The School District of Palm Beach County GEOMETRY REGULAR
... motions that preserve distance (S) and angle (A). • show how preserving correlating distances (S) and angles (A) between two triangles results in congruence. • use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the point (a, b) lies on a circle centered at the origin and containing the point (x, y). • use ...
... motions that preserve distance (S) and angle (A). • show how preserving correlating distances (S) and angles (A) between two triangles results in congruence. • use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the point (a, b) lies on a circle centered at the origin and containing the point (x, y). • use ...
Chapter 10
... A geometry (one of the many different geometries) came to be seen as one particular set of undefined terms and basic postulates. The postulates specify the relations between the terms. Why "undefined terms"? Euclid's definitions of "point," "line," "surface," and so on are not very clear anyway. Wha ...
... A geometry (one of the many different geometries) came to be seen as one particular set of undefined terms and basic postulates. The postulates specify the relations between the terms. Why "undefined terms"? Euclid's definitions of "point," "line," "surface," and so on are not very clear anyway. Wha ...
Pacing
... Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. G-CO.10 Prove27 ...
... Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. G-CO.10 Prove27 ...
2009-04-28 - Stony Brook Mathematics
... and 3 that come from reflections. How do we know that those are all of the symmetries? We can pick a vertex. Then, face up, we have three choices of where to put the vertex back and face down we have another three choices. What’s nice is that all 6 of these motions are generated by 1 rotation of 120 ...
... and 3 that come from reflections. How do we know that those are all of the symmetries? We can pick a vertex. Then, face up, we have three choices of where to put the vertex back and face down we have another three choices. What’s nice is that all 6 of these motions are generated by 1 rotation of 120 ...
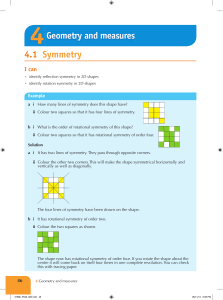
4.1 Symmetry Geometry and measures
... The shape now has rotational symmetry of order four. If you rotate the shape about the centre it will come back on itself four times in one complete revolution. You can check this with tracing paper. ...
... The shape now has rotational symmetry of order four. If you rotate the shape about the centre it will come back on itself four times in one complete revolution. You can check this with tracing paper. ...
Lesson 1-1
... probably have to review how to divide by a square root. This is a good time to tell them they should know how to give the answer as a square root and also as a decimal. ...
... probably have to review how to divide by a square root. This is a good time to tell them they should know how to give the answer as a square root and also as a decimal. ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)