Segment and Angle Bisectors
... Recall, the midpoint of a segment is ___________________________________ a point which divides (or bisects) the segment into two congruent segments. ___________________________________. A segment bisector is _________________ a segment, ray, line, or plane which intersects a segment at its _________ ...
... Recall, the midpoint of a segment is ___________________________________ a point which divides (or bisects) the segment into two congruent segments. ___________________________________. A segment bisector is _________________ a segment, ray, line, or plane which intersects a segment at its _________ ...
Geometry Common Core
... needed to frame a sloping roof, rendering computer graphics, or designing a sewing pattern for the most efficient use of material. Although there are many types of geometry, school mathematics is devoted primarily to plane Euclidean geometry, studied both synthetically (without coordinates) and anal ...
... needed to frame a sloping roof, rendering computer graphics, or designing a sewing pattern for the most efficient use of material. Although there are many types of geometry, school mathematics is devoted primarily to plane Euclidean geometry, studied both synthetically (without coordinates) and anal ...
Geometry Pre-AP
... Which equation describes a line that passes through (–5, –8) and is perpendicular to ...
... Which equation describes a line that passes through (–5, –8) and is perpendicular to ...
Geometry A Course
... Content Standard 2. Students will identify and describe types of triangles and their special segments. They will use logic to apply the properties of congruence, similarity, and inequalities. The students will apply the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric ratios to solve problems in real world sit ...
... Content Standard 2. Students will identify and describe types of triangles and their special segments. They will use logic to apply the properties of congruence, similarity, and inequalities. The students will apply the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric ratios to solve problems in real world sit ...
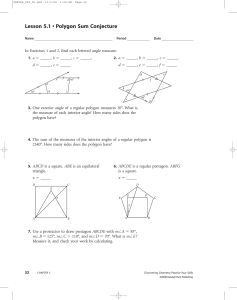
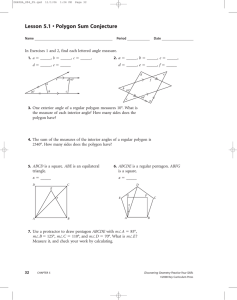
Lesson 5.1 • Polygon Sum Conjecture
... 8. _____ Opposite sides are congruent. 10. _____ Both diagonals bisect angles. ...
... 8. _____ Opposite sides are congruent. 10. _____ Both diagonals bisect angles. ...
Lecture 2
... which will be of immense use in the sequel. Let g be the inverse of f and A be closed in X then g −1 (A) = f (A) is closed in Y from which continuity of g follows. Definition 2.2 (The Lebsesgue number for a cover): Given an open covering {G α } of a metric space X, a Lebesgue number for the covering ...
... which will be of immense use in the sequel. Let g be the inverse of f and A be closed in X then g −1 (A) = f (A) is closed in Y from which continuity of g follows. Definition 2.2 (The Lebsesgue number for a cover): Given an open covering {G α } of a metric space X, a Lebesgue number for the covering ...