Phonon-Induced Spin Relaxation of Conduction Electrons in
... phonons and impurities, as suggested by Elliott [2] and Yafet [3]. There are two physical processes to be considered. (A) The periodic, ion-induced spin-orbit interaction is modified by phonons [4]. Electrons scattering by the modified interaction can directly change their spin states. (B) Because o ...
... phonons and impurities, as suggested by Elliott [2] and Yafet [3]. There are two physical processes to be considered. (A) The periodic, ion-induced spin-orbit interaction is modified by phonons [4]. Electrons scattering by the modified interaction can directly change their spin states. (B) Because o ...
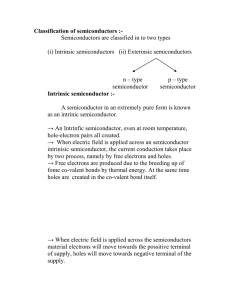
Classification of semiconductors :-
... → When electric field is applied across the semiconductors material electrons will move towards the possitive terminal of supply, holes will move towards negative terminal of the ...
... → When electric field is applied across the semiconductors material electrons will move towards the possitive terminal of supply, holes will move towards negative terminal of the ...
Topological Insulators - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... A&M p354 discussion to motivate understanding surface effects • We have ignored surface effect for the most part so far, often treating out solids as infinite in size. ...
... A&M p354 discussion to motivate understanding surface effects • We have ignored surface effect for the most part so far, often treating out solids as infinite in size. ...
Interplay of AharonovBohm and Berry Phases for a Quantum Cloud
... function of the nucleus is much more concentrated and semifluxons rarely penetrate it. Thus, its geometrical phase is simply the usual AB phase, which we neglect in the following.) The rule allows that we can replace the electron cloud with a point charge at the center of the atom and the semifluxon ...
... function of the nucleus is much more concentrated and semifluxons rarely penetrate it. Thus, its geometrical phase is simply the usual AB phase, which we neglect in the following.) The rule allows that we can replace the electron cloud with a point charge at the center of the atom and the semifluxon ...
Pauli exclusion principle - University of Illinois Archives
... the outermost shell, which gives rise to the periodic table of the elements. ...
... the outermost shell, which gives rise to the periodic table of the elements. ...
Higher Physics Electricity
... ability to conduct electricity. Give examples of each type Classifying materials By considering their electrical properties, we can divide materials into three groups: Materials with many free electrons. These elections can Conductors easily be made to flow through the material. For example, all m ...
... ability to conduct electricity. Give examples of each type Classifying materials By considering their electrical properties, we can divide materials into three groups: Materials with many free electrons. These elections can Conductors easily be made to flow through the material. For example, all m ...
t = |T – T c
... the critical pressures, densities, and temperatures are very different for different fluids! Even more remarkably, a class of uniaxial ferromagnets also shares these exponents! This phenomenon is called universality. We also see that the exponents do not appear to be simple numbers. However, all cri ...
... the critical pressures, densities, and temperatures are very different for different fluids! Even more remarkably, a class of uniaxial ferromagnets also shares these exponents! This phenomenon is called universality. We also see that the exponents do not appear to be simple numbers. However, all cri ...
Temporal Coherence of Photons Emitted by Single Nitrogen
... Coherent control of single quantum systems and the generation of nonclassical states has attracted widespread attention because of their application in quantum physics and quantum information science. Solid state systems are often considered to be promising and also difficult because of inhomogeneit ...
... Coherent control of single quantum systems and the generation of nonclassical states has attracted widespread attention because of their application in quantum physics and quantum information science. Solid state systems are often considered to be promising and also difficult because of inhomogeneit ...
Multiphoton adiabatic rapid passage: classical transition induced by separatrix crossing
... quantum picture involving a multiphoton resonance. An important aspect of this process is the relative frequencies involved. The transition frequency to go directly from n = 72 to 82 using ten identical photons is 14.5 GHz1 . Thus, the driving frequency is red detuned by roughly 2.8 GHz for single-p ...
... quantum picture involving a multiphoton resonance. An important aspect of this process is the relative frequencies involved. The transition frequency to go directly from n = 72 to 82 using ten identical photons is 14.5 GHz1 . Thus, the driving frequency is red detuned by roughly 2.8 GHz for single-p ...
quantum dynamics of integrable spin chains
... [27], and Abraham, Barouch, Gallavotti and Martin-Löf [1, 2, 3] have found the same kind of behavior for the XX model with an impurity. So, definitely, this unusual behavior of such systems could be discouraging, since, as Lebowitz pointed out in [16] discussing just these topics: almost all physica ...
... [27], and Abraham, Barouch, Gallavotti and Martin-Löf [1, 2, 3] have found the same kind of behavior for the XX model with an impurity. So, definitely, this unusual behavior of such systems could be discouraging, since, as Lebowitz pointed out in [16] discussing just these topics: almost all physica ...
Microscopic theory for quantum mirages in quantum corrals D. Porras, J. Ferna´ndez-Rossier,
... the presence of the corral is accounted for by replacing the plane waves, which diagonalize the free-surface electron Hamiltonian, by the corral states. Throughout the paper, we neglect the magnetic moment of the corral atoms. This is justified because the mirage appears also when the corral atoms a ...
... the presence of the corral is accounted for by replacing the plane waves, which diagonalize the free-surface electron Hamiltonian, by the corral states. Throughout the paper, we neglect the magnetic moment of the corral atoms. This is justified because the mirage appears also when the corral atoms a ...
What are electric and magnetic fields?
... health effects of exposure to ELF fields, and include margins for safety. The basis for the guidelines has remained unchanged for over twenty years, but subsequent reviews have refined the numerical limits. The most recent revision was published in 2010. ICNIRP continues to review research in the ar ...
... health effects of exposure to ELF fields, and include margins for safety. The basis for the guidelines has remained unchanged for over twenty years, but subsequent reviews have refined the numerical limits. The most recent revision was published in 2010. ICNIRP continues to review research in the ar ...
Diamagnetism and flux creep in bilayer exciton superfluids P. R. Eastham,
... We now consider the response of the disordered system to an in-plane field at zero temperature. We will see that the disordered system has a different diamagnetic response from the clean system. It does not have a commensurateincommensurate transition controlled by an intrinsic length scale λJ [see ...
... We now consider the response of the disordered system to an in-plane field at zero temperature. We will see that the disordered system has a different diamagnetic response from the clean system. It does not have a commensurateincommensurate transition controlled by an intrinsic length scale λJ [see ...
Topological aspects of systems with broken time-reversal symmetry
... In chapter 3, we consider analogs of quantum Hall effect edge modes in photonic systems. Formal aspects of our formulation of the problem are presented in full detail, and are supplemented with technical details, including especially the consideration of Berry curvature in the case of frequency depe ...
... In chapter 3, we consider analogs of quantum Hall effect edge modes in photonic systems. Formal aspects of our formulation of the problem are presented in full detail, and are supplemented with technical details, including especially the consideration of Berry curvature in the case of frequency depe ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.