Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 11 – Chapter 25 sec. 4-5
... – Calculate the currents that flow in an electric circuit composed of voltage sources and resistors ...
... – Calculate the currents that flow in an electric circuit composed of voltage sources and resistors ...
In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent
... In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits with respect to Zload in the circuits below. Please write the values for the sources and equivalent impedances in phasor notation. Note that the values of the components in the circuits are impedances and are written in rectangula ...
... In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits with respect to Zload in the circuits below. Please write the values for the sources and equivalent impedances in phasor notation. Note that the values of the components in the circuits are impedances and are written in rectangula ...
GCP 557 T8 LED FAQ
... of the LED and the TM-21 calculator. This calculator is based on the Illuminating Engineering Society's TM-21-11: Projecting Long Term Lumen Maintenance of LED Light Sources. It is the industry standard in determining life span of an LED lighting source. The procedure for determining the products L7 ...
... of the LED and the TM-21 calculator. This calculator is based on the Illuminating Engineering Society's TM-21-11: Projecting Long Term Lumen Maintenance of LED Light Sources. It is the industry standard in determining life span of an LED lighting source. The procedure for determining the products L7 ...
OHM`S LAW Experiment 10
... measured in amperes. Charges flow due to a difference in electric potential or voltage between the two ends of a conductor. This is analogous to water flowing through a pipe due to the difference in pressure between the two ends of a pipe. When charges flow through any material, they experience a re ...
... measured in amperes. Charges flow due to a difference in electric potential or voltage between the two ends of a conductor. This is analogous to water flowing through a pipe due to the difference in pressure between the two ends of a pipe. When charges flow through any material, they experience a re ...
Check Your Understanding – Parallel Circuits – KEY (see highlights)
... Check Your Understanding – Parallel Circuits – KEY (see highlights) 1. As more and more resistors are added in parallel to a circuit, the equivalent resistance of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases) and the total current of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases). ...
... Check Your Understanding – Parallel Circuits – KEY (see highlights) 1. As more and more resistors are added in parallel to a circuit, the equivalent resistance of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases) and the total current of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases). ...
Electromotive Force and Potential difference
... A Voltmeter is always connected in parallel with whatever it is measuring. ...
... A Voltmeter is always connected in parallel with whatever it is measuring. ...
HID Distributor Training - Universal Lighting Technologies
... Standard ignitors are limited from some applications by the distance that they can be mounted from the lamp. ...
... Standard ignitors are limited from some applications by the distance that they can be mounted from the lamp. ...
Solid State Relais
... A Solid State Relay is actually not a relay at all. There is no 'relay' present, just the electronics which does the switching. It works the same way as a relay; you can use a low voltage to switch a higher voltage or better. This 'relay' is positioned in between one of the 115/220V AC wires althoug ...
... A Solid State Relay is actually not a relay at all. There is no 'relay' present, just the electronics which does the switching. It works the same way as a relay; you can use a low voltage to switch a higher voltage or better. This 'relay' is positioned in between one of the 115/220V AC wires althoug ...
Lab Activity: Investigating Circuits with Multiple Resistors
... Now predict V1, V2, V3, and IT for a VT of your choosing. Once the predictions are complete, set the circuit up and test using the meter. ...
... Now predict V1, V2, V3, and IT for a VT of your choosing. Once the predictions are complete, set the circuit up and test using the meter. ...
150quiz2-3 Assignment Page
... T F 4. The specific gravity of a substance is the ratio of its weight to the weight of water. T F 5. Nickel-cadmium cells are a very popular secondary cell. T F 6. Ionization of the neon in a lamp occurs between two metal electrodes inside the bulb. T F 7. A resistor’s major purposes are to control ...
... T F 4. The specific gravity of a substance is the ratio of its weight to the weight of water. T F 5. Nickel-cadmium cells are a very popular secondary cell. T F 6. Ionization of the neon in a lamp occurs between two metal electrodes inside the bulb. T F 7. A resistor’s major purposes are to control ...
AP Quiz #24 Circuits
... 3. A battery with an emf of 24 volts and an internal resistance of 1 ohm is connected to an external circuit as shown above. Determine each of the following (a) the equivalent resistance of the combination of the 4-ohm, 8-ohm, and 12-ohm resistors ...
... 3. A battery with an emf of 24 volts and an internal resistance of 1 ohm is connected to an external circuit as shown above. Determine each of the following (a) the equivalent resistance of the combination of the 4-ohm, 8-ohm, and 12-ohm resistors ...
Compare the voltage drop across resistors connected in series
... Name: _____________________________ Date: ______________________________ ...
... Name: _____________________________ Date: ______________________________ ...
Thevenin and Norton equivalents
... For any combination of simple voltages and linear resistors, you can find an equivalent circuit composed of a single voltage source and a single equivalent resistor, that will produce the same current (and voltage) through RL. (AND Vth and Rth are independent. of RL.) ...
... For any combination of simple voltages and linear resistors, you can find an equivalent circuit composed of a single voltage source and a single equivalent resistor, that will produce the same current (and voltage) through RL. (AND Vth and Rth are independent. of RL.) ...
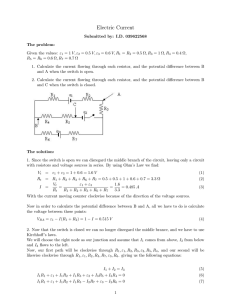
Electric Current
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.