Magnetism - HouseWscience
... Only iron, nickel, cobalt and steel can be magnetized (CINS) You make magnets by aligning the domains Stroke iron, cobalt, nickel or steel In one direction with a magnet The more you stroke the stronger the magnet b/c the domains are aligned Place iron, cobalt, nickel or steel in a stron ...
... Only iron, nickel, cobalt and steel can be magnetized (CINS) You make magnets by aligning the domains Stroke iron, cobalt, nickel or steel In one direction with a magnet The more you stroke the stronger the magnet b/c the domains are aligned Place iron, cobalt, nickel or steel in a stron ...
Magnetism - Practice - Little Miami Schools
... Ferromagnetic materials are made up of regions known as domains. Within each domain, the magnetic fields of all the atoms are lined up in the same direction. When exposed to a magnetic field, the domains tend to line up with the field. Due to the existence of domains, ferromagnetic materials are eas ...
... Ferromagnetic materials are made up of regions known as domains. Within each domain, the magnetic fields of all the atoms are lined up in the same direction. When exposed to a magnetic field, the domains tend to line up with the field. Due to the existence of domains, ferromagnetic materials are eas ...
Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging
... f. Both NMR and MRI use the nuclear spins as reporters of structure and dynamics of a system under study. g. The total magnetization of a sample at equilibrium always points to the direction of the applied magnetic field. h. It may take very long time (seconds or longer) for a nuclear spin to make a ...
... f. Both NMR and MRI use the nuclear spins as reporters of structure and dynamics of a system under study. g. The total magnetization of a sample at equilibrium always points to the direction of the applied magnetic field. h. It may take very long time (seconds or longer) for a nuclear spin to make a ...
engineering physics ii magnetic materials
... 4. There is no permanent dipole moment, so they are called weak magnets 5. When temperature is less than critical temperature diamagnetic become normal material Examples: Gold, Germanium, Silicon, etc., 3.3.2 PARAMAGNETIC MATERIALS In the case of paramagnetic materials, the spins in two opposite dir ...
... 4. There is no permanent dipole moment, so they are called weak magnets 5. When temperature is less than critical temperature diamagnetic become normal material Examples: Gold, Germanium, Silicon, etc., 3.3.2 PARAMAGNETIC MATERIALS In the case of paramagnetic materials, the spins in two opposite dir ...
Zeeman Effect
... Without a magnetic field, configurations a, b and c have the same energy, as do d, e and f. The presence of a magnetic field splits the energy levels. A line produced by a transition from a, b or c to d, e or f now will be several lines between different combinations of a, b, c and d, e, f. Not all ...
... Without a magnetic field, configurations a, b and c have the same energy, as do d, e and f. The presence of a magnetic field splits the energy levels. A line produced by a transition from a, b or c to d, e or f now will be several lines between different combinations of a, b, c and d, e, f. Not all ...
File - Lagan Physics
... Q4 E.g., the axle of the electric motor could be used to turn a (large) pulley wheel, around which the lift cables could wind or unwind to raise or lower the lift. Q5 current, magnetic, field, force, amplifier, move, frequency, sound. ...
... Q4 E.g., the axle of the electric motor could be used to turn a (large) pulley wheel, around which the lift cables could wind or unwind to raise or lower the lift. Q5 current, magnetic, field, force, amplifier, move, frequency, sound. ...
Year 9 Magnetism Key Words
... electromagnet stronger a coil of wire with electricity flowing in it. An electromagnet has a magnetic field like a bar magnet a metal that is a magnetic material tiny pieces of iron that are sometimes used to find the shape of a magnetic a natural rock that has magnetic properties something that can ...
... electromagnet stronger a coil of wire with electricity flowing in it. An electromagnet has a magnetic field like a bar magnet a metal that is a magnetic material tiny pieces of iron that are sometimes used to find the shape of a magnetic a natural rock that has magnetic properties something that can ...
Unit 3_electricity and magnetism_97
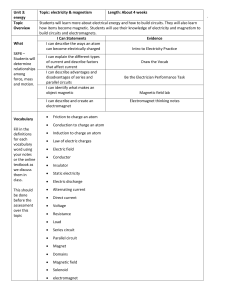
... how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electrically charged Intro to Electricity Practice I can explain the different types of current and des ...
... how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electrically charged Intro to Electricity Practice I can explain the different types of current and des ...
magnetism - bYTEBoss
... FERROMAGNETIC (IRON-LIKE) S N • FERROMAGNETIC MATERIALS ARE – IRON – COBALT – NICKLE ...
... FERROMAGNETIC (IRON-LIKE) S N • FERROMAGNETIC MATERIALS ARE – IRON – COBALT – NICKLE ...
Electromagnetic Forces
... current on or off, you just turn it on or off. To change the direction of the magnetic field, reverse the direction of the current There are 2 ways to change the strength of the magnetic field. 1. Increase the amount of current in the wire 2. Make a loop or coil in a wire ...
... current on or off, you just turn it on or off. To change the direction of the magnetic field, reverse the direction of the current There are 2 ways to change the strength of the magnetic field. 1. Increase the amount of current in the wire 2. Make a loop or coil in a wire ...
ELECTRIC MOTOR
... A change in magnetic field associated with a conductor will induce a electric current in the conductor. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand ...
... A change in magnetic field associated with a conductor will induce a electric current in the conductor. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand ...
Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
Chapter-36-four-square-questions_-answer
... Q6: How can spinning electrons work together or work against each other? A pair of spinning electrons can work together by spinning in the SAME direction which results in a stronger magnet. They can work against each other by spinning in opposite directions which cancels out their magnetic field. Q7 ...
... Q6: How can spinning electrons work together or work against each other? A pair of spinning electrons can work together by spinning in the SAME direction which results in a stronger magnet. They can work against each other by spinning in opposite directions which cancels out their magnetic field. Q7 ...
Magnetism f08
... single magnetic domain. Storage density in particulate media is ~1.5 x 105 bits/mm2, while storage density for thin films exceeds 108 bits/mm2. ...
... single magnetic domain. Storage density in particulate media is ~1.5 x 105 bits/mm2, while storage density for thin films exceeds 108 bits/mm2. ...
notes13-- Interactions of electrons with an electromagnetic field
... This is the magnetic flux quantization-- a direct consequence of Gauge invariant. Example: Consider a magnet having the shape of a donut. At normal temperature the magnet is a normal metal and the magnetic flux lines can penetrate the hole as well as the metal. At low temperature where the metal bec ...
... This is the magnetic flux quantization-- a direct consequence of Gauge invariant. Example: Consider a magnet having the shape of a donut. At normal temperature the magnet is a normal metal and the magnetic flux lines can penetrate the hole as well as the metal. At low temperature where the metal bec ...
Magnets Notes
... What happens when you break a magnet? Draw it after breaking the magnet in half twice. ...
... What happens when you break a magnet? Draw it after breaking the magnet in half twice. ...
15 HW 5.1 Magnetism.pub
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
How can you make the field stronger? Add more loops!!!
... 0Magnetic Fields and Magnetic force and Electromagnetic Induction A. Magnetic Fields – permanent magnets 1. What are permanent magnets made of? Why can these materials become magnets? ...
... 0Magnetic Fields and Magnetic force and Electromagnetic Induction A. Magnetic Fields – permanent magnets 1. What are permanent magnets made of? Why can these materials become magnets? ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.