Glossary of Buddhist Terms
... ‘Fetter’. The Ten Fetters tie beings to the wheel of birth and death. They are: belief in a substantial self, skeptical doubt, clinging to rules and ritual, sensual craving, ill will, craving for fine-material existence, craving for immaterial existence, conceit (mana), restlessness and ignorance. T ...
... ‘Fetter’. The Ten Fetters tie beings to the wheel of birth and death. They are: belief in a substantial self, skeptical doubt, clinging to rules and ritual, sensual craving, ill will, craving for fine-material existence, craving for immaterial existence, conceit (mana), restlessness and ignorance. T ...
Buddhism
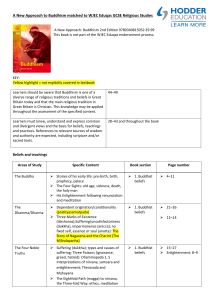
... everyone is influenced by past actions (karma). rebirth can occur in human form, animal form, as a ghost, in a blissful state or in a state of woe, although beliefs about rebirth vary. The Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path 1. The central teachings of all schools of Buddhism are based on t ...
... everyone is influenced by past actions (karma). rebirth can occur in human form, animal form, as a ghost, in a blissful state or in a state of woe, although beliefs about rebirth vary. The Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path 1. The central teachings of all schools of Buddhism are based on t ...
Understanding the Buddhist Mind
... • Within 1500 years it became a major Asian religion • Some scholars say there are 1.2 billion adherents to Buddhist teaching worldwide. • A. Theravada – conservative kind found across Southeast Asia and Sri Lanka • B. Mahayana – liberal kind is found in East Asia, Japan, and Korea. ...
... • Within 1500 years it became a major Asian religion • Some scholars say there are 1.2 billion adherents to Buddhist teaching worldwide. • A. Theravada – conservative kind found across Southeast Asia and Sri Lanka • B. Mahayana – liberal kind is found in East Asia, Japan, and Korea. ...
Buddhism - Australian Lutheran World Service
... Village Life in Cambodia—ALWS Awareness Week 2014 ...
... Village Life in Cambodia—ALWS Awareness Week 2014 ...
Buddhism
... in reincarnation, or the rebirth of the soul. They also believe in karma— the idea that the soul carries the effects of past deeds (good or bad). They do believe in something called dharma, but do not embrace the notion of the caste system. They believe people to be equal and able to achieve enlight ...
... in reincarnation, or the rebirth of the soul. They also believe in karma— the idea that the soul carries the effects of past deeds (good or bad). They do believe in something called dharma, but do not embrace the notion of the caste system. They believe people to be equal and able to achieve enlight ...
All courses are offered on a semester basis
... MBS Course List 2009-10 All courses are offered on a semester basis. Candidates must complete eight courses by selecting two compulsory foundation courses plus six elective courses, and may select to offer a dissertation in lieu of two elective courses. Foundation courses Early Buddhism Mahayana Bud ...
... MBS Course List 2009-10 All courses are offered on a semester basis. Candidates must complete eight courses by selecting two compulsory foundation courses plus six elective courses, and may select to offer a dissertation in lieu of two elective courses. Foundation courses Early Buddhism Mahayana Bud ...
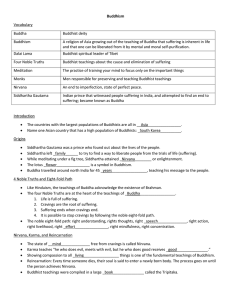
Main beliefs and practices Language Key dates and
... Catherine Chambers guides you through the basic beliefs of the six core religions. This month: Buddhism ...
... Catherine Chambers guides you through the basic beliefs of the six core religions. This month: Buddhism ...
Buddhism
... Selfhood: The "permanent identity" that the mind, in its ignorance, ascribes to things (and to itself) Atman: the soul; the core of "self" erroneously ascribed to mental activity Bodhisattva -- An enlightened being who remains in the Cycle in order to "ferry" other beings to nirvana ...
... Selfhood: The "permanent identity" that the mind, in its ignorance, ascribes to things (and to itself) Atman: the soul; the core of "self" erroneously ascribed to mental activity Bodhisattva -- An enlightened being who remains in the Cycle in order to "ferry" other beings to nirvana ...
Buddhism - RE Weobley
... However, when he saw the suffering of old age, sickness and death, he decided to renounce his life in the palace and live among the holy men of the day in search of truth and enlightenment. His search took him six years, but he became enlightened whilst meditating under a Bodhi tree. Following this ...
... However, when he saw the suffering of old age, sickness and death, he decided to renounce his life in the palace and live among the holy men of the day in search of truth and enlightenment. His search took him six years, but he became enlightened whilst meditating under a Bodhi tree. Following this ...
Buddhism - globalstudies11
... ending of avijja (ignorance) which perpetuates the will (citta/mind) from passing thru samsara life after life, which causes (and is caused by) among other things craving, consciousness, birth, death, greed, hate, delusion, ignorance. Nirvana, then, is not a place nor a state, it is an absolute trut ...
... ending of avijja (ignorance) which perpetuates the will (citta/mind) from passing thru samsara life after life, which causes (and is caused by) among other things craving, consciousness, birth, death, greed, hate, delusion, ignorance. Nirvana, then, is not a place nor a state, it is an absolute trut ...
Buddhism - Lomira School District
... the extremes of self-indulgence and self-mortification. After 49 days of meditation he achieved “bodhi” or “enlightenment” Bodhi carries the same meaning as Nirvana, an understanding of the true nature of reality. It also requires a distinction of greed, hate, and delusion. Nirvana is the unch ...
... the extremes of self-indulgence and self-mortification. After 49 days of meditation he achieved “bodhi” or “enlightenment” Bodhi carries the same meaning as Nirvana, an understanding of the true nature of reality. It also requires a distinction of greed, hate, and delusion. Nirvana is the unch ...
Ajivikas An ascetic sect that emerged in India about the same time
... on animal sacrifices and practised vegetarianism (a requirement of Mahayana texts), while Shaivites came to downgrade caste-distinctions as not relevant to religious practice. Invasion by foreign rulers like Huns, Mahmud Of Ghazni, Mongols etc. ...
... on animal sacrifices and practised vegetarianism (a requirement of Mahayana texts), while Shaivites came to downgrade caste-distinctions as not relevant to religious practice. Invasion by foreign rulers like Huns, Mahmud Of Ghazni, Mongols etc. ...
Buddhism notes
... Found in southern Asia. The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” ...
... Found in southern Asia. The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” ...
Mid-Term Review
... 1. What are the three characteristics of Saṃsāra according to the Buddha's early teachings? 2. What are the five groups of processes that constitute the self from the Buddhist point of view? 3. What are the Four Noble Truths taught by the Buddha in his first sermon and how might these truths be expl ...
... 1. What are the three characteristics of Saṃsāra according to the Buddha's early teachings? 2. What are the five groups of processes that constitute the self from the Buddhist point of view? 3. What are the Four Noble Truths taught by the Buddha in his first sermon and how might these truths be expl ...
buddhism_191-210
... less attached to things and people. Knowing their impermanence prepares us to be more free. Craving, by contrast, comes from believing that life and things are permanent. We cling to our experience and this causes, potentially, real suffering. When our girlfriend/boyfriend wants to break up with us, ...
... less attached to things and people. Knowing their impermanence prepares us to be more free. Craving, by contrast, comes from believing that life and things are permanent. We cling to our experience and this causes, potentially, real suffering. When our girlfriend/boyfriend wants to break up with us, ...
Section 3 Buddhism
... ease to find the causes of human suffering Gautama studied with Hindu philosophers (monk), but their ideas did not satisfy him He decided to stop looking outwardly for answers and tried to find understanding in his own mind by meditation. He believed he found the answer after 49 days of meditation a ...
... ease to find the causes of human suffering Gautama studied with Hindu philosophers (monk), but their ideas did not satisfy him He decided to stop looking outwardly for answers and tried to find understanding in his own mind by meditation. He believed he found the answer after 49 days of meditation a ...
- Hodder Education
... (lakshanas);Suffering/unsatisfactoriness (dukkha), impermanence (anicca); no fixed self, essence or soul (anatta): The Story of Nagasena and the Chariot (The Milindapanha) ...
... (lakshanas);Suffering/unsatisfactoriness (dukkha), impermanence (anicca); no fixed self, essence or soul (anatta): The Story of Nagasena and the Chariot (The Milindapanha) ...
Sacred Text Buddhism
... The Great Prajna Paramita Heart Sutra Avalokiteshvara Bodhisattva, practicing deep Prajna Paramita, Clearly saw that all five skandhas are empty, Transforming anguish and distress. Shariputra, form is no other than emptiness, Emptiness no other than form; Form is exactly emptiness, emptiness exactl ...
... The Great Prajna Paramita Heart Sutra Avalokiteshvara Bodhisattva, practicing deep Prajna Paramita, Clearly saw that all five skandhas are empty, Transforming anguish and distress. Shariputra, form is no other than emptiness, Emptiness no other than form; Form is exactly emptiness, emptiness exactl ...
For a Buddhist`s Death
... Believe that the purpose of life is to develop compassion for all living beings without discrimination and to work for their welfare and peace; and to develop wisdom leading to the realization of Ultimate Truth ...
... Believe that the purpose of life is to develop compassion for all living beings without discrimination and to work for their welfare and peace; and to develop wisdom leading to the realization of Ultimate Truth ...
Document
... Buddhism is one of the world’s major religions. It was founded in India about 500 B.C., or shortly afterward, by a teacher called the Buddha. At various times, Buddhism has been a dominant religious, cultural, and social force in most of Asia. Today, Buddhism has about 350 million followers. Most li ...
... Buddhism is one of the world’s major religions. It was founded in India about 500 B.C., or shortly afterward, by a teacher called the Buddha. At various times, Buddhism has been a dominant religious, cultural, and social force in most of Asia. Today, Buddhism has about 350 million followers. Most li ...
Answers
... The state of __mind______________ free from cravings is called Nirvana. Karma teaches “he who does evil, meets with evil, but he who does good receives _good_______________.” Showing compassion to all _living_________________ things is one of the fundamental teachings of Buddhism. Reincarnation: Eve ...
... The state of __mind______________ free from cravings is called Nirvana. Karma teaches “he who does evil, meets with evil, but he who does good receives _good_______________.” Showing compassion to all _living_________________ things is one of the fundamental teachings of Buddhism. Reincarnation: Eve ...