Shinnyo-En at a glance What is Shinnyo-En? - Saisho-Goma
... The oldest and most significant school of esoteric Buddhism in Japan is Shingon Buddhism. Shinnyo-En was founded by Shinjo Ito, who as a holy man had received the highest consecration of Shingon. Shinjo Ito underwent his entire spiritual training as an ordained monk and all of the ascetic teachings ...
... The oldest and most significant school of esoteric Buddhism in Japan is Shingon Buddhism. Shinnyo-En was founded by Shinjo Ito, who as a holy man had received the highest consecration of Shingon. Shinjo Ito underwent his entire spiritual training as an ordained monk and all of the ascetic teachings ...
2306 Foundations of Buddhism
... The paper deals with the main doctrines and practices of mainstream (pre-Mahāyāna) Buddhism, as reflected by the surviving literature of the various schools. Tutorials will enable students to further discuss and analyse the main topics dealt with during the course, thus representing an ideal complem ...
... The paper deals with the main doctrines and practices of mainstream (pre-Mahāyāna) Buddhism, as reflected by the surviving literature of the various schools. Tutorials will enable students to further discuss and analyse the main topics dealt with during the course, thus representing an ideal complem ...
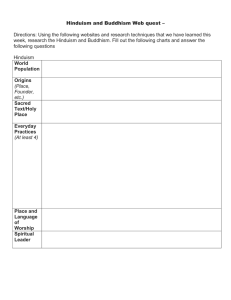
Hinduism and Buddhism Webquest
... 6. Describe what the Caste System is and fill out the following chart with the names of the levels and who they represent. ...
... 6. Describe what the Caste System is and fill out the following chart with the names of the levels and who they represent. ...
A Secular Buddhist
... reconfiguration of a traditional form of Asian Buddhism. It is neither a reformed Theravada Buddhism (like the Vipassana movement), a reformed Tibetan tradition (like Shambhala Buddhism), a reformed Nichiren school (like the Soka Gakkai), a reformed Zen lineage (like the Order of Interbeing), nor a ...
... reconfiguration of a traditional form of Asian Buddhism. It is neither a reformed Theravada Buddhism (like the Vipassana movement), a reformed Tibetan tradition (like Shambhala Buddhism), a reformed Nichiren school (like the Soka Gakkai), a reformed Zen lineage (like the Order of Interbeing), nor a ...
Right Thought
... To avoid lies, idle talk, abuse, slander, and deceit. Once our intentions are pure--attaining happiness. ...
... To avoid lies, idle talk, abuse, slander, and deceit. Once our intentions are pure--attaining happiness. ...
buddhism WHAT`S THE DIFFERENCE? REINCARNATION
... to Blow Out, extinguishing the flame. Conflict in understanding this term has led to divergent views of Buddha and Buddhism. Some Buddhist worship Buddha as a divine being other Buddhist view him as an ordinary man. Tibetan Buddhist, see the Dali Lama as the reincarnated Buddha, who was not annihila ...
... to Blow Out, extinguishing the flame. Conflict in understanding this term has led to divergent views of Buddha and Buddhism. Some Buddhist worship Buddha as a divine being other Buddhist view him as an ordinary man. Tibetan Buddhist, see the Dali Lama as the reincarnated Buddha, who was not annihila ...
Religious Experience in Buddhism
... personal discipline aiming at self-induced 'mystical' attaimnents? Might we not call it a religious atheism or, at any rate, a nontheistic religion? Naturally there is some element of truth in all these descriptions, however much they seem to contradict one another. But the real difficulty is not ou ...
... personal discipline aiming at self-induced 'mystical' attaimnents? Might we not call it a religious atheism or, at any rate, a nontheistic religion? Naturally there is some element of truth in all these descriptions, however much they seem to contradict one another. But the real difficulty is not ou ...
Buddhism
... • As he was meditating, he was able to understand the whole universe, the end of suffering, and the way to inner peace ...
... • As he was meditating, he was able to understand the whole universe, the end of suffering, and the way to inner peace ...
- Hodder Education
... Learners should be aware that Buddhism is one of a diverse range of religious traditions and beliefs in Great Britain today and that the main religious tradition in Great Britain is Christian. This knowledge may be applied throughout the assessment of the specified content. ...
... Learners should be aware that Buddhism is one of a diverse range of religious traditions and beliefs in Great Britain today and that the main religious tradition in Great Britain is Christian. This knowledge may be applied throughout the assessment of the specified content. ...
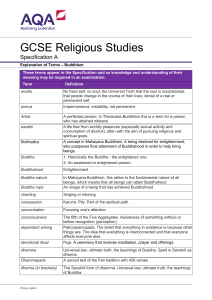
GCSE Religious Studies A Specification A - Buddhism
... Literally ‘emptiness’. In Mahayana Buddhism, it refers to the absence of an intrinsic nature (or identity) in all phenomena Craving / desire, which causes suffering. The attempt to grasp at the things we enjoy. A structure reserved for religious or spiritual activities, such as prayer. The kind of B ...
... Literally ‘emptiness’. In Mahayana Buddhism, it refers to the absence of an intrinsic nature (or identity) in all phenomena Craving / desire, which causes suffering. The attempt to grasp at the things we enjoy. A structure reserved for religious or spiritual activities, such as prayer. The kind of B ...
A Stoic Look at Buddhism - San Diego Stoics 2015-06-20
... "The Buddha's teaching, particularly his way of 'meditation', aims at producing a state of perfect mental health, equilibrium and tranquillity." It is often misunderstood as an escape, or mystical trance, or an attempt to obtain superpowers. The two forms of mediation are 1) "the development of ment ...
... "The Buddha's teaching, particularly his way of 'meditation', aims at producing a state of perfect mental health, equilibrium and tranquillity." It is often misunderstood as an escape, or mystical trance, or an attempt to obtain superpowers. The two forms of mediation are 1) "the development of ment ...
Buddhism
... Chinese takeover of Tibet in the 1950s. Tibetan Buddhist leaders were forced to flee, many ending up in India or the West. • Sogyal Rinpoche founded the Shambhala Center, which organized a publishing company, established retreat centers in Colorado and Vermont, and started Naropa University in Color ...
... Chinese takeover of Tibet in the 1950s. Tibetan Buddhist leaders were forced to flee, many ending up in India or the West. • Sogyal Rinpoche founded the Shambhala Center, which organized a publishing company, established retreat centers in Colorado and Vermont, and started Naropa University in Color ...
Zen Character Desc... - The Ecclesbourne School Online
... C.E. Lived for fifty – three years. First studied Zen under Eisai in Japan; went to China and perfected zazen methods, eventually returning and founding Soto school there. ...
... C.E. Lived for fifty – three years. First studied Zen under Eisai in Japan; went to China and perfected zazen methods, eventually returning and founding Soto school there. ...
Glossary of Terms for Siddhartha
... Advaita: non duality, identity of the spirit and matter - essentially are all 'one'. The philosophical belief that underlies the teaching in the Bhagavad Gita and Upanishads. There is only one Consciousness, one Supreme Spirit, despite multiplicity; this is the 'ultimate truth' in the text known to ...
... Advaita: non duality, identity of the spirit and matter - essentially are all 'one'. The philosophical belief that underlies the teaching in the Bhagavad Gita and Upanishads. There is only one Consciousness, one Supreme Spirit, despite multiplicity; this is the 'ultimate truth' in the text known to ...
Buddhism vocabulary - Trinity Evangelical Free Church
... used in Zen Buddhism to show the weakness of logic and reason. • Mahayana – The most popular form of Buddhism. Mahayana is prevalent in Tibet and East Asia. Mahayana Buddhists emphasize compassion (karuna) and the desire to bring all beings to enlightenment. • Maitreya – The future Buddha who will a ...
... used in Zen Buddhism to show the weakness of logic and reason. • Mahayana – The most popular form of Buddhism. Mahayana is prevalent in Tibet and East Asia. Mahayana Buddhists emphasize compassion (karuna) and the desire to bring all beings to enlightenment. • Maitreya – The future Buddha who will a ...
Roots of Hinduism and Buddhism
... were able to spread his faith over large parts of Asia. Buddhist missionaries went to Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia in the third century b.c. Buddhist ideas also traveled along Central Asian trade routes to China. CONNECT to TODAY However, Buddhism never gained a significant foothold in India, the Bu ...
... were able to spread his faith over large parts of Asia. Buddhist missionaries went to Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia in the third century b.c. Buddhist ideas also traveled along Central Asian trade routes to China. CONNECT to TODAY However, Buddhism never gained a significant foothold in India, the Bu ...
Buddhism and it`s relevance to the world situation
... people prefer to be inspired by positive qualities of Buddhist teachings such as universal love, compassion, purity, insight and wisdom. They do not respond very well to the attempts to motivate them by suffering and fear of hell. In the Western world the different schools of Buddhism are not geogra ...
... people prefer to be inspired by positive qualities of Buddhist teachings such as universal love, compassion, purity, insight and wisdom. They do not respond very well to the attempts to motivate them by suffering and fear of hell. In the Western world the different schools of Buddhism are not geogra ...
Slide 1 - pptfun
... Humans are capable to achieve the highest spiritual state Scriptures have no authority (guide) Human experience or self realization is the ultimate authority Primary Path ƒ Path of Knowledge (Jnan Yoga) ƒ Realization of unique and supreme self through knowledge ...
... Humans are capable to achieve the highest spiritual state Scriptures have no authority (guide) Human experience or self realization is the ultimate authority Primary Path ƒ Path of Knowledge (Jnan Yoga) ƒ Realization of unique and supreme self through knowledge ...
Hinduism and Buddhism
... all birth—animal, human or Godly—and seek to alleviate it through or the realization of our true nature. Yoga-Vedanta discriminates bedeveloping a higher awareness. Both emphasize the need to dissolve tween the Self, which is our true nature as consciousness, and the ego the ego, the sense of me and ...
... all birth—animal, human or Godly—and seek to alleviate it through or the realization of our true nature. Yoga-Vedanta discriminates bedeveloping a higher awareness. Both emphasize the need to dissolve tween the Self, which is our true nature as consciousness, and the ego the ego, the sense of me and ...
buddhism
... There are three principal sources of spiritual guidance recognized by Buddhists as scriptural or doctrinal authorities: Theravada Buddhism: Tripitaka — The Tripitaka is a canon of the southern schools of Buddhism written in India within 500 years of the time of the Buddha. It is divided into three s ...
... There are three principal sources of spiritual guidance recognized by Buddhists as scriptural or doctrinal authorities: Theravada Buddhism: Tripitaka — The Tripitaka is a canon of the southern schools of Buddhism written in India within 500 years of the time of the Buddha. It is divided into three s ...
IndianPhilosophyUpanishadsSP13
... unattached, for it does not attach itself; is unbound, does not tremble, is not injured.” Brhadaranyaka Upanishad, iv.v.15 ...
... unattached, for it does not attach itself; is unbound, does not tremble, is not injured.” Brhadaranyaka Upanishad, iv.v.15 ...
Great Vehicle: Mahayana Buddhism
... •However, they “became the focus of an intense scholastic movement that aspired to remove any doubt about the functional relation of any element of reality to any other element, the sutras being neither exhaustive on all points of doctrine nor written with a clear structural layout. With this in min ...
... •However, they “became the focus of an intense scholastic movement that aspired to remove any doubt about the functional relation of any element of reality to any other element, the sutras being neither exhaustive on all points of doctrine nor written with a clear structural layout. With this in min ...