20071008133014301
... What if our theories are wrong and there is no higgs? Without the higgs our theory of WW interactions predicts scattering cross sections greater than one… there must be something there… What could it be? – extra space-time dimensions - a bigger gauge symmetry SU(2)xSU(2)x… - something new… ...
... What if our theories are wrong and there is no higgs? Without the higgs our theory of WW interactions predicts scattering cross sections greater than one… there must be something there… What could it be? – extra space-time dimensions - a bigger gauge symmetry SU(2)xSU(2)x… - something new… ...
ERC-focus (English)
... constitute a family of elementary particles from which the known matter in the universe is built. The neutrino plays a role in the so-called weak decay of particles through the exchange of yet another set of force particles, which have large masses coming from the Higgs field. The recent likely disc ...
... constitute a family of elementary particles from which the known matter in the universe is built. The neutrino plays a role in the so-called weak decay of particles through the exchange of yet another set of force particles, which have large masses coming from the Higgs field. The recent likely disc ...
Strangeness production in Heavy Ion Collisions
... This means that strange antiquarks are most likely to combine with a light quark to form a K+ or Ko while strange quarks are more likely to combine with light quarks to form a hyperon. ...
... This means that strange antiquarks are most likely to combine with a light quark to form a K+ or Ko while strange quarks are more likely to combine with light quarks to form a hyperon. ...
New state of matter created at CERN
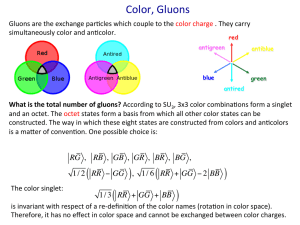
... is specified by the amounts of each of these basic colours. Just as charge can be positive or negative, every colour has its anti-colour. The strong interactions, not exhibited by leptons, are due to the exchange of colour charge through vector bosons, called gluons. QCD describes2 the theory of int ...
... is specified by the amounts of each of these basic colours. Just as charge can be positive or negative, every colour has its anti-colour. The strong interactions, not exhibited by leptons, are due to the exchange of colour charge through vector bosons, called gluons. QCD describes2 the theory of int ...
+1/2
... Eg. A 1GeV electron has a wavelength (1.23 fm) about the same as the diameter of a nucleon. ( note:- for ET >> mc2 , l = l photon with same ET ) ...
... Eg. A 1GeV electron has a wavelength (1.23 fm) about the same as the diameter of a nucleon. ( note:- for ET >> mc2 , l = l photon with same ET ) ...
Particles, Fields and Computers
... Models of nuclear structure were developed by assuming the existence of some type of interaction between the nucleons which could hold them together against electrostatic repulsion. ...
... Models of nuclear structure were developed by assuming the existence of some type of interaction between the nucleons which could hold them together against electrostatic repulsion. ...
PPTX
... either and the result wouldn’t matter • Otherwise you do this: if the gluon is hard, include it into the hard scatter, if it’s soft - you can’t do perturbative calculatiuon • You have no choice but pushing it into the fragmentation part and hope someone else knows how to calculate it ...
... either and the result wouldn’t matter • Otherwise you do this: if the gluon is hard, include it into the hard scatter, if it’s soft - you can’t do perturbative calculatiuon • You have no choice but pushing it into the fragmentation part and hope someone else knows how to calculate it ...
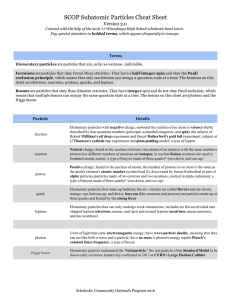
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
... exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are electrons, neutrons, protons, quarks, and leptons. Bosons are particles that obey BoseEinstein statistics. T ...
... exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are electrons, neutrons, protons, quarks, and leptons. Bosons are particles that obey BoseEinstein statistics. T ...
THINGSYOUNEEDTOKNOW-modern
... Because photon is light and must travel at c. The sum of all mass + energy is conserved in the universe. The sum of all charge is conserved in the universe. Conservation means all BEFORE = all AFTER Know the RRT Standard Model section Protons are baryons made of u-u-d quarks Neutrons are baryons mad ...
... Because photon is light and must travel at c. The sum of all mass + energy is conserved in the universe. The sum of all charge is conserved in the universe. Conservation means all BEFORE = all AFTER Know the RRT Standard Model section Protons are baryons made of u-u-d quarks Neutrons are baryons mad ...
Physics 535 lecture notes: - 3 Sep 11th, 2007 Don`t forget homework
... A milestone toward the standard model was the Z particle. A third quanta of the weak force. This particle was neutral and had similar interactions to the electromagnetic force such as e+e- -> Z -> e+e-. However it took a long time to find this particle since no one expected it! Later it was seen tha ...
... A milestone toward the standard model was the Z particle. A third quanta of the weak force. This particle was neutral and had similar interactions to the electromagnetic force such as e+e- -> Z -> e+e-. However it took a long time to find this particle since no one expected it! Later it was seen tha ...
14. Elementary Particles
... to explain some additional discrepancies in the lifetimes of some of the known particles. A new quantum number called charm C was introduced so that the new quark would have C = +1 while its anti-quark would have C = −1 and particles without the charmed quark have C = 0. Charm is similar to strangen ...
... to explain some additional discrepancies in the lifetimes of some of the known particles. A new quantum number called charm C was introduced so that the new quark would have C = +1 while its anti-quark would have C = −1 and particles without the charmed quark have C = 0. Charm is similar to strangen ...
The Quark & Bag Models
... • Another quark was needed to account for some discrepancies between predictions of the model and experimental results • Charm would be conserved in strong and electromagnetic interactions, but not in weak ...
... • Another quark was needed to account for some discrepancies between predictions of the model and experimental results • Charm would be conserved in strong and electromagnetic interactions, but not in weak ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter J3
... there is a strange quark on the left hand side of the decay but none on the right hand side. If this were a strong interaction process (or electromagnetic) the lifetime would be very short (less than about 10 20 s ). However, the decay of the lambda has a much larger lifetime (of order 10 10 s ). ...
... there is a strange quark on the left hand side of the decay but none on the right hand side. If this were a strong interaction process (or electromagnetic) the lifetime would be very short (less than about 10 20 s ). However, the decay of the lambda has a much larger lifetime (of order 10 10 s ). ...
A modern view of forces - HEP Educational Outreach
... • Theories we teach about have proven to be predictive, and therefore we believe them… but they are still falsifiable. Even Deeper Theory ...
... • Theories we teach about have proven to be predictive, and therefore we believe them… but they are still falsifiable. Even Deeper Theory ...
STEM Fair Introduction Beanium Isotopes Lab
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
16_04_2013 - IB Phys.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • The strong nuclear force is the mediator in the atom which keeps the protons and neutrons together. • Gluon exchange is the mechanism that keeps the subatomic particles inside the proton and neutrons ‘glued’ together. • The result of this exchange to the strong nuclear force is that the internal p ...
... • The strong nuclear force is the mediator in the atom which keeps the protons and neutrons together. • Gluon exchange is the mechanism that keeps the subatomic particles inside the proton and neutrons ‘glued’ together. • The result of this exchange to the strong nuclear force is that the internal p ...
Parts of an atoms - Mr-Durands
... team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton collisions performed shows a presence of a sixth quark. ...
... team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton collisions performed shows a presence of a sixth quark. ...
Chapter 17 PowerPoint
... Standard Model Summary: • All matter composed of 12 fundamental particles and their antiparticles …….. • electromagnetic force and weak nuclear force are different aspects of the same force • electromagnetic and nuclear forces mediated by virtual particles called bosons ...
... Standard Model Summary: • All matter composed of 12 fundamental particles and their antiparticles …….. • electromagnetic force and weak nuclear force are different aspects of the same force • electromagnetic and nuclear forces mediated by virtual particles called bosons ...
Standard Model
... thought of as a much heavier version of the electron. Due to their greater mass, muons are not as sharply accelerated when they encounter electromagnetic fields, and do not emit as much radiation. The muon was the first elementary particle discovered that does not appear in ordinary atoms. Muons can ...
... thought of as a much heavier version of the electron. Due to their greater mass, muons are not as sharply accelerated when they encounter electromagnetic fields, and do not emit as much radiation. The muon was the first elementary particle discovered that does not appear in ordinary atoms. Muons can ...
$doc.title
... In 1968, deep inelas5c sca7ering experiments at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center showed that the proton contained much smaller, point-‐like objects and was therefore not an elementary par1cle ...
... In 1968, deep inelas5c sca7ering experiments at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center showed that the proton contained much smaller, point-‐like objects and was therefore not an elementary par1cle ...
Quark
A quark (/ˈkwɔrk/ or /ˈkwɑrk/) is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. Due to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never directly observed or found in isolation; they can be found only within hadrons, such as baryons (of which protons and neutrons are examples), and mesons. For this reason, much of what is known about quarks has been drawn from observations of the hadrons themselves.Quarks have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, mass, color charge and spin. Quarks are the only elementary particles in the Standard Model of particle physics to experience all four fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces (electromagnetism, gravitation, strong interaction, and weak interaction), as well as the only known particles whose electric charges are not integer multiples of the elementary charge.There are six types of quarks, known as flavors: up, down, strange, charm, top, and bottom. Up and down quarks have the lowest masses of all quarks. The heavier quarks rapidly change into up and down quarks through a process of particle decay: the transformation from a higher mass state to a lower mass state. Because of this, up and down quarks are generally stable and the most common in the universe, whereas strange, charm, bottom, and top quarks can only be produced in high energy collisions (such as those involving cosmic rays and in particle accelerators). For every quark flavor there is a corresponding type of antiparticle, known as an antiquark, that differs from the quark only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign.The quark model was independently proposed by physicists Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig in 1964. Quarks were introduced as parts of an ordering scheme for hadrons, and there was little evidence for their physical existence until deep inelastic scattering experiments at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center in 1968. Accelerator experiments have provided evidence for all six flavors. The top quark was the last to be discovered at Fermilab in 1995.