Revision for Nov Exam Part 2
... In a right-angled triangle . . . the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares on the other two sides. ...
... In a right-angled triangle . . . the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares on the other two sides. ...
Math 3329-Uniform Geometries — Lecture 07 C B A a a b b c D
... We have already mentioned the SAS criterion for the congruence of triangles several times. This states that if two sides and the included angle in one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent. It is called SAS, because t ...
... We have already mentioned the SAS criterion for the congruence of triangles several times. This states that if two sides and the included angle in one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent. It is called SAS, because t ...
Geometry Handbook - Tumwater School District
... you and hope that your year is both fun and challenging. This handbook contains almost everything you need to know about this class and my expectations. Please keep it with your math notebook at all times so that you can review classroom information regularly. Geometry is one of the most useful and ...
... you and hope that your year is both fun and challenging. This handbook contains almost everything you need to know about this class and my expectations. Please keep it with your math notebook at all times so that you can review classroom information regularly. Geometry is one of the most useful and ...
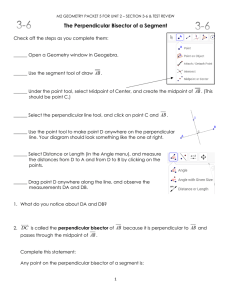
NAME - Livingston Public Schools
... 3. When drawing a circle around the vertices of a triangle, locate its _______________ ...
... 3. When drawing a circle around the vertices of a triangle, locate its _______________ ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)