Generalized Normal Bundles for Locally
... totalStiefel-Whitney class of M. Then, by a simple algebraic argument W is a unit in the cohomology ring H*(M; Z2) thereby giving rise to a unique "dual" class W such that W , W = 1. If M possesses a differential structure, then the Whitney Duality Theorem identifies W geometrically in terms of the ...
... totalStiefel-Whitney class of M. Then, by a simple algebraic argument W is a unit in the cohomology ring H*(M; Z2) thereby giving rise to a unique "dual" class W such that W , W = 1. If M possesses a differential structure, then the Whitney Duality Theorem identifies W geometrically in terms of the ...
spaces of countable and point-countable type
... type) which is not of countable type. Also see 7.4. The first two examples are known, but the third appears to be new. In fact, no space of point-countable type—not of countable type—was given in [1] or [2]. 3. Proof of Theorem 1. For the remainder of this paper, we shall usually assume that X^ßX. T ...
... type) which is not of countable type. Also see 7.4. The first two examples are known, but the third appears to be new. In fact, no space of point-countable type—not of countable type—was given in [1] or [2]. 3. Proof of Theorem 1. For the remainder of this paper, we shall usually assume that X^ßX. T ...
High School Geometry - Maury County Public Schools
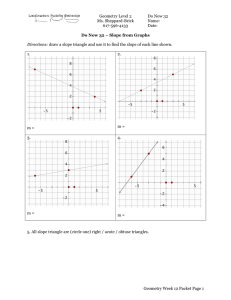
... MCC9‐12.G.C.5: Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. MCC9‐12.G.GPE.1: Derive the equation of a circ ...
... MCC9‐12.G.C.5: Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. MCC9‐12.G.GPE.1: Derive the equation of a circ ...
Handout: Rigor in Math 9-12
... area and volume formulas. Additionally, students apply their knowledge of two-dimensional shapes to consider the shapes of cross-sections and the result of rotating a two-dimensional object about a line. They reason abstractly and quantitatively to model problems using volume formulas. Module 4: Bui ...
... area and volume formulas. Additionally, students apply their knowledge of two-dimensional shapes to consider the shapes of cross-sections and the result of rotating a two-dimensional object about a line. They reason abstractly and quantitatively to model problems using volume formulas. Module 4: Bui ...
Date
... or April, draw an acute triangle. If your birthday is in May, June, July or August, draw a right triangle. If your birthday is in September, October, November or December, draw an obtuse triangle. Step 2: Write the letters a, b, and c in the interiors of the three angles of one of the triangles, and ...
... or April, draw an acute triangle. If your birthday is in May, June, July or August, draw a right triangle. If your birthday is in September, October, November or December, draw an obtuse triangle. Step 2: Write the letters a, b, and c in the interiors of the three angles of one of the triangles, and ...
Slide 1
... So far you have written proofs using direct reasoning. You began with a true hypothesis and built a logical argument to show that a conclusion was true. In an indirect proof, you begin by assuming that the conclusion is false. Then you show that this assumption leads to a contradiction. This type of ...
... So far you have written proofs using direct reasoning. You began with a true hypothesis and built a logical argument to show that a conclusion was true. In an indirect proof, you begin by assuming that the conclusion is false. Then you show that this assumption leads to a contradiction. This type of ...
Mathematics Pacing Resource Document
... Mathematics Pacing Resource Document Geometry – Triangle Strand Standard: G.T.1: Prove and apply theorems about triangles, including the following: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of ...
... Mathematics Pacing Resource Document Geometry – Triangle Strand Standard: G.T.1: Prove and apply theorems about triangles, including the following: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of ...
EXAMPLE 5 Using Deductive Reasoning to Prove a Conjecture
... SOLUTION We’ll pick a few numbers at random whose last two digits are divisible by 3, then divide them by 3, and see if there’s a remainder. ...
... SOLUTION We’ll pick a few numbers at random whose last two digits are divisible by 3, then divide them by 3, and see if there’s a remainder. ...
Section 1.1
... SOLUTION We’ll pick a few numbers at random whose last two digits are divisible by 3, then divide them by 3, and see if there’s a remainder. ...
... SOLUTION We’ll pick a few numbers at random whose last two digits are divisible by 3, then divide them by 3, and see if there’s a remainder. ...