Content Area
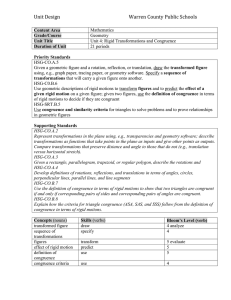
... Priority Standards HSG-CO.A.5 Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper, tracing paper, or geometry software. Specify a sequence of transformations that will carry a given figure onto another. HSG-C0.B.6 Use geometric de ...
... Priority Standards HSG-CO.A.5 Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper, tracing paper, or geometry software. Specify a sequence of transformations that will carry a given figure onto another. HSG-C0.B.6 Use geometric de ...
Final Exam: Review Packet
... 55. A right triangle has a hypotenuse of 17 cm and a height of 8 cm. Find its area and its perimeter. (Hint: find the length of the other leg first). ...
... 55. A right triangle has a hypotenuse of 17 cm and a height of 8 cm. Find its area and its perimeter. (Hint: find the length of the other leg first). ...
§5 Manifolds as topological spaces
... smooth functions on a manifold M n to separate points, then it is at least intuitively clear that there is an embedding of M n into a Euclidean space of a large dimension. So the questions about having “enough smooth functions” and about the possibility to embed a manifold into a RN are closely rela ...
... smooth functions on a manifold M n to separate points, then it is at least intuitively clear that there is an embedding of M n into a Euclidean space of a large dimension. So the questions about having “enough smooth functions” and about the possibility to embed a manifold into a RN are closely rela ...
What is Geometry? Understanding Angles
... Course: Appl. Geo. Coplanar – Points and/or lines that lie on same plane - points x and y are coplanar ...
... Course: Appl. Geo. Coplanar – Points and/or lines that lie on same plane - points x and y are coplanar ...
Review of metric spaces
... 1. Metric spaces, completeness Recall that a metric space X, d is a set X with a metric d(, ), a real-valued function such that, for x, y, z ∈ X, • (Positivity) d(x, y) ≥ 0 and d(x, y) = 0 if and only if x = y • (Symmetry) d(x, y) = d(y, x) • (Triangle inequality) d(x, z) ≤ d(x, y) + d(y, z) A metri ...
... 1. Metric spaces, completeness Recall that a metric space X, d is a set X with a metric d(, ), a real-valued function such that, for x, y, z ∈ X, • (Positivity) d(x, y) ≥ 0 and d(x, y) = 0 if and only if x = y • (Symmetry) d(x, y) = d(y, x) • (Triangle inequality) d(x, z) ≤ d(x, y) + d(y, z) A metri ...
Metrics in locally compact groups
... [2], a topological group is metrizable if and only if it is first countable. (All topological groups are understood to be To.) In this case, the metric can be taken to be left invariant. If the group is also locally compact, then the spheres with sufficiently small radii are bounded (i.e., contained ...
... [2], a topological group is metrizable if and only if it is first countable. (All topological groups are understood to be To.) In this case, the metric can be taken to be left invariant. If the group is also locally compact, then the spheres with sufficiently small radii are bounded (i.e., contained ...