Superconductors - Bryn Mawr College
... The Meissner effect in superconductors like this black ceramic yttrium based superconductor acts to exclude magnetic fields from the material. Since the electrical resistance is zero, supercurrents are generated in the material to exclude the magnetic fields from a magnet brought near it. The curren ...
... The Meissner effect in superconductors like this black ceramic yttrium based superconductor acts to exclude magnetic fields from the material. Since the electrical resistance is zero, supercurrents are generated in the material to exclude the magnetic fields from a magnet brought near it. The curren ...
Electromagnetism William Gilbert (15401603) Hans Christian
... (Re: The Magnetic Field Around a Straight Conductor) A charge moving through a straight conductor produces a circular magnetic field around the conductor. The field is represented by concentric rings. The electric current causes the magnetic field. ...
... (Re: The Magnetic Field Around a Straight Conductor) A charge moving through a straight conductor produces a circular magnetic field around the conductor. The field is represented by concentric rings. The electric current causes the magnetic field. ...
2.1.4 magnetic fields
... (North and & South). More correctly they should be referred to as the “North seeking pole” and “South seeking pole” Like poles repel each other Unlike poles attract each other ...
... (North and & South). More correctly they should be referred to as the “North seeking pole” and “South seeking pole” Like poles repel each other Unlike poles attract each other ...
8Jsumm
... You can find the shape of the magnetic field using iron filings or using a plotting compass. The Earth has a magnetic field. A compass is a small magnet that always points north. But magnetic materials placed near a compass can change the direction that it points. Magnets can be used to sort iron an ...
... You can find the shape of the magnetic field using iron filings or using a plotting compass. The Earth has a magnetic field. A compass is a small magnet that always points north. But magnetic materials placed near a compass can change the direction that it points. Magnets can be used to sort iron an ...
Basic MR Imaging (MRI) and MR spectroscopy (MRS)
... change in the direction of dipole moment and no signal ...
... change in the direction of dipole moment and no signal ...
docx: Geo Magnetic Journal
... 2. Draw and describe the following: When two magnets have the same poles (north/north or south/south) toward each other what happens? Why? (label: poles and magnetic field) ...
... 2. Draw and describe the following: When two magnets have the same poles (north/north or south/south) toward each other what happens? Why? (label: poles and magnetic field) ...
Magnetism
... The lines, called magnetic field lines, map out the magnetic field around a magnet. • Magnetic field line spread out from one pole, curve around the magnet, and return to the other pole. ...
... The lines, called magnetic field lines, map out the magnetic field around a magnet. • Magnetic field line spread out from one pole, curve around the magnet, and return to the other pole. ...
Magnetism_000
... running through its center, and the magnetic poles were near the geographic poles ...
... running through its center, and the magnetic poles were near the geographic poles ...
PH-208 Magnetism Page 1 Diamagnetism and Paramagnetism
... For the general case of N ions with angular momentum J, the allowed energy values are . So the free energy is ...
... For the general case of N ions with angular momentum J, the allowed energy values are . So the free energy is ...
Lecture_7_Magnets and Magnetism print
... Magnetic Theories Electron theory of magnetism • Electrons spin as they orbit (similar to earth) • Spin produces magnetic field • Magnetic direction depends on direction of rotation • Non-magnets → equal number of electrons spinning in opposite direction • Magnets → more spin one way than other ...
... Magnetic Theories Electron theory of magnetism • Electrons spin as they orbit (similar to earth) • Spin produces magnetic field • Magnetic direction depends on direction of rotation • Non-magnets → equal number of electrons spinning in opposite direction • Magnets → more spin one way than other ...
October 23/24th Chapter 32 Magnetism
... of magnetic dipole moments of the atoms despite thermal agitations ! This alignment gives material its permanent magnetism ...
... of magnetic dipole moments of the atoms despite thermal agitations ! This alignment gives material its permanent magnetism ...
EM_INDUCTION
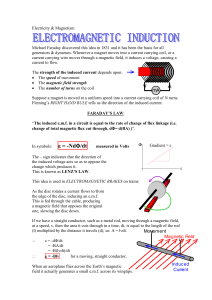
... Michael Faraday discovered this idea in 1831 and it has been the basis for all generators & dynamos. Whenever a magnet moves into a current carrying coil, or a current carrying wire moves through a magnetic field, it induces a voltage, causing a current to flow. The strength of the induced current d ...
... Michael Faraday discovered this idea in 1831 and it has been the basis for all generators & dynamos. Whenever a magnet moves into a current carrying coil, or a current carrying wire moves through a magnetic field, it induces a voltage, causing a current to flow. The strength of the induced current d ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field
... The magnetic field protects us by channeling super-fast, high energy charged particles from the Sun away from the Earth. They flow around the field This causes electrons to flow along the field lines to the poles where they rain down energizing the molecules of the atmosphere making them glow … The ...
... The magnetic field protects us by channeling super-fast, high energy charged particles from the Sun away from the Earth. They flow around the field This causes electrons to flow along the field lines to the poles where they rain down energizing the molecules of the atmosphere making them glow … The ...
Year 9 Magnetism summary sheet
... Field lines do not lead from one magnet to the other when the magnets repel each other ...
... Field lines do not lead from one magnet to the other when the magnets repel each other ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... Electricity can make a magnetic field Magnets can make electricity A current can generate a magnetic field, which makes the iron shavings move ...
... Electricity can make a magnetic field Magnets can make electricity A current can generate a magnetic field, which makes the iron shavings move ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.