Chapter7: The Religious Development of Buddhism Chapter
... Classical Buddhism is devoid of supreme deities and its austere path to salvation involving intense self-study and a rejection of the world finds little reception among the masses. As so often occurs in religion, the followers imbued the founder with god-like attributes and this resulted in a more h ...
... Classical Buddhism is devoid of supreme deities and its austere path to salvation involving intense self-study and a rejection of the world finds little reception among the masses. As so often occurs in religion, the followers imbued the founder with god-like attributes and this resulted in a more h ...
Buddhism Presentation
... • 3) The cessation of suffering: freedom from attachment and aversion. ...
... • 3) The cessation of suffering: freedom from attachment and aversion. ...
Roots of Hinduism and Buddhism
... for release from selfishness and pain. The Buddha’s teachings included many ideas from the Hindu tradition. However, they also differed sharply from that tradition. As in Hinduism, the Buddha accepted the idea of reincarnation. He also accepted a cyclical, or repetitive, view of history, where the w ...
... for release from selfishness and pain. The Buddha’s teachings included many ideas from the Hindu tradition. However, they also differed sharply from that tradition. As in Hinduism, the Buddha accepted the idea of reincarnation. He also accepted a cyclical, or repetitive, view of history, where the w ...
Good Question - Wat Thai Melbourne
... Perhaps it is because Buddhists don't feel the need to boast about the good they do. Several years ago the Japanese Buddhist leader Nikkho Nirwano received the Templeton Prize for his work in promoting inter-religious harmony. Likewise a Thai Buddhist monk was recently awarded the prestigious Magsa ...
... Perhaps it is because Buddhists don't feel the need to boast about the good they do. Several years ago the Japanese Buddhist leader Nikkho Nirwano received the Templeton Prize for his work in promoting inter-religious harmony. Likewise a Thai Buddhist monk was recently awarded the prestigious Magsa ...
Hinduism and Buddhism Webquest
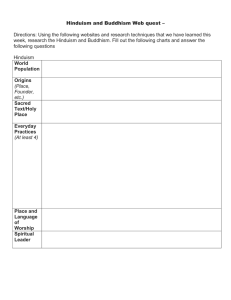
... Hinduism and Buddhism Web quest – Directions: Using the following websites and research techniques that we have learned this week, research the Hinduism and Buddhism. Fill out the following charts and answer the following questions Hinduism World Population Origins (Place, Founder, etc.) Sacred Text ...
... Hinduism and Buddhism Web quest – Directions: Using the following websites and research techniques that we have learned this week, research the Hinduism and Buddhism. Fill out the following charts and answer the following questions Hinduism World Population Origins (Place, Founder, etc.) Sacred Text ...
Buddhism in America - Sgi-Usa
... What do we mean by Buddhism? Buddhism begins with the enlightenment of a man named Siddhartha Gautama, who lived in the northeastern part of the Indian subcontinent more than five centuries before the Common Era. The term Buddha means “One who has experienced awakening” or “One who is awake.” Throu ...
... What do we mean by Buddhism? Buddhism begins with the enlightenment of a man named Siddhartha Gautama, who lived in the northeastern part of the Indian subcontinent more than five centuries before the Common Era. The term Buddha means “One who has experienced awakening” or “One who is awake.” Throu ...
buddhism - Homework Market
... floating in this sheet of paper. Without a cloud, there will be no rain; without rain, the trees cannot grow; and without trees, we cannot make paper. The cloud is essential for the paper to exist. If the cloud is not here, the sheet of paper cannot be here either. So we can say that the cloud and ...
... floating in this sheet of paper. Without a cloud, there will be no rain; without rain, the trees cannot grow; and without trees, we cannot make paper. The cloud is essential for the paper to exist. If the cloud is not here, the sheet of paper cannot be here either. So we can say that the cloud and ...
Hinduism and Buddhism Quiz Name: Which religion is based on the
... Hindus worship many gods in their own right (as gods themselves) Everyone considers Hinduism to be polytheistic The many gods of Hinduism often compete for worshipers ...
... Hindus worship many gods in their own right (as gods themselves) Everyone considers Hinduism to be polytheistic The many gods of Hinduism often compete for worshipers ...
Buddhists: Understanding Buddhism through the Lives of Practitioners
... representative of the vast majority of people who identify as Buddhists, either today or in the past. There are a number of difficulties in the conception of this volume, and Lewis is aware of them. The first is defining its scope: what is Buddhism, and who should be included within its purview? Pri ...
... representative of the vast majority of people who identify as Buddhists, either today or in the past. There are a number of difficulties in the conception of this volume, and Lewis is aware of them. The first is defining its scope: what is Buddhism, and who should be included within its purview? Pri ...
SUGGESTED UNIT OUTLINE INCLUDING TEACHING PACKS
... became Buddha make links between Buddhist stories / compare aspects of their own experiences and artefacts / religious symbols and the beliefs those of others, identifying what influences and that ‘Buddha’ means ‘awakened’ or that underlie them (L3) inspires them (L3) ‘enlightened one’ that ...
... became Buddha make links between Buddhist stories / compare aspects of their own experiences and artefacts / religious symbols and the beliefs those of others, identifying what influences and that ‘Buddha’ means ‘awakened’ or that underlie them (L3) inspires them (L3) ‘enlightened one’ that ...
Buddhism - Basic Guide
... further by providing a long term purpose within our existence, through wisdom and true understanding. Real Buddhism is very tolerant and not concerned with labels like 'Christian', Moslem','Hindu' or 'Buddhist'; that's why there have never been any wars fought in the name of Buddhism. That is also w ...
... further by providing a long term purpose within our existence, through wisdom and true understanding. Real Buddhism is very tolerant and not concerned with labels like 'Christian', Moslem','Hindu' or 'Buddhist'; that's why there have never been any wars fought in the name of Buddhism. That is also w ...
11 NonTheistic-Buddhism
... 1. Life and illumination of Gautama, the Buddha (563-483 BC) • Son of a Hindu clan ruler of Kshatriva caste in Lumbini, modern Nepal • Sheltered from harshness of life until after his marriage: he saw he could not escape sickness, old age and death. • Once exposed to reality, he abandoned his wife/ ...
... 1. Life and illumination of Gautama, the Buddha (563-483 BC) • Son of a Hindu clan ruler of Kshatriva caste in Lumbini, modern Nepal • Sheltered from harshness of life until after his marriage: he saw he could not escape sickness, old age and death. • Once exposed to reality, he abandoned his wife/ ...
mahayana buddhism - The Ecclesbourne School Online
... (prajna) without compassion (karuna) can have no motive to help others but can become centred only on one’s own enlightenment. Compassion without wisdom does not have the ability or knowledge to help others. The greatest wisdom is required not for its own sake but so that the Bodhisattva has the gre ...
... (prajna) without compassion (karuna) can have no motive to help others but can become centred only on one’s own enlightenment. Compassion without wisdom does not have the ability or knowledge to help others. The greatest wisdom is required not for its own sake but so that the Bodhisattva has the gre ...
Mandala art
... outermost circle consists of the purifying fire vajra circle: the diamond circle expresses strength and fearlessness tombs: there are eight tombs, which symbolises the eight states of consciousness*, which the person must go beyond lotus circle: expresses the open state of devotion, that is necessar ...
... outermost circle consists of the purifying fire vajra circle: the diamond circle expresses strength and fearlessness tombs: there are eight tombs, which symbolises the eight states of consciousness*, which the person must go beyond lotus circle: expresses the open state of devotion, that is necessar ...
Buddhism - University of Mount Union | Universities in Ohio
... in both Pali and Sankrit as are the writings in Hinduism and the many offshoots. Pali a language related to Sanskrit Sanskrit is called the Latin of India because of its widespread use. ...
... in both Pali and Sankrit as are the writings in Hinduism and the many offshoots. Pali a language related to Sanskrit Sanskrit is called the Latin of India because of its widespread use. ...
The Development of Buddhist Sects
... This sect relaxed some of the strict Vinaya rules of the community of monks, and in order to attract as many adherents as possible, did its utmost to instruct society in its own concepts and doctrines. With the lapse of time, there was a defection among the Mahasanghika, so that in no time it was tr ...
... This sect relaxed some of the strict Vinaya rules of the community of monks, and in order to attract as many adherents as possible, did its utmost to instruct society in its own concepts and doctrines. With the lapse of time, there was a defection among the Mahasanghika, so that in no time it was tr ...
Buddhism - and its belief that nothing is permanent, that change is
... that neither were truly beneficial, he devised what would later be ...
... that neither were truly beneficial, he devised what would later be ...
Buddhism Part 2
... to avoid improper sexual behaviour. “Buddhists should treat people with respect. The person who does not understand this can harm themselves and others. Buddhists marry and have families. Having sex with someone you are not married to is wrong. To hurt someone’s feelings or harm them sexually is wro ...
... to avoid improper sexual behaviour. “Buddhists should treat people with respect. The person who does not understand this can harm themselves and others. Buddhists marry and have families. Having sex with someone you are not married to is wrong. To hurt someone’s feelings or harm them sexually is wro ...
Rebirth Buddhism - Michael Sudduth
... unborn…the unaging…the unailing…the deathless…the sorrowless…the morally pure, unsurpassed security from bondage. The knowledge and vision arose in me: ‘My liberation is unshakable. This is the last birth. There is now no ...
... unborn…the unaging…the unailing…the deathless…the sorrowless…the morally pure, unsurpassed security from bondage. The knowledge and vision arose in me: ‘My liberation is unshakable. This is the last birth. There is now no ...
World Religions 2
... years ago by an Indian Hindu prince called Siddhartha Gautama. This man became known as the Buddha, which means ʻthe one who has gained enlightenmentʼ. He taught others about what he had discovered about life. ...
... years ago by an Indian Hindu prince called Siddhartha Gautama. This man became known as the Buddha, which means ʻthe one who has gained enlightenmentʼ. He taught others about what he had discovered about life. ...
Buddhism
... Since abortion fits all of this, the mother is killing her unborn baby. Thus, karma is now on the mother, baby, and abortionist. Hurting animals: When humans die, they are reborn through an animal. Buddhists see the connection between animals and humans. ...
... Since abortion fits all of this, the mother is killing her unborn baby. Thus, karma is now on the mother, baby, and abortionist. Hurting animals: When humans die, they are reborn through an animal. Buddhists see the connection between animals and humans. ...
File
... • To try to free one's mind from evil • To be in control of one's feelings and thoughts • To practice appropriate forms of concentration ...
... • To try to free one's mind from evil • To be in control of one's feelings and thoughts • To practice appropriate forms of concentration ...
buddhism - Distribution Access
... discipline the mind and body to go beyond desires to achieve enlightenment. ...
... discipline the mind and body to go beyond desires to achieve enlightenment. ...
Lesson Plan: The Noble Eightfold Path Introduction
... Lesson Plan: The Noble Eightfold Path Department of Museum Education Suggested Grade Level: 7-8 Estimated Time: 3 hours ...
... Lesson Plan: The Noble Eightfold Path Department of Museum Education Suggested Grade Level: 7-8 Estimated Time: 3 hours ...
Alexis Atkinson Prof. Sirpa Nelson World Religions Final Paper
... This is perhaps the most important of the noble truths because the Buddha assures that happiness can be achieved. When we don’t give in to useless cravings and temptations, when we learn how to live each day at a time, we can achieve the most desired feelings in all living beings, happiness and free ...
... This is perhaps the most important of the noble truths because the Buddha assures that happiness can be achieved. When we don’t give in to useless cravings and temptations, when we learn how to live each day at a time, we can achieve the most desired feelings in all living beings, happiness and free ...