An Overview of the Muscle Cell Cytoskeleton
... observations that the banding patterns of adjacent myofibrils are usually aligned in the muscle cell. Extraction of muscle with high salt solutions removes most of the contractile proteins, but an intricate system of filamentous material remains which can be observed by electron microscopy (Wang and ...
... observations that the banding patterns of adjacent myofibrils are usually aligned in the muscle cell. Extraction of muscle with high salt solutions removes most of the contractile proteins, but an intricate system of filamentous material remains which can be observed by electron microscopy (Wang and ...
Regulation of glycolysis ang glycogen metabolism
... Regulation of Glycolysis Reaction 1 – The amount of glucose entering the glycolysis pathway decreases when high levels of glucose-6phosphate are present in the cell. Reaction 3 – The enzyme here is inhibited by high levels of ATP (when ATP is plentiful) and activated by high levels of ADP and AMP (t ...
... Regulation of Glycolysis Reaction 1 – The amount of glucose entering the glycolysis pathway decreases when high levels of glucose-6phosphate are present in the cell. Reaction 3 – The enzyme here is inhibited by high levels of ATP (when ATP is plentiful) and activated by high levels of ADP and AMP (t ...
Biology placement flyer and study guide
... Enzymes and Membranes • Review the general structure and function of enzymes • Be able to describe temperature and pH affects on enzyme activity • Be able to identify the substrate, enzyme and products of a reaction • Describe the structure of a cell membrane • Review membrane transport mechanisms, ...
... Enzymes and Membranes • Review the general structure and function of enzymes • Be able to describe temperature and pH affects on enzyme activity • Be able to identify the substrate, enzyme and products of a reaction • Describe the structure of a cell membrane • Review membrane transport mechanisms, ...
Bio-engineered and native red blood cells from cord blood exhibit
... Krebs cycle that takes place in mitochondria, that are still present in young reticulocytes.12 These decreased concentrations might be the consequence of a high glucose concentration in the culture media, driving efficient ATP synthesis through glycolysis rather than the Krebs cycle in cRets compare ...
... Krebs cycle that takes place in mitochondria, that are still present in young reticulocytes.12 These decreased concentrations might be the consequence of a high glucose concentration in the culture media, driving efficient ATP synthesis through glycolysis rather than the Krebs cycle in cRets compare ...
Caloric value
... 4. Contractile – movement (muscles) 5. Enzymatic – speed up chem. reactions (saliva) ...
... 4. Contractile – movement (muscles) 5. Enzymatic – speed up chem. reactions (saliva) ...
Cells Are Classified by Internal Organization Cell Structure Reflects
... to an area of higher concentration. ...
... to an area of higher concentration. ...
•Deposition of unique membrane/cell wall material at rhizoid end
... apical/basal defects, do not recover at 32-cell stage, and end up looking like gnom •Functional redundancy amongst PIN genes •gnom defects are explained by improper localization of ALL PIN proteins ...
... apical/basal defects, do not recover at 32-cell stage, and end up looking like gnom •Functional redundancy amongst PIN genes •gnom defects are explained by improper localization of ALL PIN proteins ...
File
... Answer: Even though water is polar and so highly insoluble in the membrane lipids, it readily passes through the cell membrane for 2 reasons: 1. Water molecules are small enough to move through the monetary spaces created between the phospholipid molecules’ tails as they sway and move within the lip ...
... Answer: Even though water is polar and so highly insoluble in the membrane lipids, it readily passes through the cell membrane for 2 reasons: 1. Water molecules are small enough to move through the monetary spaces created between the phospholipid molecules’ tails as they sway and move within the lip ...
Full version (PDF file)
... et al. 2008). Among these isoforms, recombinant human neuregulin-1 (rhNRG-1, a component of NRG-1) is a 61-amino-acid peptide containing an EGF-like domain, the domain which is necessary for ErbB2/ErbB4 activation. The authors of this study previously reported that rhNRG-1 is capable of improving ca ...
... et al. 2008). Among these isoforms, recombinant human neuregulin-1 (rhNRG-1, a component of NRG-1) is a 61-amino-acid peptide containing an EGF-like domain, the domain which is necessary for ErbB2/ErbB4 activation. The authors of this study previously reported that rhNRG-1 is capable of improving ca ...
Osmolarity and Tonic..
... Hyperglycaemia in untreated diabetics results in ECF which is both hyperosmolar and hypertonic (as compared to the normal situation) as glucose cannot easily enter cells in these circumstances. Water moves out of the cells until the osmolar gradient is abolished. In some situations, a more operatio ...
... Hyperglycaemia in untreated diabetics results in ECF which is both hyperosmolar and hypertonic (as compared to the normal situation) as glucose cannot easily enter cells in these circumstances. Water moves out of the cells until the osmolar gradient is abolished. In some situations, a more operatio ...
Survival Mechanisms of Extremophiles
... iceberg. Most microorganisms existing in nature, particularly bacteria have yet to be identified. There is very little known to the current microbiologists on how to grow wide variety of microorganisms. In the sense of unknown growth medium for most microbial life, metagenomics have been considered t ...
... iceberg. Most microorganisms existing in nature, particularly bacteria have yet to be identified. There is very little known to the current microbiologists on how to grow wide variety of microorganisms. In the sense of unknown growth medium for most microbial life, metagenomics have been considered t ...
Microfilaments Intermediate filaments
... Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules They support cell shape and fix organelles in place Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes ...
... Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules They support cell shape and fix organelles in place Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes ...
The molecular basis for selective assembly of the UBAP1
... domain (amino acids 17–63) (Agromayor et al., 2012; de Souza and Aravind, 2010; Stefani et al., 2011). Although we failed to express UBAP1(1-63)–strep (data not shown) a slightly longer Nterminal fragment, UBAP1(1-95)–strep, that incorporates an additional predicted a-helix (Fig. 2B), could be gener ...
... domain (amino acids 17–63) (Agromayor et al., 2012; de Souza and Aravind, 2010; Stefani et al., 2011). Although we failed to express UBAP1(1-63)–strep (data not shown) a slightly longer Nterminal fragment, UBAP1(1-95)–strep, that incorporates an additional predicted a-helix (Fig. 2B), could be gener ...
On the Interaction of Adherent Cells with Thermoresponsive
... thermoresponsive polymers have become popular for providing versatile solutions to this problem. These polymers show a transition at a lower critical solution temperature (LCST): above the LCST, they facilitate cell adhesion, while below the LCST, cells cannot adhere [1–6]. This functional feature c ...
... thermoresponsive polymers have become popular for providing versatile solutions to this problem. These polymers show a transition at a lower critical solution temperature (LCST): above the LCST, they facilitate cell adhesion, while below the LCST, cells cannot adhere [1–6]. This functional feature c ...
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
... 25) Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein disposal from prokaryotic cells? A) Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to excrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system. B) The mechanism of protein excretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in ...
... 25) Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein disposal from prokaryotic cells? A) Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to excrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system. B) The mechanism of protein excretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in ...
Four common polysaccharides found in nature are starch
... Cellulose is a major component of tough cell walls that surround plant cells, and is what makes plant stems, leaves, and branches so strong. Next time you eat a salad, think about how much you have to chew it in order to be able to swallow all that plant material. It certainly takes a lot of work, a ...
... Cellulose is a major component of tough cell walls that surround plant cells, and is what makes plant stems, leaves, and branches so strong. Next time you eat a salad, think about how much you have to chew it in order to be able to swallow all that plant material. It certainly takes a lot of work, a ...
Regulatory assembly of the vacuolar proton pump VOV1
... to monitor the variable subunit composition of VOV1-ATPase parts. VOV1-ATPase shows a remarkable dis- and re-assembling process in response to nutrition conditions. In order to gain detailed information about this process we focused on subunits C and E of the V1 part. Different fluorescent proteins ...
... to monitor the variable subunit composition of VOV1-ATPase parts. VOV1-ATPase shows a remarkable dis- and re-assembling process in response to nutrition conditions. In order to gain detailed information about this process we focused on subunits C and E of the V1 part. Different fluorescent proteins ...
Protein Secretion in Plants: from the trans
... GTPase-activating proteins (ARF-GAPs) for coat recruitment and cargo selection. ARFs not only act to recruit COPI and clathrin coats to membranes but also play a role in the control of membrane lipid composition, actin remodeling and related events (18). Structurally related ARF-like proteins (ARLs) ...
... GTPase-activating proteins (ARF-GAPs) for coat recruitment and cargo selection. ARFs not only act to recruit COPI and clathrin coats to membranes but also play a role in the control of membrane lipid composition, actin remodeling and related events (18). Structurally related ARF-like proteins (ARLs) ...
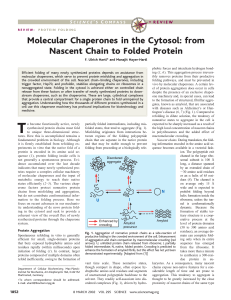
Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: from Nascent Chain to Folded
... chaperones of the Hsp100 or Clp family even have the ability to unfold proteins or to disrupt small-protein aggregates by an adenosine 5⬘triphosphate (ATP)– dependent mechanism (13). For a growing number of proteins, chap- ...
... chaperones of the Hsp100 or Clp family even have the ability to unfold proteins or to disrupt small-protein aggregates by an adenosine 5⬘triphosphate (ATP)– dependent mechanism (13). For a growing number of proteins, chap- ...
Signaling
... => Docking sites on the plasma membrane. 3. PI3K activates the downstream AKt-mTOR pathway => Regulate cell survival & proliferation. 4. Deregulation of this pathway is often found in many cancer cells. ...
... => Docking sites on the plasma membrane. 3. PI3K activates the downstream AKt-mTOR pathway => Regulate cell survival & proliferation. 4. Deregulation of this pathway is often found in many cancer cells. ...
Slide 1
... made of pyrex glass, Teflon or leucite can also be used; controlled solid shear with Hughes Press that generate pressure upto 108 Pa can be used to break plant cells. ...
... made of pyrex glass, Teflon or leucite can also be used; controlled solid shear with Hughes Press that generate pressure upto 108 Pa can be used to break plant cells. ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.