Lines and angles - Macmillan English
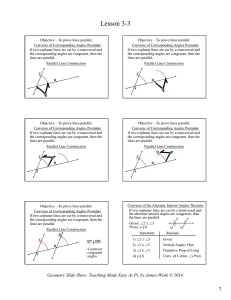
... A and B are the two end points. This line segment is 4 centimetres in length. Line segments can be measured because they have two end points. A ray is part of a line. It has one end point and the other end goes on and on forever. A ray is named with its end point first followed by any other point on ...
... A and B are the two end points. This line segment is 4 centimetres in length. Line segments can be measured because they have two end points. A ray is part of a line. It has one end point and the other end goes on and on forever. A ray is named with its end point first followed by any other point on ...
Geometric Figures
... This chapter describes how elementary students are introduced to the world of geometry. As we have seen, children first learn to measure lengths and angles and to solve arithmetic problems with measurements. By the middle of elementary school they are prepared to start studying geometry as a subject ...
... This chapter describes how elementary students are introduced to the world of geometry. As we have seen, children first learn to measure lengths and angles and to solve arithmetic problems with measurements. By the middle of elementary school they are prepared to start studying geometry as a subject ...
City of Waterbury Mathematics Department 2013 CMT Review Plan
... basic fact flash cards/timed quizzes graphs/tables/charts Students will be able to: identify place value and worth of whole numbers by more/less; expanded form, regrouping and compare magnitude. order numbers least to greatest/greatest to least. describe numbers using language: “a little m ...
... basic fact flash cards/timed quizzes graphs/tables/charts Students will be able to: identify place value and worth of whole numbers by more/less; expanded form, regrouping and compare magnitude. order numbers least to greatest/greatest to least. describe numbers using language: “a little m ...