7.2inclassnotes - Barrington 220
... adjacent to and supplementary to an interior angle of a polygon. It is formed by extending one of the sides of the polygon to the exterior. ...
... adjacent to and supplementary to an interior angle of a polygon. It is formed by extending one of the sides of the polygon to the exterior. ...
Geometry Individual Solutions
... 4. C. The average angle is equal to the sum of all the angles divided by the number of angles. In the case of a hexagon the sum of the angles is 720° so the average is 720/6 or C. 120°. 5. B. The area of a kite is the product of the diagonals divided by 2, so the area of the kite is 72in2. The price ...
... 4. C. The average angle is equal to the sum of all the angles divided by the number of angles. In the case of a hexagon the sum of the angles is 720° so the average is 720/6 or C. 120°. 5. B. The area of a kite is the product of the diagonals divided by 2, so the area of the kite is 72in2. The price ...
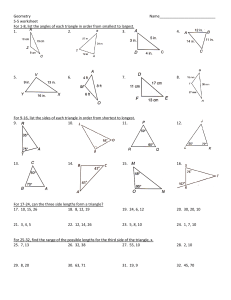
Topic 3 Test Review
... For Exercises 25-26, determine whether each of the following properties of Euclidean geometry is true in spherical geometry. 25. A line segment is the shortest distance between two points. ...
... For Exercises 25-26, determine whether each of the following properties of Euclidean geometry is true in spherical geometry. 25. A line segment is the shortest distance between two points. ...
Document
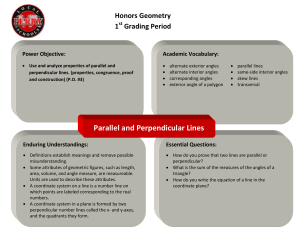
... G-GPE-5 - Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). ...
... G-GPE-5 - Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). ...