Pitt County Schools
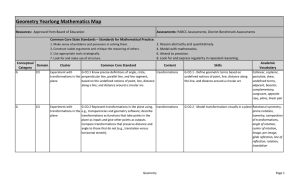
... theorems of angles and lines to solve problems and write proofs. 2.03 Apply properties, definitions, and theorems of angles and lines to solve problems and write proofs: (a) Triangles (b) Quadrilaterals (c) Other polygons Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with real numbers to solve proble ...
... theorems of angles and lines to solve problems and write proofs. 2.03 Apply properties, definitions, and theorems of angles and lines to solve problems and write proofs: (a) Triangles (b) Quadrilaterals (c) Other polygons Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with real numbers to solve proble ...
Geometry Yearlong Curriculum Map
... congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. G-CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals ...
... congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. G-CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals ...
CHAPTER 7 Similarity Theorems 1. Angle-Angle Similarity (AA~) Postulate:
... 4. Right Triangle Theorem: The altitude to the hypotenuse of a right triangle divides the triangle into two triangles that are similar to the original triangle and to each other. 5. Heartbeat Corollary ...
... 4. Right Triangle Theorem: The altitude to the hypotenuse of a right triangle divides the triangle into two triangles that are similar to the original triangle and to each other. 5. Heartbeat Corollary ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)