Lab Instructions - Ohmmmmm, Ohmmmmm
... Purpose: To study the circuits formed by connecting batteries and lamps in series and in parallel and seeing how that affects Ohm’s Law Materials: two 1.5V lamps two 1.5-volt batteries ...
... Purpose: To study the circuits formed by connecting batteries and lamps in series and in parallel and seeing how that affects Ohm’s Law Materials: two 1.5V lamps two 1.5-volt batteries ...
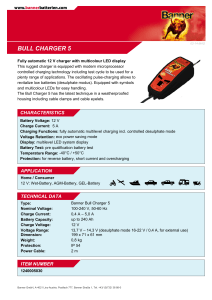
data sheet Bull Charger 5
... Fully automatic 12 V charger with multicolour LED display This rugged charger is equipped with modern microprocessor controlled charging technology including test cycle to be used for a plenty range of applications. The oscillating pulse-charging allows to revitalize low batteries (desulphate modus) ...
... Fully automatic 12 V charger with multicolour LED display This rugged charger is equipped with modern microprocessor controlled charging technology including test cycle to be used for a plenty range of applications. The oscillating pulse-charging allows to revitalize low batteries (desulphate modus) ...
numericals on current electricity
... Two resistors of same materials has been connected in series first and then in parallel. Draw a V – I graph to distinguish these connection. ...
... Two resistors of same materials has been connected in series first and then in parallel. Draw a V – I graph to distinguish these connection. ...
110V/0W = ∞A! P = VI
... For safety reason, limit the maximum voltage to be less than 12 volts for a beginner (a more relevant limitation is by the maximum power or energy). --------- Even the Ohmic law is not trivial! -----------------------------------------------------------------Make a low current voltage divider, of wh ...
... For safety reason, limit the maximum voltage to be less than 12 volts for a beginner (a more relevant limitation is by the maximum power or energy). --------- Even the Ohmic law is not trivial! -----------------------------------------------------------------Make a low current voltage divider, of wh ...
In a series circuit
... dissipated by the individual resistors or the product of the total current (It) and the source voltage (Vt). ...
... dissipated by the individual resistors or the product of the total current (It) and the source voltage (Vt). ...
P0305: Procedure For Gyroscope High Voltage To Ground Plane
... Ramp power supply to 1500 VDC in 100 V increments with a delay of ~ 30 seconds between voltage increases. Maintain 1500 VDC for > 60 minutes. After minutes, increase the DC voltage to 2000 VDC in 100 V increments. Hold the voltage at 2000 V for ~ 5 minutes, then ramp voltage down to 0 volts. Current ...
... Ramp power supply to 1500 VDC in 100 V increments with a delay of ~ 30 seconds between voltage increases. Maintain 1500 VDC for > 60 minutes. After minutes, increase the DC voltage to 2000 VDC in 100 V increments. Hold the voltage at 2000 V for ~ 5 minutes, then ramp voltage down to 0 volts. Current ...
I - R
... Ammeter -- measures current flowing in the circuit Voltmeter -- measures voltage across some device in the circuit Ammeters and voltmeters can be either analog (read out with the deflection of a needle) or digital devices. We will study how the analog devices work since they’re easier to understand ...
... Ammeter -- measures current flowing in the circuit Voltmeter -- measures voltage across some device in the circuit Ammeters and voltmeters can be either analog (read out with the deflection of a needle) or digital devices. We will study how the analog devices work since they’re easier to understand ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #6 - Due March 19
... which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ represents the large output impedance of a non-ideal voltage source, such as the element of a microph ...
... which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ represents the large output impedance of a non-ideal voltage source, such as the element of a microph ...
Which of the following are pure substances?
... D. one object will always exert a greater force on the other object. ...
... D. one object will always exert a greater force on the other object. ...
Final Presentation - ECE Senior Design
... input current, input voltage, output current, output voltage and current battery charge. ...
... input current, input voltage, output current, output voltage and current battery charge. ...
Solution Derivations for Capa #7
... current. Thus, the current through a resistor in C is the same as the current through the resistor in A. E) True. Each resistor in C has the entire voltage drop across it. However, circuit B has two equal resistors in series, so the voltage must drop across each of them. Since they are equal resista ...
... current. Thus, the current through a resistor in C is the same as the current through the resistor in A. E) True. Each resistor in C has the entire voltage drop across it. However, circuit B has two equal resistors in series, so the voltage must drop across each of them. Since they are equal resista ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... When I2 is zero, z11 can be solved by dividing V1 by I1. When I2 is zero, it means that the second port is an open circuit. We can find z21 the same way, by dividing V2 by I1. Let’s get started with the z11 parameter. When I2 is zero, that means that we have an open circuit here, so the voltage acro ...
... When I2 is zero, z11 can be solved by dividing V1 by I1. When I2 is zero, it means that the second port is an open circuit. We can find z21 the same way, by dividing V2 by I1. Let’s get started with the z11 parameter. When I2 is zero, that means that we have an open circuit here, so the voltage acro ...
Electric current
... 10. B When one light goes out, the rest stay on in a _____ circuit. 11. A When one light goes out, so do the rest in a ____ circuit. 12. C Current and resistance are inversely related. 13. A The individual resistors add up to the total resistance. 14. D Light bulbs supply current. 15. B The current ...
... 10. B When one light goes out, the rest stay on in a _____ circuit. 11. A When one light goes out, so do the rest in a ____ circuit. 12. C Current and resistance are inversely related. 13. A The individual resistors add up to the total resistance. 14. D Light bulbs supply current. 15. B The current ...
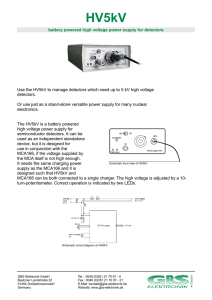
battery powered high voltage power supply for detectors Use the
... LED. In this case, reduce voltage until overload LED extinguishes and try again. In the case that the problem persists, check HV5kV without load connected; check load, and check if battery voltage is low. ...
... LED. In this case, reduce voltage until overload LED extinguishes and try again. In the case that the problem persists, check HV5kV without load connected; check load, and check if battery voltage is low. ...
Document
... negative ion Cl- . • Thus the solutions contains both positive and negative ions, both of which can conduct electricity. • Electric current can pass through dirty bath water and through you also! ...
... negative ion Cl- . • Thus the solutions contains both positive and negative ions, both of which can conduct electricity. • Electric current can pass through dirty bath water and through you also! ...
Introduction to pulse oximeters
... conditions like heart attack and asthma, sleep apnea, effectiveness of lung medications and many other applications. Though these pulse oximeters may seem compatible, they are in fact limited. In some cases, their readings can be affected by body movement, reducing accuracy as well as overhead light ...
... conditions like heart attack and asthma, sleep apnea, effectiveness of lung medications and many other applications. Though these pulse oximeters may seem compatible, they are in fact limited. In some cases, their readings can be affected by body movement, reducing accuracy as well as overhead light ...
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.