Inscribed Angles in Circles - cK-12
... measure of its intercepted arc. You’ll also learn other inscribed angle theorems and you’ll use them to solve problems about circles. What if you had a circle with two chords that share a common endpoint? How could you use the arc formed by those chords to determine the measure of the angle those ch ...
... measure of its intercepted arc. You’ll also learn other inscribed angle theorems and you’ll use them to solve problems about circles. What if you had a circle with two chords that share a common endpoint? How could you use the arc formed by those chords to determine the measure of the angle those ch ...
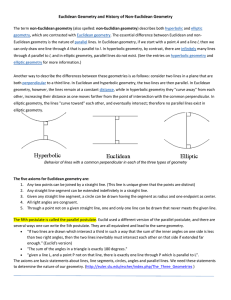
Euclidean Geometry and History of Non
... The simplest model of elliptic geometry is that of spherical geometry, where points are points on the sphere, and lines are great circles through those points. On the sphere, such as the surface of the Earth, it is easy to give an example of a triangle that requires more than 180°: For two of the si ...
... The simplest model of elliptic geometry is that of spherical geometry, where points are points on the sphere, and lines are great circles through those points. On the sphere, such as the surface of the Earth, it is easy to give an example of a triangle that requires more than 180°: For two of the si ...
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
... a. along the arc of a circle b. along the perpendicular to the line thru the point c. calculating the opposite reciprocal of the y-intercept d. constructing a circle centered at the point. 13. How many lines can be drawn through a point not on a line perpendicular to the given line? a. none b. one c ...
... a. along the arc of a circle b. along the perpendicular to the line thru the point c. calculating the opposite reciprocal of the y-intercept d. constructing a circle centered at the point. 13. How many lines can be drawn through a point not on a line perpendicular to the given line? a. none b. one c ...
January Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 A regular n
... . If a statement is true, add the corresponding value in parenthesis to . If the statement is false, subtract the corresponding value in parenthesis from . (-12) If the contrapositive statement is not true, the conditional statement is not true. (3) Converses and Inverses are not the illogical noneq ...
... . If a statement is true, add the corresponding value in parenthesis to . If the statement is false, subtract the corresponding value in parenthesis from . (-12) If the contrapositive statement is not true, the conditional statement is not true. (3) Converses and Inverses are not the illogical noneq ...
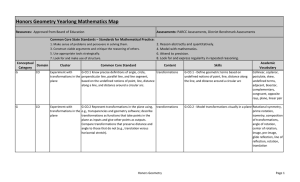
Honors Geometry Yearlong Curriculum Map
... G-GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, ...
... G-GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, ...