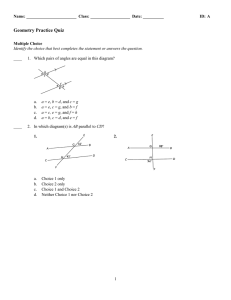
TOPIC 9-3: SIMILAR TRIANGLES
... However…if you don’t know the measures of all sides and angles, is there another way to tell? There are several theorems that allow us to show that triangles are similar. ...
... However…if you don’t know the measures of all sides and angles, is there another way to tell? There are several theorems that allow us to show that triangles are similar. ...
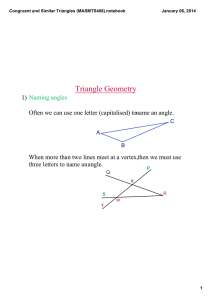
Lines and Angles
... Yes, in AOE, OC is common arm. No, they have no non-common arms on opposite side of common arm. Yes, they form linear pair. Yes, they are supplementary. Yes, they are vertically opposite angles. Vertically opposite angles of 5 is COB. ...
... Yes, in AOE, OC is common arm. No, they have no non-common arms on opposite side of common arm. Yes, they form linear pair. Yes, they are supplementary. Yes, they are vertically opposite angles. Vertically opposite angles of 5 is COB. ...
GEOM_U5_BLM_Final
... 1. Using one sheet of patty paper, copy XY and label the endpoints X’ and Y’ respectively. 2. Using a second sheet of patty paper, copy ZXY . Copy the angle only, including the sides, XZ and XY . Do not copy ZY on this paper. Label the vertex of the angle as X’ and the endpoints of the sides as Z’ ...
... 1. Using one sheet of patty paper, copy XY and label the endpoints X’ and Y’ respectively. 2. Using a second sheet of patty paper, copy ZXY . Copy the angle only, including the sides, XZ and XY . Do not copy ZY on this paper. Label the vertex of the angle as X’ and the endpoints of the sides as Z’ ...
Congruent and Similar Triangles (MASMTS408).notebook
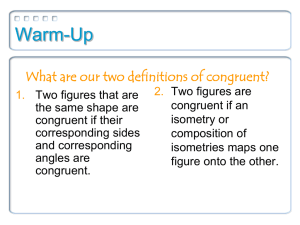
... To prove that two triangles are congruent, it is not necessary to show all six conditions. (Note: Isometric and congruent mean the same thing.) ...
... To prove that two triangles are congruent, it is not necessary to show all six conditions. (Note: Isometric and congruent mean the same thing.) ...
Honors Geometry Problem book 2013
... 1. Give an example of a point that is the same distance from (3, 0) as it is from (7, 0). Find lots of examples. Describe the configuration of all such points. In particular, how does this configuration relate to the two given points? 2. Verify that the hexagon formed by A = (0, 0), B = (2, 1), C = ...
... 1. Give an example of a point that is the same distance from (3, 0) as it is from (7, 0). Find lots of examples. Describe the configuration of all such points. In particular, how does this configuration relate to the two given points? 2. Verify that the hexagon formed by A = (0, 0), B = (2, 1), C = ...