GEOMETRY CHAPTER 6 PRACTICE TEST 1. Which one of the
... 10. Given: Trapezoid ABCD with midsegment EF . If AB = 16 and EF = 18 , find the length of DC . A ...
... 10. Given: Trapezoid ABCD with midsegment EF . If AB = 16 and EF = 18 , find the length of DC . A ...
Name
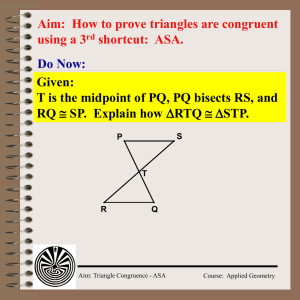
... Is it possible to prove ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF using the given information? If so, state the postulate or theorem you would use. 15. AB DE , AC DF , BC EF 16. ∠A ≅ ∠D, AB DE , BC EF 17. ∠A ≅ ∠D, ∠C ≅ ∠F, ∠B ≅ ∠E 18. ∠A ≅ ∠D, ∠C ≅ ∠F, BC EF ...
... Is it possible to prove ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF using the given information? If so, state the postulate or theorem you would use. 15. AB DE , AC DF , BC EF 16. ∠A ≅ ∠D, AB DE , BC EF 17. ∠A ≅ ∠D, ∠C ≅ ∠F, ∠B ≅ ∠E 18. ∠A ≅ ∠D, ∠C ≅ ∠F, BC EF ...
Course: Geometry- 1206310
... the historical approach taken in Geometry classes. For example, transformations are emphasized early in this course. Close attention should be paid to the introductory content for the Geometry conceptual category found in the high school standards. The Standards for Mathematical Practice apply throu ...
... the historical approach taken in Geometry classes. For example, transformations are emphasized early in this course. Close attention should be paid to the introductory content for the Geometry conceptual category found in the high school standards. The Standards for Mathematical Practice apply throu ...
Chapter 8 Notes - cloudfront.net
... point P in the plane to a point P’ so that the following properties are true: o If P is not the center point C, then the image point P’ lies on CP . The ...
... point P in the plane to a point P’ so that the following properties are true: o If P is not the center point C, then the image point P’ lies on CP . The ...
22nd-July-Bridging-the-Gap - School of Mathematical Sciences
... (courtesy of http://www.wordle.net) ...
... (courtesy of http://www.wordle.net) ...
REVISED vide circular No.63 on 22.09.2015
... monomials, binomials, trinomials. Factors and multiples. Zeros of a polynomial. Motivate and State the Remainder Theorem with examples. Statement and proof of the Factor Theorem. Factorization of ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 where a, b and c are real numbers, and of cubic polynomials using the Factor Theorem ...
... monomials, binomials, trinomials. Factors and multiples. Zeros of a polynomial. Motivate and State the Remainder Theorem with examples. Statement and proof of the Factor Theorem. Factorization of ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 where a, b and c are real numbers, and of cubic polynomials using the Factor Theorem ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)