Geometry Module 1, Topic G, Overview
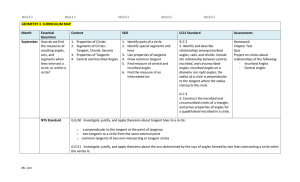
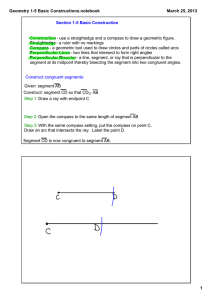
... Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including t ...
... Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including t ...
Geometry Fall 2011 Lesson 17 (S.A.S. Postulate)
... 1) Students will students will know that properties of polygons that are similar. HW # 47: Pg. 250 #’s 2-26 (Even number exercises only) Do Now 1) The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid A) are congruent b) bisect each other C) are perpendicular D) form 4 congruent angles. ...
... 1) Students will students will know that properties of polygons that are similar. HW # 47: Pg. 250 #’s 2-26 (Even number exercises only) Do Now 1) The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid A) are congruent b) bisect each other C) are perpendicular D) form 4 congruent angles. ...
Document
... Write the conditional statement and converse within the biconditional. An angle is acute iff its measure is greater than 0° and less than 90°. Let x and y represent the following. x: An angle is acute. y: An angle has a measure that is greater than 0 and less than 90. ...
... Write the conditional statement and converse within the biconditional. An angle is acute iff its measure is greater than 0° and less than 90°. Let x and y represent the following. x: An angle is acute. y: An angle has a measure that is greater than 0 and less than 90. ...
Geometry - Year 5 2017
... Polygons can be regular or irregular. Regular polygons have all sides of equal length and all angles of equal size. Irregular polygons have sides of unequal length and angles of unequal size. Sometimes we can think irregular shapes are not ‘proper’ as they look different to the more common ones. The ...
... Polygons can be regular or irregular. Regular polygons have all sides of equal length and all angles of equal size. Irregular polygons have sides of unequal length and angles of unequal size. Sometimes we can think irregular shapes are not ‘proper’ as they look different to the more common ones. The ...
6.2 Similar Triangle Theorems
... • What does it mean for figures to be similar? • Two polygons are similar if all corresponding angles are ...
... • What does it mean for figures to be similar? • Two polygons are similar if all corresponding angles are ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)