Lecture 19 - University of Windsor
... alloy microstructure - eutectic solids have two phases, but crystallize in a homogeneous mixture of microcrystals (microscopy, X-rays, NMR) Thermal analysis useful for detecting eutectics (this is done in the engineering department at the University of Windsor) This type of analysis is conducted by ...
... alloy microstructure - eutectic solids have two phases, but crystallize in a homogeneous mixture of microcrystals (microscopy, X-rays, NMR) Thermal analysis useful for detecting eutectics (this is done in the engineering department at the University of Windsor) This type of analysis is conducted by ...
Solids and Fluids
... Solution (details given in class): 22 N (directed downward in the diagram) ...
... Solution (details given in class): 22 N (directed downward in the diagram) ...
Examples of Colligative properties are
... The commonality in these properties is that the effects are entropy effects. Take, for example, the vapour pressure of a pure liquid versus one in which a solute has been dissolved. In the former case, the difference in entropy for the phase-change reaction is greater than that for the latter since ...
... The commonality in these properties is that the effects are entropy effects. Take, for example, the vapour pressure of a pure liquid versus one in which a solute has been dissolved. In the former case, the difference in entropy for the phase-change reaction is greater than that for the latter since ...
The No-Slip Boundary Condition in Fluid Mechanics
... cross-section. We discuss it here since it will be referred to frequently in the rest of the article and also because it was very helpful in the experimental verification of no-slip. The need for specification of the tangential velocity on the wall will be specially highlighted. For mathematical sim ...
... cross-section. We discuss it here since it will be referred to frequently in the rest of the article and also because it was very helpful in the experimental verification of no-slip. The need for specification of the tangential velocity on the wall will be specially highlighted. For mathematical sim ...
Intermolecular forces liquids and Solids
... – Dipole-dipole force: attractive force between polar molecules with positive end of one molecule is aligned with negative side of other. – London dispersion Forces: interactions between instantaneously formed electric dipoles on neighboring polar or nonpolar molecules. – Polarizability: ease with w ...
... – Dipole-dipole force: attractive force between polar molecules with positive end of one molecule is aligned with negative side of other. – London dispersion Forces: interactions between instantaneously formed electric dipoles on neighboring polar or nonpolar molecules. – Polarizability: ease with w ...
Chapter 6 - Department of Chemical Engineering
... attraction which must be overcome in vaporization. These potential energies are determined by the intermolecular attractive forces. Thus, if a substance has high intermolecular attractive forces, the rate of loss of molecules from its surface becomes small and the corresponding equilibrium vapor ...
... attraction which must be overcome in vaporization. These potential energies are determined by the intermolecular attractive forces. Thus, if a substance has high intermolecular attractive forces, the rate of loss of molecules from its surface becomes small and the corresponding equilibrium vapor ...
High temperature superconductors are the materials with T c value
... The central concept of low temperature superconduction is the existence of ‘cooper pair’ i.e., a pair of electrons that exist on account of the two electron’s indirect interaction via the nuclei of the atoms in the lattice .This pairing is caused by an attractive force between electrons from the exc ...
... The central concept of low temperature superconduction is the existence of ‘cooper pair’ i.e., a pair of electrons that exist on account of the two electron’s indirect interaction via the nuclei of the atoms in the lattice .This pairing is caused by an attractive force between electrons from the exc ...
10 Vapor Pressure - Blue Valley Schools
... place. Do not attach the tube or Pressure Sensor. Pour ~10 mL of the liquid to be investigated into the flask. Insert the rubber-stopper assembly into the flask. Important: Twist the stopper into the neck of the flask to ensure a tight fit. 4. Prepare the computer for data collection. You will be us ...
... place. Do not attach the tube or Pressure Sensor. Pour ~10 mL of the liquid to be investigated into the flask. Insert the rubber-stopper assembly into the flask. Important: Twist the stopper into the neck of the flask to ensure a tight fit. 4. Prepare the computer for data collection. You will be us ...
CHEMISTRY 313 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I Additional Problems for
... III.9. A saturated solution of Na2 SO4 with excess of the solid is present at equilibrium with its vapor in a closed vessel. (a) How many phases and components are present. (b) What is the variance of the system? Identify the independent variables. III.10. Suppose that the solution referred to in P ...
... III.9. A saturated solution of Na2 SO4 with excess of the solid is present at equilibrium with its vapor in a closed vessel. (a) How many phases and components are present. (b) What is the variance of the system? Identify the independent variables. III.10. Suppose that the solution referred to in P ...
Spin-liquids
... ■ Models are not crazy but contrived. It remains a huge challenge to find these phases in the lab – and develop theoretical techniques to look for them in realistic models. ...
... ■ Models are not crazy but contrived. It remains a huge challenge to find these phases in the lab – and develop theoretical techniques to look for them in realistic models. ...
9.7 - iupac
... Volume of the component divided by its amount of substance, Vm,B = V/nB. Moment of inertia (of a body about n axis) (I; kg m2) Sum (or integral) of the products of the mass elements of a body and the squares of their respective distances from the axis I=Σmiri2. Number concentration (of component B) ...
... Volume of the component divided by its amount of substance, Vm,B = V/nB. Moment of inertia (of a body about n axis) (I; kg m2) Sum (or integral) of the products of the mass elements of a body and the squares of their respective distances from the axis I=Σmiri2. Number concentration (of component B) ...
review/theory of separation (mass transfer) unit-ops
... Purpose: Separate components based on volatility Method: Selective evaporation and condensation Types: Batch & continuous ...
... Purpose: Separate components based on volatility Method: Selective evaporation and condensation Types: Batch & continuous ...
MHD problems in free liquid surfaces as plasma
... fusion devices has been considered since the very early stages of the tokamak reactor design concepts. The LM divertor/first-wall concept assumes that heat and particle fluxes (D, T, He, and ...
... fusion devices has been considered since the very early stages of the tokamak reactor design concepts. The LM divertor/first-wall concept assumes that heat and particle fluxes (D, T, He, and ...
Introduction to even-denominator FQHE: composite fermions
... • Challenge: solve Schrodinger’s equation ...
... • Challenge: solve Schrodinger’s equation ...
Introduction to even-denominator FQHE: composite fermions
... • Challenge: solve Schrodinger’s equation ...
... • Challenge: solve Schrodinger’s equation ...
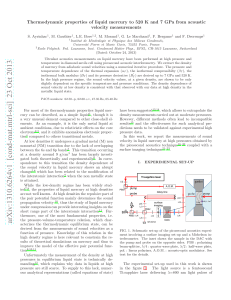
Thermodynamic properties of liquid mercury to 520 K and 7 GPa
... For most of its thermodynamic properties liquid mercury can be described, as a simple liquid1 , though it is a very unusual element compared to other close-shell elements. As an example, it is the only metal liquid at ambient conditions, due to relativistic effects on the core electrons2,3 , and it ...
... For most of its thermodynamic properties liquid mercury can be described, as a simple liquid1 , though it is a very unusual element compared to other close-shell elements. As an example, it is the only metal liquid at ambient conditions, due to relativistic effects on the core electrons2,3 , and it ...
PowerPoint - Subir Sachdev
... Avoided level crossing which becomes sharp in the infinite volume limit: second-order transition ...
... Avoided level crossing which becomes sharp in the infinite volume limit: second-order transition ...
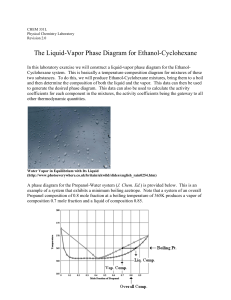
The Liquid-Vapor Phase Diagram for Ethanol
... between the Claissen Head and the distilling flask. To expedite reaching a steady state with mixtures, flush out the distillate collected in the Claissen Head several times by inserting a disposable pipet with a squeeze bulb attached and forcing Air through it. After a steady temperature has been re ...
... between the Claissen Head and the distilling flask. To expedite reaching a steady state with mixtures, flush out the distillate collected in the Claissen Head several times by inserting a disposable pipet with a squeeze bulb attached and forcing Air through it. After a steady temperature has been re ...
Characteristisation of a recirculating flow using ultrasonic Doppler velocimetry
... Duo to fringe effect, the fluctuation near the right sidewall seems stronger, but we have not observed the ideal symmetrical situation on the left side, it may cause the registered signal of UDV. The turbulence kinetic energy k computed according to Equ.(1~3). DFT analysis indicates that the energy ...
... Duo to fringe effect, the fluctuation near the right sidewall seems stronger, but we have not observed the ideal symmetrical situation on the left side, it may cause the registered signal of UDV. The turbulence kinetic energy k computed according to Equ.(1~3). DFT analysis indicates that the energy ...
In Praise of Entropy Gary D. Patterson Professor of Chemistry
... divided by the melting temperature). Liquids are more disordered than crystalline solids, but does this mean that liquids are evil?! If there were no liquids, there would be no life as we know it. Biological life requires temperatures high enough to produce liquid water, but low enough to avoid boil ...
... divided by the melting temperature). Liquids are more disordered than crystalline solids, but does this mean that liquids are evil?! If there were no liquids, there would be no life as we know it. Biological life requires temperatures high enough to produce liquid water, but low enough to avoid boil ...
Monday, Nov. 19, 2012 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... Fritz London claimed (1938) that liquid helium below the lambda point is a mixture of superfluid and normal fluid. As the temperature approaches absolute zero, the superfluid approaches 100% superfluid. ...
... Fritz London claimed (1938) that liquid helium below the lambda point is a mixture of superfluid and normal fluid. As the temperature approaches absolute zero, the superfluid approaches 100% superfluid. ...
LECTURE 10 Free Energy and Entropy Bose condensation is a
... where the exchange constant J > 0. The paramagnet has the symmetry of the Hamiltonian. In other words if you rotate all the spins in a paramagnet by the same amount, the paramagnet will look the same. But if you rotate an antiferromagnet by an arbitrary angle, it looks different. So the antiferromag ...
... where the exchange constant J > 0. The paramagnet has the symmetry of the Hamiltonian. In other words if you rotate all the spins in a paramagnet by the same amount, the paramagnet will look the same. But if you rotate an antiferromagnet by an arbitrary angle, it looks different. So the antiferromag ...
Chemistry in Focus: Tiny Thermometers
... trying to make tiny (nanoscale) gallium nitride wires. However, when they examined the results of their experiment, they discovered tiny tubes of carbon atoms that were filled with elemental gallium. Because gallium is a liquid over an unusually large temperature range, it makes a perfect working li ...
... trying to make tiny (nanoscale) gallium nitride wires. However, when they examined the results of their experiment, they discovered tiny tubes of carbon atoms that were filled with elemental gallium. Because gallium is a liquid over an unusually large temperature range, it makes a perfect working li ...
Superfluid helium-4
A superfluid is a state of matter in which the matter behaves like a fluid with zero viscosity and zero entropy. The substance, which looks like a normal liquid, will flow without friction past any surface, which allows it to continue to circulate over obstructions and through pores in containers which hold it, subject only to its own inertia.Known as a major facet in the study of quantum hydrodynamics and macroscopic quantum phenomena, the superfluidity effect was discovered by Pyotr Kapitsa and John F. Allen, and Don Misener in 1937. It has since been described through phenomenological and microscopic theories. The formation of the superfluid is known to be related to the formation of a Bose–Einstein condensate. This is made obvious by the fact that superfluidity occurs in liquid helium-4 at far higher temperatures than it does in helium-3. Each atom of helium-4 is a boson particle, by virtue of its zero spin. Helium-3, however, is a fermion particle, which can form bosons only by pairing with itself at much lower temperatures, in a process similar to the electron pairing in superconductivity.In the 1950s, Hall and Vinen performed experiments establishing the existence of quantized vortex lines in superfluid helium. In the 1960s, Rayfield and Reif established the existence of quantized vortex rings. Packard has observed the intersection of vortex lines with the free surface of the fluid, and Avenel and Varoquaux have studied the Josephson effect in superfluid helium-4. In 2006 a group at the University of Maryland visualized quantized vortices by using small tracer particles of solid hydrogen.