Proportion of Voltage to Resistance in a Series Circuit
... The total resistance, RTotal, of a series circuit is found by adding up the resistance values of the individual resistors. A single voltage, Vs, can be measured across each resistor. There exists a very important relationship between voltage and resistance: In a series electrical circuit with multip ...
... The total resistance, RTotal, of a series circuit is found by adding up the resistance values of the individual resistors. A single voltage, Vs, can be measured across each resistor. There exists a very important relationship between voltage and resistance: In a series electrical circuit with multip ...
Precision Current Source is Software
... Each incremental step of the digital pot increases or decreases the voltage VIN+ at the op amp's noninverting input. Thus, the pot's wiper voltage (VIN+) varies with respect to the reference voltage, which in turn remains stable with respect to the supply rail: ...
... Each incremental step of the digital pot increases or decreases the voltage VIN+ at the op amp's noninverting input. Thus, the pot's wiper voltage (VIN+) varies with respect to the reference voltage, which in turn remains stable with respect to the supply rail: ...
AC, DC and Electrical Signals - University of Toronto Physics
... Mains electricity in the UK has a frequency of 50Hz. See below for more details of signal properties. An AC supply is suitable for powering some devices such as lamps and heaters but almost all electronic circuits require a steady DC supply (see below). ...
... Mains electricity in the UK has a frequency of 50Hz. See below for more details of signal properties. An AC supply is suitable for powering some devices such as lamps and heaters but almost all electronic circuits require a steady DC supply (see below). ...
Electrical Currents
... Determining current, voltage, and resistance in series and parallel circuits ...
... Determining current, voltage, and resistance in series and parallel circuits ...
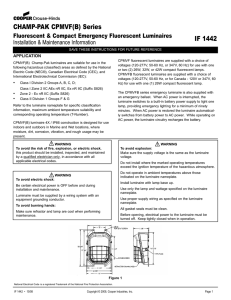
IF 1442 Revision 4
... voltages (120-277V, 50-60 Hz, or 347V, 60 Hz) for use with one or two (2) 26W, 32W, or 42W compact fluorescent lamps. CPMVFB fluorescent luminaires are supplied with a choice of voltages (120-277V, 50-60 Hz, or for Canada - 120V or 347V, 60 Hz) for use with one (1) 26W compact fluorescent lamp. The ...
... voltages (120-277V, 50-60 Hz, or 347V, 60 Hz) for use with one or two (2) 26W, 32W, or 42W compact fluorescent lamps. CPMVFB fluorescent luminaires are supplied with a choice of voltages (120-277V, 50-60 Hz, or for Canada - 120V or 347V, 60 Hz) for use with one (1) 26W compact fluorescent lamp. The ...
High Voltage Direct Current Test Procedure
... Slowly increase the voltage from 0 to 1500 volts, then to 3000 volts, and then to 4500 volts. At each step, hold for 1 minute and read the current. Record leakage current values and plot a "Leakage versus Step Voltage Curve" on a form similar to that shown in Figure 1. c) Slowly increase the voltage ...
... Slowly increase the voltage from 0 to 1500 volts, then to 3000 volts, and then to 4500 volts. At each step, hold for 1 minute and read the current. Record leakage current values and plot a "Leakage versus Step Voltage Curve" on a form similar to that shown in Figure 1. c) Slowly increase the voltage ...
cv 4-6000 e - Europower Components Ltd
... Caution, risk of electrical shock When operating the transducer, certain parts of the module can carry hazardous voltage (eg. primary busbar, power supply). Ignoring this warning can lead to injury and/or cause serious damage. This transducer is a built-in device, whose conducting parts must be inac ...
... Caution, risk of electrical shock When operating the transducer, certain parts of the module can carry hazardous voltage (eg. primary busbar, power supply). Ignoring this warning can lead to injury and/or cause serious damage. This transducer is a built-in device, whose conducting parts must be inac ...
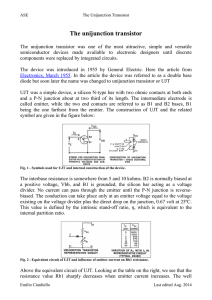
The unijunction transistor
... In the above figure we see the basic relaxation oscillator and the formulae required to calculate the value of components. Values for Rbb, η, Vp and Vv can be find on the datasheet of the unijunction device, such as for 2N4870. ...
... In the above figure we see the basic relaxation oscillator and the formulae required to calculate the value of components. Values for Rbb, η, Vp and Vv can be find on the datasheet of the unijunction device, such as for 2N4870. ...
Ch19_Circuits_parts1..
... side, a voltage drop so the voltage change is -V2. Then we go through R1 from the low V side to the high V side (since we are moving against the current flow I1): a voltage rise so the change is +I1R1. Finally, we go through R2, in the same direction as the current I2, so we have a voltage drop and ...
... side, a voltage drop so the voltage change is -V2. Then we go through R1 from the low V side to the high V side (since we are moving against the current flow I1): a voltage rise so the change is +I1R1. Finally, we go through R2, in the same direction as the current I2, so we have a voltage drop and ...
START-DET PMT-Base-H..
... The area where the wires were soldered to the PC board was also covered with conformal coating, and nothing else. The design requires that this area be further covered with silicone sealant (as in the prototype unit); however, in order to give clear access to these joints (which are most vulnerable ...
... The area where the wires were soldered to the PC board was also covered with conformal coating, and nothing else. The design requires that this area be further covered with silicone sealant (as in the prototype unit); however, in order to give clear access to these joints (which are most vulnerable ...
• - Lattice - University of Florida
... the ceramic. 5. Make sure the high voltage on the power supply is turned OFF. 6. Additonally connect the fixture to the ground terminal from the device. 7. Set the voltage limit and current limits (to just above that required for experiment) using the appropriate buttons on the power supply front pa ...
... the ceramic. 5. Make sure the high voltage on the power supply is turned OFF. 6. Additonally connect the fixture to the ground terminal from the device. 7. Set the voltage limit and current limits (to just above that required for experiment) using the appropriate buttons on the power supply front pa ...
Download T2900 Datasheet
... measures the differential current of each of the 3 phases. The differential currents are measured by connecting a current transformer for each winding in parallel with inverse polarity. The highest of the 3 currents is selected and, if it exceeds the preset level (0.04-0.4 x IN), the pick-up LED wil ...
... measures the differential current of each of the 3 phases. The differential currents are measured by connecting a current transformer for each winding in parallel with inverse polarity. The highest of the 3 currents is selected and, if it exceeds the preset level (0.04-0.4 x IN), the pick-up LED wil ...
TRANSIENT RESPONSE OF A WIND ENERGY CONVERSION
... This paper details the transient operation of a wind energy conversion system (WECS) used simultaneously as an active filter and power generator. This study is intended to address the system response to two types of transient phenomena: voltage dips (fast transients) and wind speed variations (slow ...
... This paper details the transient operation of a wind energy conversion system (WECS) used simultaneously as an active filter and power generator. This study is intended to address the system response to two types of transient phenomena: voltage dips (fast transients) and wind speed variations (slow ...
Lab Instructions - Ohmmmmm, Ohmmmmm
... Purpose: To study the circuits formed by connecting batteries and lamps in series and in parallel and seeing how that affects Ohm’s Law Materials: two 1.5V lamps two 1.5-volt batteries ...
... Purpose: To study the circuits formed by connecting batteries and lamps in series and in parallel and seeing how that affects Ohm’s Law Materials: two 1.5V lamps two 1.5-volt batteries ...
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.