Ch 3 Notes
... – Two monosaccharides join to form a double sugar called a disaccharide. – A complex sugar, or polysaccharide, is made of ...
... – Two monosaccharides join to form a double sugar called a disaccharide. – A complex sugar, or polysaccharide, is made of ...
Chapter 16
... Release of Neurotransmitters by Photoreceptors 36. Discuss the sequence of interactions between photopigments, enzymes, ...
... Release of Neurotransmitters by Photoreceptors 36. Discuss the sequence of interactions between photopigments, enzymes, ...
mb_ch03
... – Two monosaccharides join to form a double sugar called a disaccharide. – A complex sugar, or polysaccharide, is made of ...
... – Two monosaccharides join to form a double sugar called a disaccharide. – A complex sugar, or polysaccharide, is made of ...
Gene Section MIER1 (mesoderm induction early response 1 homolog (Xenopus laevis))
... revealed that MIER1alpha protein is expressed primarily in ductal epithelial cells in normal breast tissue, with little or no expression in the surrounding stroma; in breast carcinoma samples, its expression is restricted to tumour cells. While there is no difference in expression levels, the subcel ...
... revealed that MIER1alpha protein is expressed primarily in ductal epithelial cells in normal breast tissue, with little or no expression in the surrounding stroma; in breast carcinoma samples, its expression is restricted to tumour cells. While there is no difference in expression levels, the subcel ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... 2. Multiple forms of enzymes (isozymes). Used at distinct locations or times. Differ slightly in structure, in Km & Vmax values, and in regulatory properties 3. Reversible covalent modification. Activities altered by covalent attachment of modifying group, mostly a phosphoryl group 4. Protleolytic a ...
... 2. Multiple forms of enzymes (isozymes). Used at distinct locations or times. Differ slightly in structure, in Km & Vmax values, and in regulatory properties 3. Reversible covalent modification. Activities altered by covalent attachment of modifying group, mostly a phosphoryl group 4. Protleolytic a ...
The Prototype Immunoglobulin Molecule
... J-Chain and secretory component The major immunoglobulin of secretions Not found in serum ...
... J-Chain and secretory component The major immunoglobulin of secretions Not found in serum ...
Functional and quantitative proteomics using SILAC
... To differentially quantify two proteomes, a stable isotope can be introduced in various ways, most commonly by chemical modification or by metabolic labelling6. Chemical labelling can be done on any proteome, including body fluids and biopsis material, whereas metabolic strategies require living cel ...
... To differentially quantify two proteomes, a stable isotope can be introduced in various ways, most commonly by chemical modification or by metabolic labelling6. Chemical labelling can be done on any proteome, including body fluids and biopsis material, whereas metabolic strategies require living cel ...
Selective Gene Delivery to Head and Neck Cancer Cells via an
... aVb3 and aVb5 class (37–39). Relative resistance to adenoviral vectors has been noted to occur based on a deficiency of either or both of these cellular receptor classes (17, 18, 40). On this basis, we evaluated the relative levels of both receptor classes in the resistance of SCCHN cell lines as co ...
... aVb3 and aVb5 class (37–39). Relative resistance to adenoviral vectors has been noted to occur based on a deficiency of either or both of these cellular receptor classes (17, 18, 40). On this basis, we evaluated the relative levels of both receptor classes in the resistance of SCCHN cell lines as co ...
Poster for RCPSC mee.. - University of Alberta
... irradiation), and chemotherapeutic agents. The accumulation of ceramide activates JNK/SAPK, PKCζ, caspases as well as PP1 and PP2A (6). Substrates of PP1 and PP2A that are dephosphorylated in response to either ceramide-inducing agonists or addition of exogenous ceramide include c-jun, SR proteins, ...
... irradiation), and chemotherapeutic agents. The accumulation of ceramide activates JNK/SAPK, PKCζ, caspases as well as PP1 and PP2A (6). Substrates of PP1 and PP2A that are dephosphorylated in response to either ceramide-inducing agonists or addition of exogenous ceramide include c-jun, SR proteins, ...
Transport Across Membranes
... by metabolic energy derived from ATP • Active Transport allows cells to uptake necessary ions and molecules and remove waste products • These Mechanisms often referred to as Pumps • Most common is Sodium Pump ...
... by metabolic energy derived from ATP • Active Transport allows cells to uptake necessary ions and molecules and remove waste products • These Mechanisms often referred to as Pumps • Most common is Sodium Pump ...
Laboratory of Dr. Wayne L. Hubbell Protocol designed by Carlos J
... incubator. The following day, inoculate the starter culture into 1-L of LB medium containing the aforementioned antibiotics and grow at 37°C in a shaking incubator to an OD600 of 0.75. Add 0.25 g of the unnatural amino acid and induce expression with 1mM isopropyl--Dthiogalactopyranoside and 0.02% ...
... incubator. The following day, inoculate the starter culture into 1-L of LB medium containing the aforementioned antibiotics and grow at 37°C in a shaking incubator to an OD600 of 0.75. Add 0.25 g of the unnatural amino acid and induce expression with 1mM isopropyl--Dthiogalactopyranoside and 0.02% ...
Protein Stability Protein Folding
... • Some enzymes from thermophiles that are very stable at normal temperatures have low activities at the lower temperatures. • There are is a compromise between the stability and activity in the structure of the active site of a protein. • There are several positions in the active site can be mutated ...
... • Some enzymes from thermophiles that are very stable at normal temperatures have low activities at the lower temperatures. • There are is a compromise between the stability and activity in the structure of the active site of a protein. • There are several positions in the active site can be mutated ...
Section 19-1 Bacteria
... b. They lack a cell wall. c. They lack peptidoglycan. d. They look very similar to eubacteria. 11. What is significant about the DNA sequences of key archaebacterial genes? ...
... b. They lack a cell wall. c. They lack peptidoglycan. d. They look very similar to eubacteria. 11. What is significant about the DNA sequences of key archaebacterial genes? ...
Immune System Overview - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... The special shape that a particular lymphocyte recognizes is called an antigenic determinant and is formed by the three-dimensional structure of a large molecule called an antigen. Antigens are usually proteins, but they can also be large carbohydrates or nucleic acids. The surface of any give ...
... The special shape that a particular lymphocyte recognizes is called an antigenic determinant and is formed by the three-dimensional structure of a large molecule called an antigen. Antigens are usually proteins, but they can also be large carbohydrates or nucleic acids. The surface of any give ...
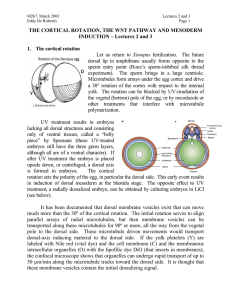
the cortical rotation, the wnt pathway
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
Purifying rfp Protein
... One molecular attribute commonly used in purification is protein hydrophobicity. The term hydrophobicity is related to the behavior of a molecule in water. If a molecule is hydrophobic, it fears water while hydrophilic molecules love water. For example, oils, waxes and fats are hydrophobic; they do ...
... One molecular attribute commonly used in purification is protein hydrophobicity. The term hydrophobicity is related to the behavior of a molecule in water. If a molecule is hydrophobic, it fears water while hydrophilic molecules love water. For example, oils, waxes and fats are hydrophobic; they do ...
introduction
... increased. This potential is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). • The excitatory transmitter opens Na or Ca channels in the postsynaptic membrane. • Stimulation of some inputs produces hyperpolarizing responses and excitability of the neuron to other stimuli decreases. This potential i ...
... increased. This potential is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). • The excitatory transmitter opens Na or Ca channels in the postsynaptic membrane. • Stimulation of some inputs produces hyperpolarizing responses and excitability of the neuron to other stimuli decreases. This potential i ...
A consensus sequence in the endothelin
... However, the mechanism responsible for the receptor specificity of NHE3 regulation remains unclear. We previously showed that ET-1 causes similar patterns of protein tyrosine phosphorylation, adenylyl cyclase inhibition, and increases in cell [Ca2⫹] in ETA- and ETB-expressing OKP cells, implying tha ...
... However, the mechanism responsible for the receptor specificity of NHE3 regulation remains unclear. We previously showed that ET-1 causes similar patterns of protein tyrosine phosphorylation, adenylyl cyclase inhibition, and increases in cell [Ca2⫹] in ETA- and ETB-expressing OKP cells, implying tha ...
Immune System Overview - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... • The special shape that a particular lymphocyte recognizes is called an antigenic determinant and is formed by the three-dimensional structure of a large molecule called an antigen. • Antigens are usually proteins, but they can also be large carbohydrates or nucleic acids. • The surface of any give ...
... • The special shape that a particular lymphocyte recognizes is called an antigenic determinant and is formed by the three-dimensional structure of a large molecule called an antigen. • Antigens are usually proteins, but they can also be large carbohydrates or nucleic acids. • The surface of any give ...
Slajdovi sa predavanja
... biologiju sistema kao interdisciplinarne grane relvantne za kompiuterske nauke ...
... biologiju sistema kao interdisciplinarne grane relvantne za kompiuterske nauke ...
Taste
... selectively to specific G proteincoupled membrane receptors. Individual taste cells may employ ...
... selectively to specific G proteincoupled membrane receptors. Individual taste cells may employ ...
Word file
... Supplementary Figure 2. EZH2 protein levels are elevated in metastatic prostate cancer independent of metastatic site. a, Tissue microarray analysis of EZH2 expression considered per patient. The mean EZH2 protein expression for the indicated prostate tissues is summarized using error bars with 95% ...
... Supplementary Figure 2. EZH2 protein levels are elevated in metastatic prostate cancer independent of metastatic site. a, Tissue microarray analysis of EZH2 expression considered per patient. The mean EZH2 protein expression for the indicated prostate tissues is summarized using error bars with 95% ...
ch9 FA 11 - Cal State LA
... – GDP-bound tubulin can release only from “plus” end – GDP-bound tubulin cannot release from “minus” end or from central region ...
... – GDP-bound tubulin can release only from “plus” end – GDP-bound tubulin cannot release from “minus” end or from central region ...
Insulin Signaling
... proteins to bind. – Active site uses ATP to phosphorylate its targets. Tyrosine Kinase domain of IR showing inactive (PDB ID 1IRK) and active (PDB IDs 1IR3) forms ...
... proteins to bind. – Active site uses ATP to phosphorylate its targets. Tyrosine Kinase domain of IR showing inactive (PDB ID 1IRK) and active (PDB IDs 1IR3) forms ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.