cells. - Effingham County Schools
... 8. All living things must maintain a stable internal environment called _____________ homeostasis ...
... 8. All living things must maintain a stable internal environment called _____________ homeostasis ...
lecture 1
... • Embryogenesis in mammals occurs in utero - difficult to observe. • Important to study because of direct relevance for understanding and treating disease. • Mouse is preferred model; ...
... • Embryogenesis in mammals occurs in utero - difficult to observe. • Important to study because of direct relevance for understanding and treating disease. • Mouse is preferred model; ...
File
... shadier side cause greater growth (cell elongation) on this side, so the stems curves towards the source brighter light. The leaves attached to the stem will therefore receive more light and be able to photosynthesize at a greater rate. ...
... shadier side cause greater growth (cell elongation) on this side, so the stems curves towards the source brighter light. The leaves attached to the stem will therefore receive more light and be able to photosynthesize at a greater rate. ...
Intercalary meristems are primary.. Intercalary meristems are primary
... and functional aspects of every layer and every part of the organ. The student can practice with the following sub-headings: a) Epidermis b) Cortex c) Stele For example, the description of the epidermis of the root:It is a multicellular single layered living cells arranged without intercellular spac ...
... and functional aspects of every layer and every part of the organ. The student can practice with the following sub-headings: a) Epidermis b) Cortex c) Stele For example, the description of the epidermis of the root:It is a multicellular single layered living cells arranged without intercellular spac ...
lec03
... H. The Cytoskeleton • Intermediate filaments are formed of keratins and add strength to cell structure. • Anchorage of nucleus and other organelles. • Formation of nuclear lamina, foundation ...
... H. The Cytoskeleton • Intermediate filaments are formed of keratins and add strength to cell structure. • Anchorage of nucleus and other organelles. • Formation of nuclear lamina, foundation ...
Cells in Biology. - AssistiveTechAIU
... worry about being correct or writing correct sentences. You want to be quick to jump start your thinking. Do this for one minute. ...
... worry about being correct or writing correct sentences. You want to be quick to jump start your thinking. Do this for one minute. ...
cells
... Similarities between all living things (continued..) • They maintain homeostasis • Ability of an organism to maintain proper internal conditions despite changes in the environment. • They use energy • All organisms require energy for everyday life functions (staying organized, carrying on activitie ...
... Similarities between all living things (continued..) • They maintain homeostasis • Ability of an organism to maintain proper internal conditions despite changes in the environment. • They use energy • All organisms require energy for everyday life functions (staying organized, carrying on activitie ...
Student notes part 1
... genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes: notably the enzymes involved in transcription and translation. The archaea exploit a much greater variety of sources of energy than eukaryotes: ranging from familiar organic compounds such as sugars, to us ...
... genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes: notably the enzymes involved in transcription and translation. The archaea exploit a much greater variety of sources of energy than eukaryotes: ranging from familiar organic compounds such as sugars, to us ...
Objective 7: TSWBAT identify factors which stimulate and
... Objective 7: TSWBAT identify factors which stimulate and inhibit cell division. ...
... Objective 7: TSWBAT identify factors which stimulate and inhibit cell division. ...
lecture notes-microbiology-3-Eucaryotes
... Meiosis In Meiosis - The diploid cell's chromosomes (DNA) is replicated once and separated twice, producing four sets of haploid cells each containing half of the original cell's chromosomes. - These resultant haploid cells will fertilize with other haploid cells of the opposite gender to form a di ...
... Meiosis In Meiosis - The diploid cell's chromosomes (DNA) is replicated once and separated twice, producing four sets of haploid cells each containing half of the original cell's chromosomes. - These resultant haploid cells will fertilize with other haploid cells of the opposite gender to form a di ...
Chapter 5 Review Answers (1)
... The Purposes of Cell Division are: Healing and Tissue Repair Growth Reproduction of Organisms 10. Describe each purpose. Healing and repair of damaged or old tissues occur because of cell division. Organisms continuously replace cells throughout their life. Growth- When a cell surpasses a maxi ...
... The Purposes of Cell Division are: Healing and Tissue Repair Growth Reproduction of Organisms 10. Describe each purpose. Healing and repair of damaged or old tissues occur because of cell division. Organisms continuously replace cells throughout their life. Growth- When a cell surpasses a maxi ...
3D Cell Model Project
... cell or a plant cell, but do not do both. This project should not be expensive. You may use things you find around home and school to make the cell; you may also use things you find at craft and hobby stores. Color of the organelles does not matter (except for chloroplasts, which should be green). M ...
... cell or a plant cell, but do not do both. This project should not be expensive. You may use things you find around home and school to make the cell; you may also use things you find at craft and hobby stores. Color of the organelles does not matter (except for chloroplasts, which should be green). M ...
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
... concentration of water than inside the cell water molecules move out of the cell the cell shrinks as water moves out Active Transport when a cell uses its own energy to move materials from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration while you sleep, 30% - 40 % of your total energ ...
... concentration of water than inside the cell water molecules move out of the cell the cell shrinks as water moves out Active Transport when a cell uses its own energy to move materials from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration while you sleep, 30% - 40 % of your total energ ...
Skills Worksheet
... Section: From Cell to Organism Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. Many prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes live on their own. These organisms thrive independently. However, other unicellular organisms form cell groups. For example, some types of bacteria form cell grou ...
... Section: From Cell to Organism Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. Many prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes live on their own. These organisms thrive independently. However, other unicellular organisms form cell groups. For example, some types of bacteria form cell grou ...
Unit 2: Cells & Microscope
... 4. Know the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. 5. Know the 12 organelles in Eukaryotic cells. 6. Know the differences between plant and animal cells. ...
... 4. Know the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. 5. Know the 12 organelles in Eukaryotic cells. 6. Know the differences between plant and animal cells. ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... • Cells develop and grow • Somatic cells (body cells) of a multicellular organism perform specialized functions to keep the organism functioning • Life cycle of a cell is called the Cell Cycle – Interphase – Mitosis ...
... • Cells develop and grow • Somatic cells (body cells) of a multicellular organism perform specialized functions to keep the organism functioning • Life cycle of a cell is called the Cell Cycle – Interphase – Mitosis ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Process of Endocytosis • Plasma membrane surrounds material • Edges of membrane meet • Membranes fuse to form vesicle ...
... Process of Endocytosis • Plasma membrane surrounds material • Edges of membrane meet • Membranes fuse to form vesicle ...
PepTivator® CEF MHC Class I Plus – premium grade
... 2.1 Cell preparation For induction of cytokine secretion by virus–specific T cells, best results are achieved by stimulation of fresh PBMCs, whole blood, or other leukocyte-containing single-cell preparations from tissues or cell lines. Alternatively, frozen cell preparations can be used. ...
... 2.1 Cell preparation For induction of cytokine secretion by virus–specific T cells, best results are achieved by stimulation of fresh PBMCs, whole blood, or other leukocyte-containing single-cell preparations from tissues or cell lines. Alternatively, frozen cell preparations can be used. ...
Long-term Monitoring of Bacteria Undergoing Programmed Population Control in a Microchemostat
... growth to probe qualitative behavior and to prepare starter cultures for microchemostat experiments. To measure population control circuit dynamics, cells were grown in pHbuffered LBK medium. The population control circuit plasmid was maintained with 50 µg/ml of kanamycin. When applicable, 1mM IPTG ...
... growth to probe qualitative behavior and to prepare starter cultures for microchemostat experiments. To measure population control circuit dynamics, cells were grown in pHbuffered LBK medium. The population control circuit plasmid was maintained with 50 µg/ml of kanamycin. When applicable, 1mM IPTG ...
HW 9/14 Two Kinds of Cells
... Inside each cell are a variety of different small organs called organelles. These really small organs perform many of the same type of jobs that your organs perform. There are organelles that are similar to your stomach; there are organelles similar to your kidneys; and there are organelles similar ...
... Inside each cell are a variety of different small organs called organelles. These really small organs perform many of the same type of jobs that your organs perform. There are organelles that are similar to your stomach; there are organelles similar to your kidneys; and there are organelles similar ...
Student Activity DOC
... There is a great variety among living things, but all living things have common characteristics. The basic unit of life is the same. This allows us to carry out common activities such as growing, responding, reproducing, and using energy. This basic unit of life is cells. ...
... There is a great variety among living things, but all living things have common characteristics. The basic unit of life is the same. This allows us to carry out common activities such as growing, responding, reproducing, and using energy. This basic unit of life is cells. ...
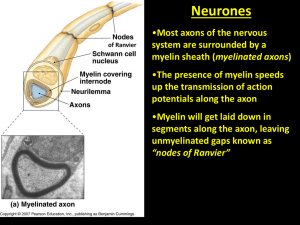
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
Student Activity PDF - TI Education
... There is a great variety among living things, but all living things have common characteristics. The basic unit of life is the same. This allows us to carry out common activities such as growing, responding, reproducing, and using energy. This basic unit of life is cells. ...
... There is a great variety among living things, but all living things have common characteristics. The basic unit of life is the same. This allows us to carry out common activities such as growing, responding, reproducing, and using energy. This basic unit of life is cells. ...
Cell theory
... cell theory. The cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. The cell theory states: • All living things or organisms are made of cells and their products. • New cells are created by old cells dividing into two. • Cells are the basic building uni ...
... cell theory. The cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. The cell theory states: • All living things or organisms are made of cells and their products. • New cells are created by old cells dividing into two. • Cells are the basic building uni ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.