiscal Crisis in Eighteenth Century France France under Louis XV was in a constant state of financial crisis. The crisis was made worse by the huge debts contracted to finance the Seven Years’ War ...
... toppled. In America, the 13 British colonies attained their independence from England. B. Political and Fiscal Crisis in Eighteenth Century France France under Louis XV was in a constant state of financial crisis. The crisis was made worse by the huge debts contracted to finance the Seven Years’ War ...
Modern France Assignment
... help American colonists rebel against France’s rival England. National economic problems led to a very high tax rate to pay of Frances debts in the time of Louis XVI, leading poverty and unemployment. As well, there was a famine in the 1780s. Already influenced by nationalist ideas, many French disc ...
... help American colonists rebel against France’s rival England. National economic problems led to a very high tax rate to pay of Frances debts in the time of Louis XVI, leading poverty and unemployment. As well, there was a famine in the 1780s. Already influenced by nationalist ideas, many French disc ...
Chapter 19
... Destruction of the Old Regime Seigneurial rights abolished, August 4, 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen Olympe de Gouges, Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen, 1791 ...
... Destruction of the Old Regime Seigneurial rights abolished, August 4, 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen Olympe de Gouges, Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen, 1791 ...
A Revolutionary France
... • a government run by elected representatives instead of a monarch. – It may or may not keep the monarch as a symbolic ...
... • a government run by elected representatives instead of a monarch. – It may or may not keep the monarch as a symbolic ...
The French Revolution - Mat
... Louis XVI • Led by Maximilien Robespierre and his Committee of Public Safety • Traitors and enemies of the revolution = executed with the guillotine • An estimated 40,000 people were killed in this 1 year ...
... Louis XVI • Led by Maximilien Robespierre and his Committee of Public Safety • Traitors and enemies of the revolution = executed with the guillotine • An estimated 40,000 people were killed in this 1 year ...
Graphic Organizer Answer Key - Marion County Public Schools
... French Revolution. The King denies the new voting ...
... French Revolution. The King denies the new voting ...
Unit Organizer - Lyndhurst Schools
... Directions: Read each of the Big Ideas below and support with evidence from the day’s lesson. Your responses should include AT LEAST 3-4 TOPICS for each Big Idea. Economic and social inequalities in the Old Regime helped cause the French Revolution. ...
... Directions: Read each of the Big Ideas below and support with evidence from the day’s lesson. Your responses should include AT LEAST 3-4 TOPICS for each Big Idea. Economic and social inequalities in the Old Regime helped cause the French Revolution. ...
French Revolution
... French Revolution 35. King Louis XVI 36. Marie Antoinette 37. First Estate 38. Second Estate 39. Third Estate 40. Bourgeoisie 41. Sans Culottes 42. Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen 43. Radical 44. Maximilien Robespierre 45. Guillotine 46. Counterrevolution 47. Reign of Terror 48. ...
... French Revolution 35. King Louis XVI 36. Marie Antoinette 37. First Estate 38. Second Estate 39. Third Estate 40. Bourgeoisie 41. Sans Culottes 42. Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen 43. Radical 44. Maximilien Robespierre 45. Guillotine 46. Counterrevolution 47. Reign of Terror 48. ...
Reign of Terror

The Reign of Terror (5 September 1793 – 28 July 1794), also known as The Terror (French: la Terreur), was a period of violence that occurred after the onset of the French Revolution, incited by conflict between two rival political factions, the Girondins and the Jacobins, and marked by mass executions of ""enemies of the revolution"". The death toll ranged in the tens of thousands, with 16,594 executed by guillotine (2,639 in Paris), and another 25,000 in summary executions across France.The guillotine (called the ""National Razor"") became the symbol of the revolutionary cause, strengthened by a string of executions: King Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette, the Girondins, Philippe Égalité (Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans), and Madame Roland, and others such as pioneering chemist Antoine Lavoisier, lost their lives under its blade. During 1794, revolutionary France was beset with conspiracies by internal and foreign enemies. Within France, the revolution was opposed by the French nobility, which had lost its inherited privileges. The Roman Catholic Church opposed the revolution, which had turned the clergy into employees of the state and required they take an oath of loyalty to the nation (through the Civil Constitution of the Clergy). In addition, the French First Republic was engaged in a series of wars with neighboring powers, and parts of France were engaging in civil war against the republican regime.The extension of civil war and the advance of foreign armies on national territory produced a political crisis and increased the already present rivalry between the Girondins and the more radical Jacobins. The latter were eventually grouped in the parliamentary faction called the Mountain, and they had the support of the Parisian population. The French government established the Committee of Public Safety, which took its final form on 6 September 1793, in order to suppress internal counter-revolutionary activities and raise additional French military forces.Through the Revolutionary Tribunal, the Terror's leaders exercised broad powers and used them to eliminate the internal and external enemies of the republic. The repression accelerated in June and July 1794, a period called la Grande Terreur (the Great Terror), and ended in the coup of 9 Thermidor Year II (27 July 1794), leading to the Thermidorian Reaction, in which several instigators of the Reign of Terror were executed, including Saint-Just and Robespierre.