Tender text
... - deep discharge protection with restart inhibit - automatic cut off in case of failures within the lamp circuit - intelligent charge: integrated capacity control for optimized recharge in case of partial discharge - manual function test or duration test with test button - Blocking function via CG-C ...
... - deep discharge protection with restart inhibit - automatic cut off in case of failures within the lamp circuit - intelligent charge: integrated capacity control for optimized recharge in case of partial discharge - manual function test or duration test with test button - Blocking function via CG-C ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... A series RLC circuit is given in this problem. A sinusoidal voltage source is applied to this circuit. We want to find the average power absorbed by the resistor, inductor, and capacitor. For a circuit in sinusoidal steady-state, if we know the voltage and current, the average power can be computed ...
... A series RLC circuit is given in this problem. A sinusoidal voltage source is applied to this circuit. We want to find the average power absorbed by the resistor, inductor, and capacitor. For a circuit in sinusoidal steady-state, if we know the voltage and current, the average power can be computed ...
Electric Current Test Review Sheet Name Unit The unit for power
... 4. A flashlight bulb is rated at 9.0 W. If the light bulb drops 3.0 V, how much current goes through it? ___ ___ (number and unit) 5. The current through the starter motor of a car is 120 A. If the battery maintains 10 V across the motor, how much electric energy is delivered to the starter in 10 s? ...
... 4. A flashlight bulb is rated at 9.0 W. If the light bulb drops 3.0 V, how much current goes through it? ___ ___ (number and unit) 5. The current through the starter motor of a car is 120 A. If the battery maintains 10 V across the motor, how much electric energy is delivered to the starter in 10 s? ...
Electric Current
... Your answer is correct! This circuit is called a bridge circuit. It can be used to determine the value of an unknown resistor (RX) by varying one of the other resistors until the current between the two legs is zero. You should have found that this condition requires RX to be determined totally by t ...
... Your answer is correct! This circuit is called a bridge circuit. It can be used to determine the value of an unknown resistor (RX) by varying one of the other resistors until the current between the two legs is zero. You should have found that this condition requires RX to be determined totally by t ...
EX: a) Find a symbolic expression for v3 in the circuit below using
... SOL'N: a) Because the problem says nothing about what method of solution must be used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special confi ...
... SOL'N: a) Because the problem says nothing about what method of solution must be used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special confi ...
BAŞKENT UNIVERSITY
... Fig.6 3.2 Set up the circuit in figure 6. Measure necessary V L and IL values and calculate PL values for different RL values. Put a variable resistor with a range between 0-20 kohm for RL. (Hint: convert a 3 pinned variable resitor to 2 pinned variable resitor by connecting inner pin to one of oute ...
... Fig.6 3.2 Set up the circuit in figure 6. Measure necessary V L and IL values and calculate PL values for different RL values. Put a variable resistor with a range between 0-20 kohm for RL. (Hint: convert a 3 pinned variable resitor to 2 pinned variable resitor by connecting inner pin to one of oute ...
Ohm`s Law and Kirchhoff`s Rules
... The loop rule: The algebraic sum of the voltage differences around a circuit must equal zero. Another way to put this is: The sum of the voltage rises must equal the sum of the voltage drops. As current passes through a resistor it must do work to get through the resistor material. It loses energy w ...
... The loop rule: The algebraic sum of the voltage differences around a circuit must equal zero. Another way to put this is: The sum of the voltage rises must equal the sum of the voltage drops. As current passes through a resistor it must do work to get through the resistor material. It loses energy w ...
Eco-$mart, Inc.
... light commercial buildings in the United States. Most lighting fixtures and ballasts are designed to run on at this voltage level. Hertz (Hz), or cycles per second, is a unit of frequency of electric current. 60 Hertz is the common U.S. rating. 277V 60Hz AC 277-Volt Alternating Current is a common v ...
... light commercial buildings in the United States. Most lighting fixtures and ballasts are designed to run on at this voltage level. Hertz (Hz), or cycles per second, is a unit of frequency of electric current. 60 Hertz is the common U.S. rating. 277V 60Hz AC 277-Volt Alternating Current is a common v ...
File
... important safety mechanisms in your home. Whenever electrical wiring in a building has too much current flowing through it, these simple machines cut the power until somebody can fix the problem. Without circuit breakers (or the alternative, fuses), household electricity would be impractical because ...
... important safety mechanisms in your home. Whenever electrical wiring in a building has too much current flowing through it, these simple machines cut the power until somebody can fix the problem. Without circuit breakers (or the alternative, fuses), household electricity would be impractical because ...
Sample Problem Topic: Thévenin and Norton
... Statement of Problem: Given the circuit shown in the figure below ...
... Statement of Problem: Given the circuit shown in the figure below ...
2) In the circuit in Fig. 1, using modified nodal analysis
... (Problems 2 and 3: Copyright © L.R.Linares 2009) ...
... (Problems 2 and 3: Copyright © L.R.Linares 2009) ...
June 2000 - Vicphysics
... These forces produce an initial rotation. 900 later the forces are still in the same direction, pulling the coil apart, but not making it turn. It is possible that if there is little friction in the system, then there may be some oscillation, hence B The commutator reverses the current twice every c ...
... These forces produce an initial rotation. 900 later the forces are still in the same direction, pulling the coil apart, but not making it turn. It is possible that if there is little friction in the system, then there may be some oscillation, hence B The commutator reverses the current twice every c ...
Voltage Dividers
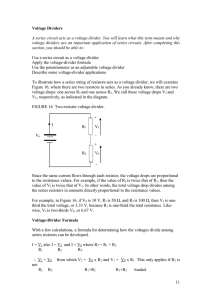
... Describe some voltage-divider applications To illustrate how a series string of resistors acts as a voltage divider, we will examine Figure 16, where there are two resistors in series. As you already know, there are two voltage drops: one across R1 and one across R2. We call these voltage drops V1 a ...
... Describe some voltage-divider applications To illustrate how a series string of resistors acts as a voltage divider, we will examine Figure 16, where there are two resistors in series. As you already know, there are two voltage drops: one across R1 and one across R2. We call these voltage drops V1 a ...
LXMG1626-12-45TrainingKit_rev1.1
... • A dedicated Pin allows the module to detect an open/shorted lamp condition • In addition when only one of the two lamps in the LCD fails open, the second lamp will continue to operate with a FAULT signal toggling to indicate the failed condition. • Perfect for Industrial/Consumer Application where ...
... • A dedicated Pin allows the module to detect an open/shorted lamp condition • In addition when only one of the two lamps in the LCD fails open, the second lamp will continue to operate with a FAULT signal toggling to indicate the failed condition. • Perfect for Industrial/Consumer Application where ...
PROBLEM SET Current, Voltage, and Resistance
... a. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 1 second? b. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 5 seconds? 2. (I) If electric current flows in only one direction it is called _____ current. Current that changes direction is called _____ current. 3. (I)In the United States alternati ...
... a. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 1 second? b. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 5 seconds? 2. (I) If electric current flows in only one direction it is called _____ current. Current that changes direction is called _____ current. 3. (I)In the United States alternati ...
solution
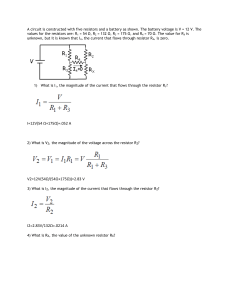
... Reading: Practical Electronics for Inventors: p 1-80, 159-164. 1) The circuit shown to the right is a “voltage divider.” a) Show that the voltage, V, from the supply splits across the two resistors according to the fraction of the total resistance R1 in each segment. In particular: V1 = V. R1 + R2 L ...
... Reading: Practical Electronics for Inventors: p 1-80, 159-164. 1) The circuit shown to the right is a “voltage divider.” a) Show that the voltage, V, from the supply splits across the two resistors according to the fraction of the total resistance R1 in each segment. In particular: V1 = V. R1 + R2 L ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm`s Law
... Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law Goals of Experiment: To gain familiarity with the ideas of voltage, current and resistance and to become familiar with the tools and equipment used in simple electrical measurements. Necessary Equipment 1. Resistors of various magnitudes 2. Digital Multimet ...
... Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law Goals of Experiment: To gain familiarity with the ideas of voltage, current and resistance and to become familiar with the tools and equipment used in simple electrical measurements. Necessary Equipment 1. Resistors of various magnitudes 2. Digital Multimet ...
Ohm’s Law
... Circuit Requirements • Circuit - complete path of conductors for electrons (closed loop) • Battery - Power Source - pushes electrons around • Something to use the current - light bulb • Switch ...
... Circuit Requirements • Circuit - complete path of conductors for electrons (closed loop) • Battery - Power Source - pushes electrons around • Something to use the current - light bulb • Switch ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law
... Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law Goals of Experiment: To gain familiarity with the ideas of voltage, current and resistance and to become familiar with the tools and equipment used in simple electrical measurements. Necessary Equipment 1. Resistors of various magnitudes 2. Digital Multimet ...
... Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law Goals of Experiment: To gain familiarity with the ideas of voltage, current and resistance and to become familiar with the tools and equipment used in simple electrical measurements. Necessary Equipment 1. Resistors of various magnitudes 2. Digital Multimet ...
Work sheet 2 fundamentals of electricity The (engineering) unit used
... Work sheet 2 fundamentals of electricity 1. The (engineering) unit used for measuring power is _________. [answer- watts or wattage] 2. In Ohm’s Law formula the letter “I” represents ______________. [answer- current] 3. Which letter is used to represent voltage in the Ohm’s Law formula? [answer- “E” ...
... Work sheet 2 fundamentals of electricity 1. The (engineering) unit used for measuring power is _________. [answer- watts or wattage] 2. In Ohm’s Law formula the letter “I” represents ______________. [answer- current] 3. Which letter is used to represent voltage in the Ohm’s Law formula? [answer- “E” ...
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.